Intro
Explore the US Army organization chart, understanding its hierarchical structure, military ranks, and units, including brigades, battalions, and companies, to learn about the armys operational framework and command chain.
The US Army is a large and complex organization with a rich history and a wide range of responsibilities. Understanding the US Army organization chart is essential for anyone interested in the military, whether as a career soldier, a historian, or simply a curious individual. In this article, we will delve into the structure of the US Army, exploring its various components, units, and ranks.
The US Army is a branch of the US Armed Forces, responsible for land-based military operations. It is the largest branch of the military, with over 475,000 active-duty soldiers and more than 500,000 reserve soldiers. The Army is led by the Secretary of the Army, who is a civilian official appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate. The Chief of Staff of the Army is the highest-ranking military officer in the Army and is responsible for the day-to-day operations of the service.
US Army Organization Chart Overview
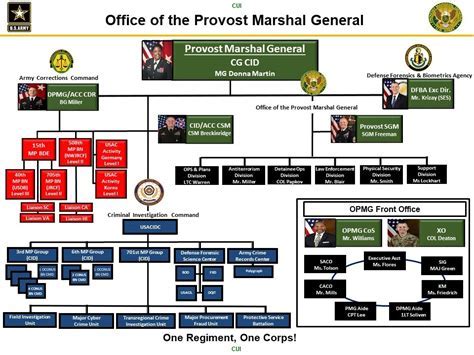
The US Army organization chart is divided into several levels, each with its own unique structure and responsibilities. The highest level is the Department of the Army, which is headed by the Secretary of the Army. The Department of the Army is responsible for setting overall policy and direction for the Army, as well as overseeing the various branches and units that make up the service.
US Army Branches

The US Army is divided into several branches, each with its own unique mission and responsibilities. The main branches of the Army include:
- Infantry: The infantry is the backbone of the Army, responsible for conducting ground combat operations.
- Armor: The armor branch is responsible for operating tanks and other armored vehicles.
- Artillery: The artillery branch is responsible for providing firepower support to infantry and armor units.
- Engineers: The engineers branch is responsible for constructing and maintaining infrastructure, such as roads and bridges.
- Signal Corps: The signal corps is responsible for providing communication support to Army units.
US Army Units
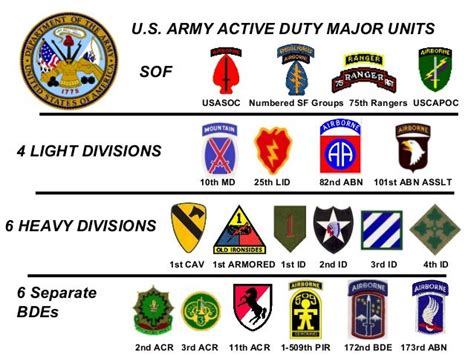
The US Army is organized into several types of units, each with its own unique structure and responsibilities. The main types of units include:
- Companies: A company is a small unit of soldiers, typically consisting of 60-200 personnel.
- Battalions: A battalion is a larger unit, typically consisting of 300-1,000 personnel.
- Brigades: A brigade is a still larger unit, typically consisting of 3,000-5,000 personnel.
- Divisions: A division is the largest type of unit, typically consisting of 10,000-20,000 personnel.
US Army Ranks
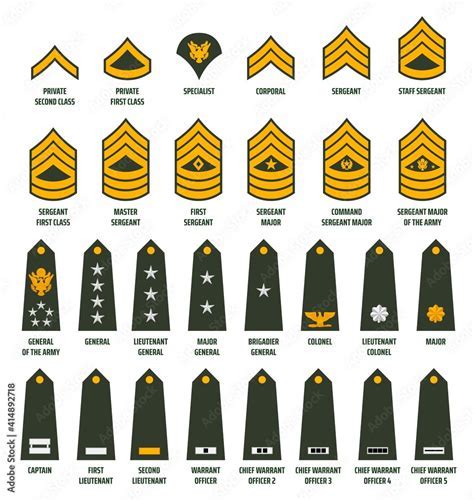

The US Army uses a system of ranks to denote an individual's level of responsibility and authority. The main ranks in the Army include:
- Enlisted Ranks: Enlisted ranks include private, private first class, specialist, and sergeant.
- Warrant Officer Ranks: Warrant officer ranks include warrant officer 1 and chief warrant officer 5.
- Officer Ranks: Officer ranks include second lieutenant, first lieutenant, captain, major, lieutenant colonel, colonel, brigadier general, major general, lieutenant general, and general.
US Army Special Operations

The US Army has several special operations units, each with its own unique mission and responsibilities. The main special operations units include:
- US Army Special Forces (Green Berets): The Green Berets are an elite unit trained in unconventional warfare, foreign language skills, and cultural expertise.
- US Army Rangers: The Rangers are an elite unit trained in airborne operations, special reconnaissance, and direct action.
- US Army Delta Force: The Delta Force is an elite unit trained in counter-terrorism, hostage rescue, and high-risk arrests.
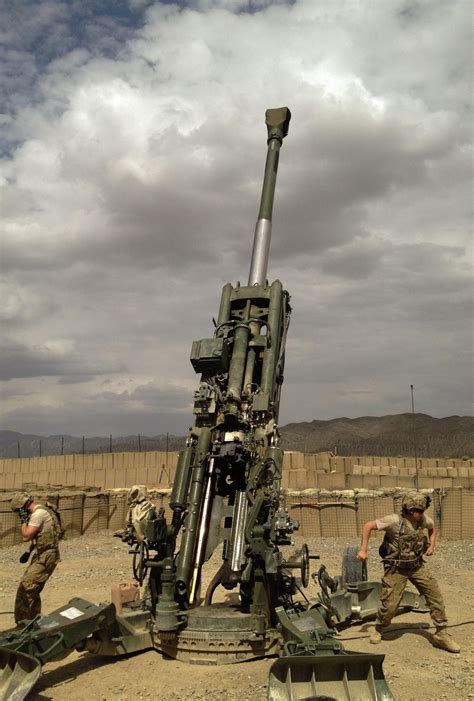
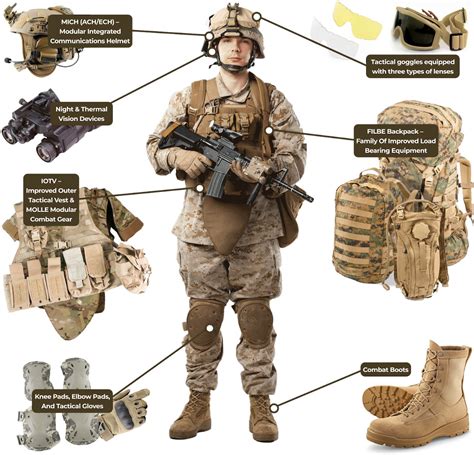
US Army Equipment

The US Army uses a wide range of equipment, including tanks, infantry fighting vehicles, artillery pieces, and small arms. The main types of equipment used by the Army include:
- Tanks: The Army uses several types of tanks, including the M1 Abrams and the M2 Bradley.
- Infantry Fighting Vehicles: The Army uses several types of infantry fighting vehicles, including the M2 Bradley and the Stryker.
- Artillery Pieces: The Army uses several types of artillery pieces, including the M109 Paladin and the M777 Howitzer.
- Small Arms: The Army uses several types of small arms, including the M4 carbine and the M9 pistol.
US Army Vehicles

The US Army uses a wide range of vehicles, including trucks, cars, and motorcycles. The main types of vehicles used by the Army include:
- Trucks: The Army uses several types of trucks, including the M35 and the M915.
- Cars: The Army uses several types of cars, including the M37 and the M151.
- Motorcycles: The Army uses several types of motorcycles, including the M101 and the M103.
US Army Bases
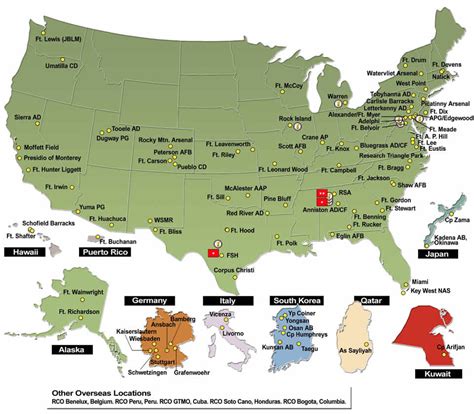
The US Army has several bases located around the world, each with its own unique mission and responsibilities. The main types of bases include:
- Forts: A fort is a large base that serves as a headquarters for a division or corps.
- Camps: A camp is a smaller base that serves as a training area or logistics hub.
- Stations: A station is a small base that serves as a headquarters for a brigade or battalion.
US Army Training

The US Army provides a wide range of training programs for its soldiers, including basic training, advanced individual training, and specialized training. The main types of training include:
- Basic Training: Basic training is a 10-week program that teaches new recruits the basics of soldiering, including first aid, map reading, and marksmanship.
- Advanced Individual Training: Advanced individual training is a program that teaches soldiers a specific skill or trade, such as infantry, artillery, or engineering.
- Specialized Training: Specialized training is a program that teaches soldiers a specific skill or trade, such as special forces, ranger, or sniper.
US Army Image Gallery










What is the US Army's primary mission?
+The US Army's primary mission is to protect the American people and the nation's interests by fighting and winning wars, as well as conducting humanitarian and disaster relief operations.
What are the different branches of the US Army?
+The US Army has several branches, including infantry, armor, artillery, engineers, and signal corps.
What is the US Army's rank structure?
+The US Army uses a system of ranks to denote an individual's level of responsibility and authority, with enlisted ranks, warrant officer ranks, and officer ranks.
What types of equipment does the US Army use?
+The US Army uses a wide range of equipment, including tanks, infantry fighting vehicles, artillery pieces, and small arms.
What is the US Army's training program like?
+The US Army provides a wide range of training programs for its soldiers, including basic training, advanced individual training, and specialized training.
In conclusion, the US Army is a complex and multifaceted organization with a rich history and a wide range of responsibilities. Understanding the US Army organization chart is essential for anyone interested in the military, whether as a career soldier, a historian, or simply a curious individual. By exploring the various components, units, and ranks that make up the Army, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the sacrifices and contributions of our men and women in uniform. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about the US Army in the comments below, and to explore the many resources available for those interested in learning more about our nation's military.
