Intro
Boost barley yields with 5 expert field tips, covering soil preparation, crop rotation, irrigation management, pest control, and harvesting techniques for optimal barley farming practices.
Barley fields have been a staple of agriculture for thousands of years, providing a versatile and nutritious crop for both human consumption and animal feed. However, managing a barley field can be a complex and challenging task, requiring careful planning, attention to detail, and a deep understanding of the crop's needs. In this article, we will explore five barley field tips to help you optimize your crop's potential, improve yields, and reduce the risk of disease and pests.
Barley is a cool-season crop, which means it thrives in the cooler temperatures of spring and fall. It is an excellent choice for farmers who want to diversify their crop rotation and reduce their reliance on warm-season crops like corn and soybeans. Barley is also a great option for farmers who want to improve soil health, as it has a deep root system that helps to break up compacted soil and improve drainage. Whether you are a seasoned farmer or just starting out, barley is a crop that is definitely worth considering.
One of the key benefits of barley is its versatility. It can be used for a variety of purposes, including food, feed, and even brewing. Barley is a key ingredient in many types of beer, and is also used to make whiskey, bread, and other baked goods. In addition to its many uses, barley is also a relatively low-maintenance crop, requiring less fertilizer and pesticide than many other crops. This makes it an attractive option for farmers who want to reduce their environmental impact and improve their bottom line.
Understanding Barley Field Basics

Choosing the Right Variety
Choosing the right variety of barley is critical to the success of your crop. There are many different varieties to choose from, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. Some varieties are better suited to certain climates or soil types, while others may be more resistant to disease or pests. It's essential to do your research and choose a variety that is well-suited to your specific needs and conditions.Tip 1: Soil Preparation

Benefits of Proper Soil Preparation
Proper soil preparation can have a significant impact on the health and productivity of your barley crop. By providing the right conditions for growth, you can help to ensure a strong and vigorous crop that is better able to resist disease and pests. This can lead to improved yields and reduced losses, which can have a significant impact on your bottom line.Tip 2: Planting at the Right Time
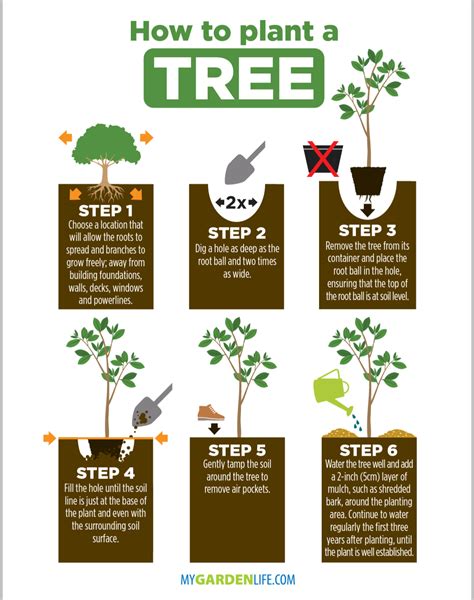
Factors to Consider When Planting
When planting barley, there are several factors to consider. These include the weather, soil conditions, and the variety of barley you are planting. It's essential to choose a variety that is well-suited to your climate and soil type, and to plant at a time when the weather is likely to be favorable. This can help to ensure a strong and healthy crop that is better able to resist disease and pests.Tip 3: Water Management

Benefits of Proper Water Management
Proper water management can have a significant impact on the health and productivity of your barley crop. By providing the right amount of moisture, you can help to ensure a strong and vigorous crop that is better able to resist disease and pests. This can lead to improved yields and reduced losses, which can have a significant impact on your bottom line.Tip 4: Fertilization and Pest Control

Integrated Pest Management
Integrated pest management (IPM) is a holistic approach to managing pests and diseases in barley fields. IPM involves using a combination of techniques, including cultural controls, biological controls, and chemical controls, to minimize the risk of pest and disease outbreaks. This can help to reduce the environmental impact of barley production, while also improving the health and productivity of the crop.Tip 5: Harvesting and Storage
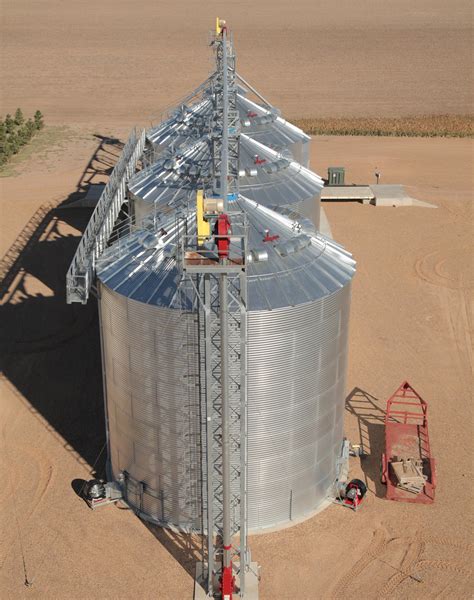

Best Practices for Harvesting and Storage
There are several best practices to keep in mind when harvesting and storing barley. These include harvesting the crop at the right time, drying the grain to the correct moisture level, and storing the grain in a cool, dry place. By following these best practices, you can help to ensure that your barley crop remains healthy and productive, and that you get the best possible price for your grain.Barley Field Image Gallery










What is the ideal soil pH for barley production?
+The ideal soil pH for barley production is between 6.0 and 7.0.
How often should I irrigate my barley field?
+The frequency of irrigation will depend on weather conditions, soil type, and the growth stage of the crop. As a general rule, barley requires consistent moisture, especially during the germination and seedling stages.
What are some common pests and diseases that affect barley crops?
+Some common pests and diseases that affect barley crops include aphids, wireworms, powdery mildew, and leaf rust. It's essential to monitor the crop regularly and take action promptly if you detect any problems.
How can I improve the yield and quality of my barley crop?
+To improve the yield and quality of your barley crop, make sure to choose a high-quality variety, prepare the soil properly, plant at the right time, and provide adequate nutrients and water. It's also essential to monitor the crop regularly and take action promptly if you detect any problems.
What are some best practices for harvesting and storing barley?
+Some best practices for harvesting and storing barley include harvesting the crop at the right time, drying the grain to the correct moisture level, and storing the grain in a cool, dry place. It's also essential to handle the grain gently to minimize damage and prevent spoilage.
In conclusion, managing a barley field requires careful planning, attention to detail, and a deep understanding of the crop's needs. By following the five barley field tips outlined in this article, you can help to ensure a healthy and productive crop that is better able to resist disease and pests. Remember to choose the right variety, prepare the soil properly, plant at the right time, manage water and nutrients effectively, and harvest and store the crop properly. With the right techniques and strategies, you can optimize your barley crop's potential and achieve a successful harvest. We hope you found this article informative and helpful. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with barley field management, please don't hesitate to comment below.
