Intro
Discover 7 Army Officer Jobs, including combat and non-combat roles, with careers in leadership, strategy, and specialized fields like aviation and engineering, offering varied military career paths.
The role of an army officer is multifaceted and crucial to the functioning of any military unit. Army officers are responsible for leading troops, making strategic decisions, and ensuring the safety and success of their teams. With a wide range of specializations and career paths available, army officers can choose from various jobs that suit their skills, interests, and strengths. Here, we will explore seven different army officer jobs, each with its unique responsibilities, challenges, and rewards.
Army officers play a vital role in maintaining national security, defending against threats, and participating in humanitarian missions. They are trained to lead by example, make tough decisions, and work effectively under pressure. Whether they are commanding troops, analyzing intelligence, or providing medical care, army officers are essential to the success of military operations. With their advanced training, leadership skills, and commitment to service, army officers are highly respected and admired professionals.
The diversity of army officer jobs is a significant factor in attracting talented individuals to this career path. From combat roles to support functions, army officers can choose from a variety of specializations that align with their interests, skills, and values. For example, those who enjoy working with technology might be interested in signals or intelligence roles, while those who prefer working with people might be suited to personnel or medical jobs. With so many options available, army officers can find a career path that is both fulfilling and challenging.
Introduction to Army Officer Jobs

Army officer jobs can be broadly categorized into several groups, including combat, combat support, and combat service support roles. Combat roles involve direct engagement with enemy forces, while combat support roles provide essential services such as artillery, engineering, or signals support. Combat service support roles, on the other hand, focus on providing logistical, administrative, and medical support to troops. Each of these categories offers a range of job opportunities, from infantry and armor officers to logistics and personnel managers.
1. Infantry Officer

Infantry officers are responsible for leading infantry units, which are the backbone of any army. They are trained to fight on foot, using a range of weapons and tactics to engage enemy forces. Infantry officers must be physically fit, able to work well under pressure, and possess strong leadership skills. They are responsible for planning and executing missions, as well as training and mentoring their troops.
Key Responsibilities of Infantry Officers
Some of the key responsibilities of infantry officers include: * Leading infantry units in combat and training exercises * Planning and executing missions, including reconnaissance and patrols * Training and mentoring troops, including new recruits and experienced soldiers * Coordinating with other units, such as artillery and engineering teams * Making tactical decisions, including deploying troops and allocating resources2. Logistics Officer

Logistics officers are responsible for managing the supply chain and ensuring that troops have the equipment, food, and fuel they need to operate effectively. They must be able to plan and coordinate complex logistics operations, including transportation, storage, and maintenance. Logistics officers work closely with other units, including infantry, artillery, and engineering teams, to ensure that resources are allocated efficiently and effectively.
Key Responsibilities of Logistics Officers
Some of the key responsibilities of logistics officers include: * Managing the supply chain, including procurement, storage, and distribution * Coordinating transportation, including air, land, and sea movements * Planning and executing maintenance operations, including vehicle and equipment repair * Allocating resources, including fuel, food, and ammunition * Working with other units, including infantry, artillery, and engineering teams3. Signals Officer

Signals officers are responsible for managing communication systems, including radio, telephone, and computer networks. They must be able to plan and execute communication operations, including deploying communication equipment and training personnel. Signals officers work closely with other units, including infantry, artillery, and logistics teams, to ensure that communication systems are secure, reliable, and effective.
Key Responsibilities of Signals Officers
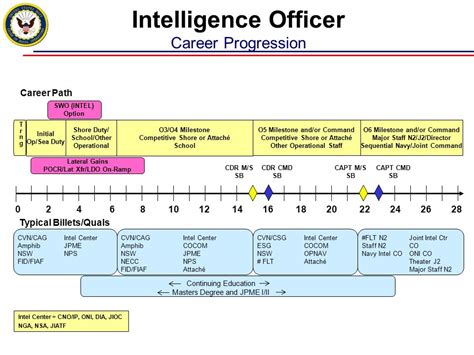
Some of the key responsibilities of signals officers include: * Managing communication systems, including radio, telephone, and computer networks * Planning and executing communication operations, including deploying communication equipment * Training personnel, including signals operators and maintenance technicians * Coordinating with other units, including infantry, artillery, and logistics teams * Ensuring communication security, including encryption and authentication4. Intelligence Officer

Intelligence officers are responsible for gathering, analyzing, and disseminating intelligence information. They must be able to plan and execute intelligence operations, including reconnaissance and surveillance. Intelligence officers work closely with other units, including infantry, artillery, and logistics teams, to ensure that intelligence information is accurate, relevant, and timely.
Key Responsibilities of Intelligence Officers
Some of the key responsibilities of intelligence officers include: * Gathering, analyzing, and disseminating intelligence information * Planning and executing intelligence operations, including reconnaissance and surveillance * Training personnel, including intelligence analysts and operators * Coordinating with other units, including infantry, artillery, and logistics teams * Ensuring intelligence security, including classification and authentication5. Medical Officer

Medical officers are responsible for providing medical care to troops, including diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of illness and injury. They must be able to plan and execute medical operations, including deploying medical equipment and training personnel. Medical officers work closely with other units, including infantry, artillery, and logistics teams, to ensure that medical care is timely, effective, and efficient.
Key Responsibilities of Medical Officers
Some of the key responsibilities of medical officers include: * Providing medical care to troops, including diagnosis, treatment, and prevention * Planning and executing medical operations, including deploying medical equipment * Training personnel, including medical technicians and nurses * Coordinating with other units, including infantry, artillery, and logistics teams * Ensuring medical security, including infection control and patient confidentiality6. Personnel Officer

Personnel officers are responsible for managing human resources, including recruitment, training, and personnel administration. They must be able to plan and execute personnel operations, including deploying personnel and training teams. Personnel officers work closely with other units, including infantry, artillery, and logistics teams, to ensure that personnel are properly trained, equipped, and supported.
Key Responsibilities of Personnel Officers
Some of the key responsibilities of personnel officers include: * Managing human resources, including recruitment, training, and personnel administration * Planning and executing personnel operations, including deploying personnel and training teams * Training personnel, including new recruits and experienced soldiers * Coordinating with other units, including infantry, artillery, and logistics teams * Ensuring personnel security, including classification and authentication7. Engineer Officer

Engineer officers are responsible for designing, building, and maintaining infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings. They must be able to plan and execute engineering operations, including deploying engineering equipment and training personnel. Engineer officers work closely with other units, including infantry, artillery, and logistics teams, to ensure that infrastructure is safe, secure, and effective.
Key Responsibilities of Engineer Officers
Some of the key responsibilities of engineer officers include: * Designing, building, and maintaining infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings * Planning and executing engineering operations, including deploying engineering equipment * Training personnel, including engineering technicians and operators * Coordinating with other units, including infantry, artillery, and logistics teams * Ensuring engineering security, including safety and quality controlArmy Officer Jobs Image Gallery









What are the different types of army officer jobs?
+There are several types of army officer jobs, including infantry, logistics, signals, intelligence, medical, personnel, and engineer officers. Each of these roles has unique responsibilities and requirements.
What are the key responsibilities of an infantry officer?
+Infantry officers are responsible for leading infantry units, planning and executing missions, training and mentoring troops, and coordinating with other units. They must be physically fit, able to work well under pressure, and possess strong leadership skills.
How do I become an army officer?
+To become an army officer, you typically need to complete a bachelor's degree, attend officer candidate school, and complete additional training and education. You must also meet the physical and mental requirements for army service and pass a background check.
What are the benefits of being an army officer?
+Army officers enjoy a range of benefits, including competitive pay, comprehensive health insurance, and opportunities for education and career advancement. They also have the opportunity to serve their country, develop leadership skills, and work with a diverse and talented team.
How long does it take to become an army officer?
+The length of time it takes to become an army officer varies depending on the individual's circumstances and the branch of service they are applying to. Typically, it takes around 4-6 years to complete a bachelor's degree and attend officer candidate school, followed by additional training and education.
In conclusion, army officer jobs offer a range of exciting and challenging career opportunities for individuals who are passionate about serving their country and developing their leadership skills. Whether you are interested in combat, combat support, or combat service support roles, there is an army officer job that can match your skills, interests, and strengths. By understanding the different types of army officer jobs, their key responsibilities, and the benefits and requirements of army service, you can make an informed decision about whether this career path is right for you. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences about army officer jobs, and to ask any questions you may have about this rewarding and challenging career.
