Intro
Discover the SPc meaning in the Army, exploring Specialist ranks, military occupational specialties, and enlisted personnel roles, to understand Army hierarchy and career progression.
The United States Army is a complex and multifaceted organization, with a wide range of roles, responsibilities, and specialties. One of the key components of the Army's personnel system is the use of Military Occupational Specialties, or MOS. An MOS is a specific job or career field that a soldier is trained and qualified to perform. Within the Army, there are numerous MOS codes, each representing a unique occupation or skill set. One such MOS code is 92Y, which corresponds to the Unit Supply Specialist. However, the term "SPC" has a different meaning in the Army.
SPC is an abbreviation for Specialist, which is a military rank in the United States Army. It is above the rank of Private First Class (PFC) and below the rank of Sergeant (SGT). The rank of Specialist is typically held by soldiers who have specialized skills or training in a particular area, such as communications, intelligence, or medicine. Specialists are often responsible for performing specific tasks or functions within their unit, and may serve as team leaders or mentors to junior soldiers.
The rank of Specialist is denoted by the pay grade of E-4, which is the same pay grade as the rank of Corporal (CPL). However, while Corporals are typically considered non-commissioned officers (NCOs) and are expected to perform leadership roles, Specialists are not always considered NCOs and may not have the same level of leadership responsibility.
In terms of responsibilities, a Specialist in the Army may be expected to perform a variety of tasks, depending on their specific MOS and unit. Some common responsibilities of Specialists include:
- Performing specialized tasks or functions, such as operating communications equipment or providing medical care
- Serving as team leaders or mentors to junior soldiers
- Assisting in the planning and execution of unit operations
- Maintaining equipment and supplies
- Providing training and guidance to other soldiers
Specialists may also be expected to have advanced knowledge and skills in their specific area of expertise, and may be required to complete specialized training or certification programs.
Role of a Specialist in the Army

The role of a Specialist in the Army is critical to the success of the organization. Specialists bring specialized skills and knowledge to their units, which enables them to perform specific tasks and functions that are essential to the mission. Without Specialists, the Army would not be able to function effectively, as many of the specialized tasks and functions that they perform are critical to the success of operations.
Some of the key benefits of having Specialists in the Army include:
- Increased efficiency and effectiveness: Specialists are trained to perform specific tasks and functions, which enables them to complete them quickly and effectively.
- Improved morale: Specialists are often recognized and rewarded for their specialized skills and knowledge, which can improve morale and motivation.
- Enhanced capability: Specialists bring unique skills and knowledge to their units, which enables them to perform tasks and functions that might not be possible otherwise.
Types of Specialists in the Army
There are many different types of Specialists in the Army, each with their own unique skills and knowledge. Some examples include:- Communications Specialists: These soldiers are responsible for operating and maintaining communications equipment, such as radios and satellite systems.
- Intelligence Specialists: These soldiers are responsible for gathering and analyzing intelligence information, such as enemy troop movements and capabilities.
- Medical Specialists: These soldiers are responsible for providing medical care and treatment to other soldiers, as well as maintaining medical equipment and supplies.
- Supply Specialists: These soldiers are responsible for managing and maintaining unit supplies, such as food, water, and ammunition.
Each of these types of Specialists plays a critical role in the success of the Army, and is essential to the mission.
How to Become a Specialist in the Army

Becoming a Specialist in the Army typically requires a combination of education, training, and experience. Here are the steps to become a Specialist:
- Meet the basic qualifications: To become a Specialist, you must meet the basic qualifications for enlistment in the Army, such as being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35, and meeting the physical and medical standards.
- Choose an MOS: You must choose an MOS that corresponds to the type of Specialist you want to become. For example, if you want to become a Communications Specialist, you would choose the MOS code 25Q.
- Complete Basic Combat Training (BCT): All new soldiers must complete BCT, which is a 10-week training program that teaches the basics of soldiering, such as first aid, map reading, and combat skills.
- Complete Advanced Individual Training (AIT): After completing BCT, you will attend AIT, which is a specialized training program that teaches you the skills and knowledge you need to perform your specific MOS.
- Gain experience: Once you have completed your training, you will be assigned to a unit and will begin to gain experience as a Specialist. You will work under the supervision of more experienced soldiers and will be expected to perform your duties to the best of your ability.
- Get promoted: As you gain experience and demonstrate your skills and knowledge, you may be eligible for promotion to the rank of Specialist.
Benefits of Being a Specialist in the Army
There are many benefits to being a Specialist in the Army, including:- Specialized training and education: As a Specialist, you will receive specialized training and education in your specific area of expertise, which can enhance your skills and knowledge.
- Increased pay: Specialists are typically paid more than junior soldiers, which can provide a higher standard of living.
- Leadership opportunities: As a Specialist, you may have opportunities to lead teams or mentor junior soldiers, which can help you develop your leadership skills.
- Career advancement: With experience and training, you may be eligible for promotion to higher ranks or for assignment to more senior leadership positions.
Overall, being a Specialist in the Army can be a rewarding and challenging career, with many opportunities for advancement and professional growth.
Specialist Vs. Corporal: What's the Difference?
In the Army, the ranks of Specialist and Corporal are often confused with one another. While both ranks are considered junior non-commissioned officers (NCOs), there are some key differences between them.
Here are the main differences:
- Leadership responsibilities: Corporals are typically considered to be leadership ranks, and are expected to perform leadership duties such as leading teams or mentoring junior soldiers. Specialists, on the other hand, may not have the same level of leadership responsibility, and may be focused more on performing specialized tasks or functions.
- Pay grade: Both Specialists and Corporals are paid at the E-4 pay grade, which means that they receive the same basic pay.
- MOS: Corporals can be found in a wide range of MOSs, while Specialists are typically found in more specialized MOSs, such as communications or intelligence.
- Promotion requirements: The requirements for promotion to Corporal and Specialist are slightly different. To be promoted to Corporal, a soldier typically needs to have a certain amount of time in service, as well as a certain level of performance and achievement. To be promoted to Specialist, a soldier typically needs to have completed a certain amount of training or education, as well as having a certain level of performance and achievement.
Overall, while both Specialists and Corporals are important ranks in the Army, they have different responsibilities and requirements.
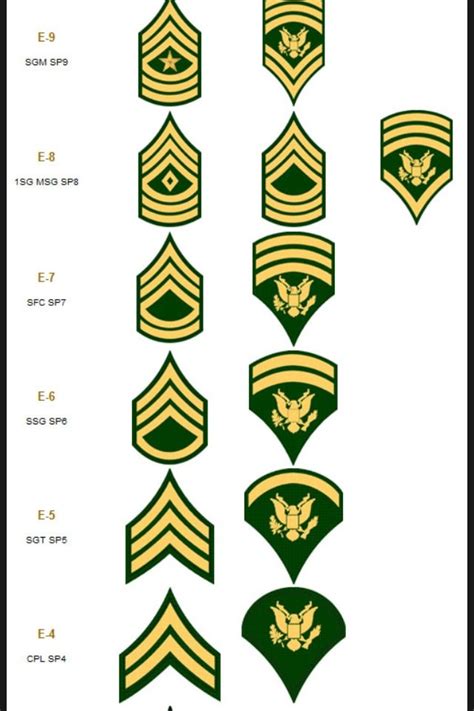
Specialist Rank Insignia
The rank insignia for a Specialist in the Army is a single chevron, which is worn on the sleeve of the uniform. The chevron is pointed upwards, and is typically worn on the upper arm.The rank insignia for a Specialist is as follows:
- One chevron, pointed upwards
- Worn on the sleeve of the uniform
- Typically worn on the upper arm
It's worth noting that the rank insignia for a Specialist can vary slightly depending on the specific uniform being worn. For example, the insignia may be slightly different on the Army Combat Uniform (ACU) versus the Army Service Uniform (ASU).
Specialist Pay and Benefits

As a Specialist in the Army, you can expect to receive a competitive salary and benefits package. Here are some of the key pay and benefits that you can expect:
- Basic pay: As a Specialist, you will receive a basic pay rate of E-4, which is currently $2,515.10 per month.
- Allowances: In addition to your basic pay, you may also be eligible for allowances such as Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) and Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS).
- Special pay: Depending on your specific MOS and assignment, you may be eligible for special pay such as hazardous duty pay or jump pay.
- Benefits: As a member of the Army, you will also be eligible for a range of benefits, including health insurance, retirement benefits, and education assistance.
Overall, the pay and benefits package for a Specialist in the Army is competitive and can provide a high standard of living.
Specialist Job Description
The job description for a Specialist in the Army can vary depending on the specific MOS and assignment. However, here are some of the key responsibilities and duties that you can expect:- Perform specialized tasks or functions: As a Specialist, you will be responsible for performing specialized tasks or functions, such as operating communications equipment or providing medical care.
- Serve as a team leader or mentor: Depending on your specific assignment, you may be responsible for leading a team or mentoring junior soldiers.
- Maintain equipment and supplies: You will be responsible for maintaining equipment and supplies, such as communications gear or medical equipment.
- Provide training and guidance: You may be responsible for providing training and guidance to other soldiers, either in a formal or informal setting.
Overall, the job description for a Specialist in the Army is varied and can include a range of responsibilities and duties.
Specialist Image Gallery








What is the role of a Specialist in the Army?
+The role of a Specialist in the Army is to perform specialized tasks or functions, such as operating communications equipment or providing medical care. They may also serve as team leaders or mentors to junior soldiers.
How do I become a Specialist in the Army?
+To become a Specialist in the Army, you must meet the basic qualifications for enlistment, choose an MOS, complete Basic Combat Training and Advanced Individual Training, and gain experience in your specific field.
What are the benefits of being a Specialist in the Army?
+The benefits of being a Specialist in the Army include specialized training and education, increased pay, leadership opportunities, and career advancement.
What is the difference between a Specialist and a Corporal in the Army?
+The main difference between a Specialist and a Corporal in the Army is that a Corporal is typically considered a leadership rank, while a Specialist is not. Corporals are also typically responsible for leading teams or mentoring junior soldiers, while Specialists may not have the same level of leadership responsibility.
What is the pay grade for a Specialist in the Army?
+The pay grade for a Specialist in the Army is E-4, which is the same pay grade as a Corporal.
In summary, the rank of Specialist in the Army is a critical component of the organization's personnel system. Specialists bring specialized skills and knowledge to their units, which enables them to perform specific tasks and functions that are essential to the mission. If you are interested in becoming a Specialist in the Army, you must meet the basic qualifications for enlistment, choose an MOS, complete Basic Combat Training and Advanced Individual Training, and gain experience in your specific field. As a Specialist, you can expect to receive a competitive salary and benefits package, as well as opportunities for leadership and career advancement. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the role of a Specialist in the Army. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more, please don't hesitate to comment or share this article with others.
