Intro
Discover US Air Force pilot requirements, including education, training, and physical standards, to pursue a career as a military aviator, meeting strict eligibility criteria and rigorous flight testing demands.
Becoming a pilot in the US Air Force is an esteemed career goal for many individuals who are passionate about aviation and serving their country. The US Air Force is one of the most advanced and respected air forces in the world, and its pilots are highly trained and skilled professionals. To become a pilot in the US Air Force, one must meet specific requirements and undergo rigorous training. In this article, we will explore the requirements and process of becoming a US Air Force pilot.
The US Air Force is constantly looking for talented and dedicated individuals to join its ranks as pilots. These individuals must possess a unique combination of skills, education, and personal qualities that make them suitable for the demands of military aviation. From flying complex aircraft to making critical decisions in high-pressure situations, US Air Force pilots must be able to perform at the highest level. Whether you are a student, a career changer, or simply someone who is passionate about flying, the US Air Force offers a challenging and rewarding career path for those who are willing to put in the time and effort.
To be eligible to become a US Air Force pilot, one must meet certain basic requirements. These include being a US citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 29, and having a high school diploma or equivalent. Additionally, applicants must score well on the Air Force Officer Qualifying Test (AFOQT) and meet certain physical and medical standards. The AFOQT is a multiple-choice test that measures a candidate's knowledge and skills in areas such as verbal comprehension, quantitative reasoning, and aviation knowledge. The test is an important component of the pilot selection process, as it helps to identify candidates who have the cognitive abilities and knowledge required to succeed as a pilot.
Education and Training Requirements
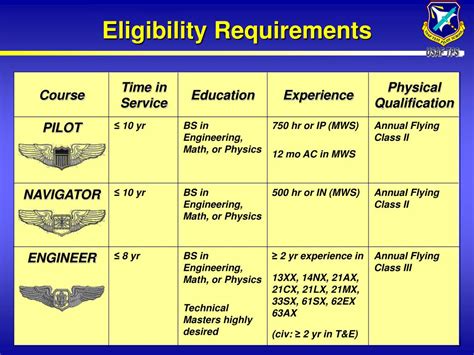
In addition to meeting the basic requirements, US Air Force pilot candidates must also complete a series of education and training programs. These programs are designed to provide candidates with the knowledge, skills, and experience needed to become a successful pilot. The first step in the process is to earn a bachelor's degree from a accredited college or university. The degree can be in any field, but courses in mathematics, science, and engineering are highly recommended. While pursuing their degree, candidates can also enroll in the Air Force Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC) program, which provides leadership training and experience.
After completing their degree, candidates must attend Officer Training School (OTS) or the Air Force Academy. OTS is a 12-week program that provides training in leadership, management, and military protocol. The Air Force Academy, on the other hand, is a four-year program that provides a bachelor's degree and a commission as an officer in the US Air Force. Both programs are highly competitive, and candidates must meet certain academic and physical standards to be eligible. Upon completion of OTS or the Air Force Academy, candidates are commissioned as officers in the US Air Force and begin their pilot training.
Pilot Training Program

The US Air Force Pilot Training Program is a rigorous and highly competitive program that provides candidates with the training and experience needed to become a successful pilot. The program is divided into several phases, each of which is designed to build on the skills and knowledge learned in the previous phase. The first phase of the program is Undergraduate Pilot Training (UPT), which is a 12-month program that provides training in aircraft systems, weather, navigation, and regulations. Candidates learn to fly the T-6 Texan II, a single-engine turboprop aircraft, and receive training in aerobatics, formation flying, and emergency procedures.
After completing UPT, candidates progress to Introduction to Fighter Fundamentals (IFF) or Introduction to Airlift, Tanker, and Transport (IATT). IFF is a 6-week program that provides training in fighter aircraft systems, tactics, and procedures. IATT, on the other hand, is a 6-week program that provides training in airlift, tanker, and transport aircraft systems, tactics, and procedures. Both programs are designed to prepare candidates for their specific aircraft type and mission. Upon completion of IFF or IATT, candidates are assigned to a specific aircraft type and begin their advanced training.
Advanced Training

Advanced training is the final phase of the US Air Force Pilot Training Program. During this phase, candidates receive training in their specific aircraft type and learn to perform complex missions and tasks. The training is highly specialized and is designed to prepare candidates for their specific role in the US Air Force. For example, fighter pilots receive training in air-to-air combat, while airlift pilots receive training in cargo transport and airdrop procedures. The advanced training phase can last from several months to a year or more, depending on the aircraft type and mission.
In addition to flight training, US Air Force pilots must also complete a series of ground school courses and simulator training sessions. These courses and sessions provide candidates with the knowledge and skills needed to operate their aircraft safely and effectively. Candidates learn about aircraft systems, weather, navigation, and regulations, as well as tactics and procedures for their specific mission. The ground school courses and simulator training sessions are highly interactive and provide candidates with a realistic and immersive learning experience.
Physical and Medical Requirements

To become a US Air Force pilot, one must meet certain physical and medical standards. These standards are designed to ensure that pilots are able to perform their duties safely and effectively. The physical standards include a minimum height of 5 feet 4 inches and a maximum height of 6 feet 5 inches, as well as a minimum weight of 110 pounds and a maximum weight of 235 pounds. Pilots must also have a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or less and be able to pass a physical fitness test.
In addition to the physical standards, US Air Force pilots must also meet certain medical standards. These standards include having 20/20 vision in each eye, with or without corrective lenses, as well as normal color vision and depth perception. Pilots must also be free from certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, epilepsy, and heart disease. The medical standards are highly stringent, and candidates must undergo a thorough medical examination to ensure that they meet the requirements.
Mental and Emotional Requirements

In addition to the physical and medical standards, US Air Force pilots must also meet certain mental and emotional requirements. These requirements include being able to perform under stress and pressure, as well as being able to make quick and effective decisions in high-pressure situations. Pilots must also be able to work well in a team environment and be able to communicate effectively with their crew members and other personnel.
To become a US Air Force pilot, one must also be willing to commit to a minimum of 10 years of service. This commitment includes 4 years of undergraduate pilot training, as well as 6 years of service after completion of training. During this time, pilots will be required to fly a variety of missions, including combat, transport, and training missions. They will also be required to participate in ongoing training and education to maintain their skills and knowledge.
Benefits and Career Opportunities

Becoming a US Air Force pilot offers a range of benefits and career opportunities. These benefits include competitive pay and benefits, as well as the opportunity to fly some of the most advanced aircraft in the world. US Air Force pilots also have the opportunity to travel and experience different cultures, as well as to participate in a variety of missions and operations.
In addition to the benefits, US Air Force pilots also have a range of career opportunities. These opportunities include flying combat missions, transporting cargo and personnel, and participating in search and rescue operations. Pilots can also specialize in specific areas, such as fighter aircraft, airlift, or tanker operations. With experience and advancement, pilots can also move into leadership roles, such as squadron commander or wing commander.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, becoming a US Air Force pilot is a challenging and rewarding career path that requires a unique combination of skills, education, and personal qualities. From meeting the basic requirements to completing the pilot training program, candidates must be willing to put in the time and effort to succeed. With its competitive pay and benefits, opportunities for advancement, and chance to fly some of the most advanced aircraft in the world, the US Air Force offers a career path that is unmatched in the civilian world.
If you are considering a career as a US Air Force pilot, we encourage you to learn more about the requirements and process. With dedication and hard work, you can achieve your goal and become a part of one of the most respected and advanced air forces in the world.
US Air Force Pilot Image Gallery










What are the basic requirements to become a US Air Force pilot?
+To become a US Air Force pilot, one must be a US citizen, be between the ages of 17 and 29, and have a high school diploma or equivalent. Additionally, applicants must score well on the Air Force Officer Qualifying Test (AFOQT) and meet certain physical and medical standards.
What is the US Air Force Pilot Training Program?
+The US Air Force Pilot Training Program is a rigorous and highly competitive program that provides candidates with the training and experience needed to become a successful pilot. The program is divided into several phases, each of which is designed to build on the skills and knowledge learned in the previous phase.
What are the benefits of becoming a US Air Force pilot?
+Becoming a US Air Force pilot offers a range of benefits, including competitive pay and benefits, the opportunity to fly some of the most advanced aircraft in the world, and the chance to participate in a variety of missions and operations. US Air Force pilots also have the opportunity to travel and experience different cultures, as well as to participate in ongoing training and education to maintain their skills and knowledge.
How long does it take to become a US Air Force pilot?
+The length of time it takes to become a US Air Force pilot can vary depending on the individual's circumstances and the specific requirements of the program. However, in general, it can take around 2-3 years to complete the undergraduate pilot training program, and an additional 1-2 years to complete advanced training and become a fully qualified pilot.
What is the minimum commitment required to become a US Air Force pilot?
+To become a US Air Force pilot, one must be willing to commit to a minimum of 10 years of service. This commitment includes 4 years of undergraduate pilot training, as well as 6 years of service after completion of training.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the requirements and process of becoming a US Air Force pilot. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with others who may be interested. With dedication and hard work, you can achieve your goal and become a part of one of the most respected and advanced air forces in the world.
