Intro
Discover the 5 South China Sea drills, including naval exercises, joint operations, and maritime training, amidst regional tensions and territorial disputes, showcasing military strength and strategic cooperation.
The South China Sea has become a focal point of geopolitical tensions in recent years, with various nations conducting military drills in the region to assert their claims and protect their interests. These drills have significant implications for regional stability and global security. In this article, we will explore the context and significance of five notable South China Sea drills, examining their objectives, participants, and impact on the region.
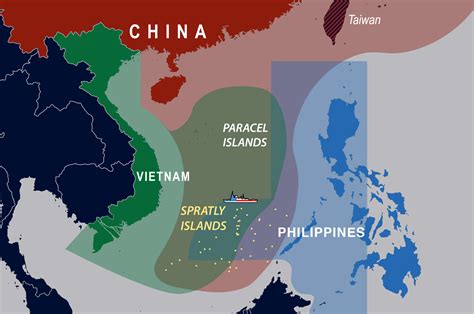
The South China Sea is a critical body of water, providing a conduit for international trade and serving as a rich source of natural resources, including fish, oil, and gas. However, the region is also characterized by overlapping territorial claims, with several countries, including China, the Philippines, Vietnam, Malaysia, and Taiwan, asserting sovereignty over various islands and maritime areas. These competing claims have led to increased military activity in the region, as nations seek to demonstrate their resolve and capabilities.
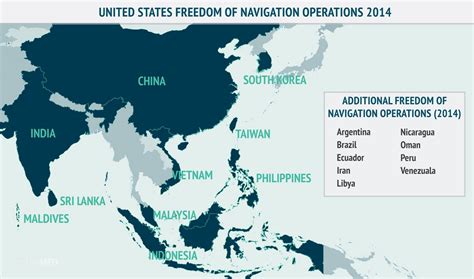
The United States, as a global maritime power, has a significant interest in maintaining freedom of navigation and overflight in the South China Sea. In response to China's growing assertiveness, the US has conducted several high-profile military drills in the region, often in collaboration with regional partners. These exercises aim to promote interoperability, build trust, and demonstrate a collective commitment to regional security.
South China Sea Drills

The first notable drill is the annual Balikatan exercise, conducted by the US and the Philippines. This bilateral exercise focuses on enhancing interoperability, promoting cooperation, and addressing common security challenges. The drill typically involves a range of activities, including amphibious landings, live-fire exercises, and humanitarian assistance operations. By conducting these exercises, the US and the Philippines demonstrate their commitment to their mutual defense treaty and reinforce their partnership in maintaining regional stability.
Objectives and Participants
The objectives of the Balikatan exercise are multifaceted, encompassing both military and humanitarian aspects. The drill aims to enhance the readiness and responsiveness of US and Philippine forces, while also promoting cooperation and trust between the two nations. The exercise typically involves a range of participants, including ground, air, and naval units from both countries. The US has also invited other regional partners to participate in the exercise, including Australia and Japan, to promote a collective approach to regional security.Regional Security Implications

The second notable drill is the Rim of the Pacific (RIMPAC) exercise, conducted biennially by the US Pacific Fleet. RIMPAC is the world's largest international maritime exercise, involving over 20 nations and thousands of personnel. The drill focuses on promoting cooperation, enhancing interoperability, and addressing common maritime security challenges. RIMPAC exercises typically involve a range of activities, including live-fire exercises, amphibious landings, and maritime interdiction operations.
Benefits and Challenges
The benefits of RIMPAC are significant, as the exercise promotes cooperation, builds trust, and enhances the readiness and responsiveness of participating nations. However, the drill also presents several challenges, including the need to coordinate complex operations, manage competing interests, and address the risk of accidents or miscalculations. Despite these challenges, RIMPAC remains a critical component of regional security architecture, providing a platform for nations to engage, cooperate, and address common challenges.Freedom of Navigation Operations

The third notable drill is the Freedom of Navigation Operation (FONOP), conducted by the US Navy in the South China Sea. FONOPs aim to challenge excessive maritime claims, promote freedom of navigation, and demonstrate US commitment to upholding international law. These operations typically involve US warships transiting through disputed waters, often in close proximity to Chinese-occupied features. By conducting FONOPs, the US seeks to reinforce its position on maritime rights, promote stability, and deter aggressive behavior.
International Law and Diplomacy
The FONOPs have significant implications for international law and diplomacy, as they challenge China's expansive maritime claims and promote a rules-based order. The US has argued that its operations are consistent with international law, including the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS). However, China has responded by accusing the US of violating its sovereignty and undermining regional stability. The FONOPs have become a focal point of US-China tensions, highlighting the need for diplomacy and dialogue to resolve competing claims and promote cooperation.China's Military Modernization

The fourth notable drill is China's annual military exercise in the South China Sea, which aims to demonstrate its growing military capabilities and assert its claims. China's exercises typically involve a range of activities, including live-fire drills, amphibious landings, and maritime interdiction operations. By conducting these exercises, China seeks to promote its military modernization, enhance its readiness and responsiveness, and deter potential challengers.
Regional Response and Cooperation
The regional response to China's military exercises has been mixed, with some nations expressing concern over the growing militarization of the South China Sea. The US, in particular, has been critical of China's actions, arguing that they undermine regional stability and promote a destabilizing narrative. However, other nations, including Russia and Pakistan, have expressed support for China's exercises, highlighting the need for cooperation and dialogue to address common security challenges.ASEAN's Role in Regional Security

The fifth notable drill is the ASEAN Defense Ministers' Meeting (ADMM) exercise, which aims to promote cooperation and enhance regional security. The ADMM exercise typically involves a range of activities, including tabletop exercises, field training exercises, and humanitarian assistance operations. By conducting these exercises, ASEAN nations seek to promote cooperation, build trust, and address common security challenges.
Challenges and Opportunities
The ADMM exercise presents both challenges and opportunities for regional security. On the one hand, the exercise promotes cooperation and enhances the readiness and responsiveness of ASEAN nations. On the other hand, the exercise also highlights the need for greater coordination and cooperation among ASEAN nations, as well as between ASEAN and external partners. By addressing these challenges and opportunities, ASEAN can play a critical role in promoting regional security and stability.South China Sea Drills Image Gallery








What are the main objectives of the South China Sea drills?
+The main objectives of the South China Sea drills are to promote cooperation, enhance interoperability, and address common security challenges. The drills aim to demonstrate the readiness and responsiveness of participating nations, while also promoting a rules-based order and deterring aggressive behavior.
Which nations participate in the South China Sea drills?
+The South China Sea drills involve a range of nations, including the US, China, the Philippines, Vietnam, Malaysia, and Taiwan. Other regional partners, such as Australia and Japan, also participate in the exercises to promote a collective approach to regional security.
What are the implications of the South China Sea drills for regional security?
+The South China Sea drills have significant implications for regional security, as they promote cooperation, enhance interoperability, and address common security challenges. The drills also demonstrate the commitment of participating nations to upholding international law and promoting a rules-based order, which is critical for maintaining regional stability and security.
How do the South China Sea drills impact US-China relations?
+The South China Sea drills have a significant impact on US-China relations, as they highlight the competing interests and claims of the two nations. The drills demonstrate the US commitment to upholding international law and promoting a rules-based order, while also challenging China's expansive maritime claims. The exercises have become a focal point of US-China tensions, highlighting the need for diplomacy and dialogue to resolve competing claims and promote cooperation.
What is the role of ASEAN in promoting regional security?
+ASEAN plays a critical role in promoting regional security, as it provides a platform for nations to engage, cooperate, and address common security challenges. The ASEAN Defense Ministers' Meeting (ADMM) exercise is a key component of regional security architecture, promoting cooperation and enhancing the readiness and responsiveness of ASEAN nations. By addressing common security challenges and promoting cooperation, ASEAN can play a critical role in maintaining regional stability and security.
In conclusion, the South China Sea drills are a critical component of regional security architecture, promoting cooperation, enhancing interoperability, and addressing common security challenges. The drills demonstrate the commitment of participating nations to upholding international law and promoting a rules-based order, which is critical for maintaining regional stability and security. As the region continues to evolve, it is essential to promote dialogue, cooperation, and diplomacy to address competing claims and promote a peaceful resolution to disputes. We invite our readers to share their thoughts and opinions on the South China Sea drills and their implications for regional security. Please feel free to comment, share this article, or take specific actions to promote cooperation and understanding in the region.
