Intro
Unlock the rigorous US Army Special Forces medic training, involving advanced tactical combat casualty care, wilderness medicine, and emergency medical technician skills, to become an elite Green Beret medic.
The US Army Special Forces, also known as the Green Berets, are an elite group of soldiers who undergo rigorous training to conduct unconventional warfare, foreign internal defense, and direct action missions. One of the most critical components of a Special Forces team is the medic, who provides medical care and support to the team in the field. US Army Special Forces medic training is a challenging and comprehensive program that prepares medics to provide high-quality medical care in a variety of environments.
The importance of Special Forces medics cannot be overstated. They are responsible for providing medical care to their teammates, as well as to civilians and indigenous forces in the area of operation. This requires a high level of medical expertise, as well as the ability to work independently and make quick decisions in high-stress situations. Special Forces medics must also be able to communicate effectively with their teammates and other medical personnel, both in person and over radio and satellite communications.
To become a Special Forces medic, a soldier must first complete Basic Combat Training and Advanced Individual Training as a medic. They must then volunteer for Special Forces duty and complete the Special Forces Qualification Course, also known as the "Q Course." The Q Course is a 24-month program that includes training in languages, cultural awareness, and advanced first aid, as well as specialized training in areas such as parachuting, diving, and survival skills.
Special Forces Medic Training Overview

The Special Forces medic training program is designed to provide medics with the skills and knowledge they need to provide high-quality medical care in a variety of environments. The program includes training in advanced first aid, trauma care, and surgical skills, as well as training in areas such as pharmacology, laboratory testing, and medical evacuation procedures. Medics must also be able to communicate effectively with their teammates and other medical personnel, both in person and over radio and satellite communications.
Key Components of Special Forces Medic Training
The key components of Special Forces medic training include: * Advanced first aid and trauma care * Surgical skills and procedures * Pharmacology and medication management * Laboratory testing and medical diagnostics * Medical evacuation procedures and aeromedical evacuation * Communication skills and radio operations * Survival skills and wilderness medicineAdvanced First Aid and Trauma Care

Advanced first aid and trauma care are critical components of Special Forces medic training. Medics must be able to provide high-quality medical care in a variety of environments, including in the field and in austere environments. This includes training in areas such as:
- Tourniquet application and hemorrhage control
- Suturing and wound closure
- Fracture management and splinting
- Burn care and management
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation and advanced cardiac life support
Surgical Skills and Procedures
Surgical skills and procedures are also an important part of Special Forces medic training. Medics must be able to perform a variety of surgical procedures, including: * Craniotomy and neurosurgical procedures * Thoracotomy and cardiothoracic procedures * Laparotomy and abdominal procedures * Amputation and surgical debridementPharmacology and Medication Management
Pharmacology and medication management are critical components of Special Forces medic training. Medics must be able to manage medications and provide pharmacological interventions in a variety of environments. This includes training in areas such as:
- Medication administration and dosing
- Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
- Medication side effects and adverse reactions
- Medication interactions and contraindications
Laboratory Testing and Medical Diagnostics
Laboratory testing and medical diagnostics are also important components of Special Forces medic training. Medics must be able to perform a variety of laboratory tests and medical diagnostics, including: * Complete blood counts and blood chemistry tests * Urinalysis and urine culture * Electrocardiogram and cardiac monitoring * Pulmonary function tests and respiratory monitoringMedical Evacuation Procedures and Aeromedical Evacuation
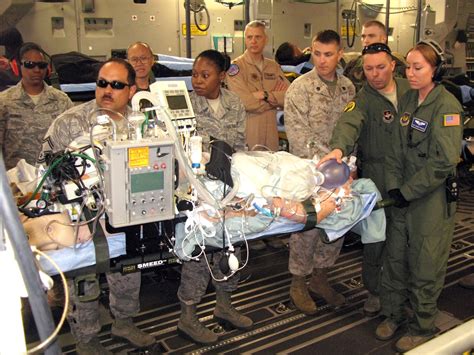
Medical evacuation procedures and aeromedical evacuation are critical components of Special Forces medic training. Medics must be able to evacuate patients safely and efficiently, using a variety of transportation methods, including:
- Ground evacuation and ambulance operations
- Air evacuation and aeromedical evacuation
- Sea evacuation and maritime operations
Communication Skills and Radio Operations
Communication skills and radio operations are also important components of Special Forces medic training. Medics must be able to communicate effectively with their teammates and other medical personnel, both in person and over radio and satellite communications. This includes training in areas such as: * Radio operations and communication protocols * Satellite communications and satellite phone operations * Secure communication methods and encryptionSurvival Skills and Wilderness Medicine

Survival skills and wilderness medicine are critical components of Special Forces medic training. Medics must be able to survive in a variety of environments, including in the wilderness and in austere environments. This includes training in areas such as:
- Shelter and warmth management
- Water purification and food procurement
- Signaling and navigation
- Wilderness first aid and emergency medical care
Special Forces Medic Training Image Gallery










What is the role of a Special Forces medic?
+The role of a Special Forces medic is to provide medical care and support to the Special Forces team in the field. This includes providing advanced first aid, trauma care, and surgical skills, as well as managing medications and performing laboratory tests and medical diagnostics.
What kind of training do Special Forces medics receive?
+Special Forces medics receive comprehensive training in advanced first aid, trauma care, and surgical skills, as well as training in pharmacology, laboratory testing, and medical evacuation procedures. They also receive training in survival skills and wilderness medicine, as well as communication skills and radio operations.
How long does it take to become a Special Forces medic?
+It typically takes 24 months to complete the Special Forces Qualification Course, which includes training in languages, cultural awareness, and advanced first aid, as well as specialized training in areas such as parachuting, diving, and survival skills. Additional training and certification may be required to become a Special Forces medic.
In conclusion, US Army Special Forces medic training is a challenging and comprehensive program that prepares medics to provide high-quality medical care in a variety of environments. The program includes training in advanced first aid, trauma care, and surgical skills, as well as training in pharmacology, laboratory testing, and medical evacuation procedures. Special Forces medics play a critical role in the success of Special Forces missions, and their training and expertise are essential to the safety and well-being of their teammates. If you are interested in learning more about Special Forces medic training, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with others who may be interested.
