Intro
Discover the US Army Sergeant names list, featuring notable Non-Commissioned Officers, Sergeant ranks, and enlisted leaders, highlighting military hierarchy and promotions.
The United States Army has a long history of producing exceptional leaders, and Army Sergeants are no exception. These non-commissioned officers (NCOs) play a crucial role in the Army's hierarchy, serving as a bridge between enlisted personnel and commissioned officers. In this article, we will explore the importance of Army Sergeants, their roles and responsibilities, and provide a list of notable Army Sergeant names.
The Army Sergeant rank is a symbol of excellence, leadership, and dedication. To become a Sergeant, one must demonstrate exceptional skills, knowledge, and character. Army Sergeants are responsible for leading teams, mentoring junior soldiers, and making critical decisions in high-pressure situations. They are the backbone of the Army, and their contributions are essential to the success of military operations.
Throughout history, many Army Sergeants have made significant contributions to the military and beyond. Some have become famous for their heroic actions, while others have gone on to become successful leaders in various fields. Here are a few notable Army Sergeant names:
Introduction to Army Sergeants

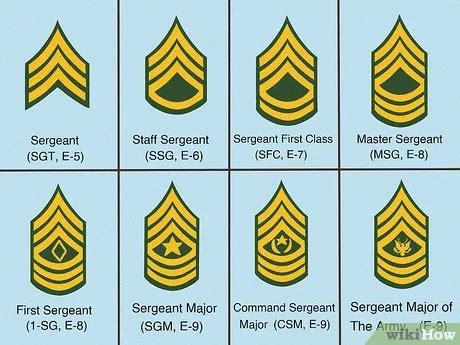
The Army Sergeant rank is divided into several categories, including Sergeant (E-5), Staff Sergeant (E-6), Sergeant First Class (E-7), Master Sergeant (E-8), and First Sergeant (E-8). Each category has its unique responsibilities and requirements. Army Sergeants can specialize in various fields, such as infantry, artillery, engineering, and communications.
Roles and Responsibilities

Army Sergeants play a vital role in the Army's chain of command. They are responsible for:
- Leading and mentoring junior soldiers
- Developing and implementing training programs
- Conducting missions and operations
- Maintaining equipment and supplies
- Providing guidance and counsel to soldiers
Some notable Army Sergeant names include:
- Sergeant Alvin York, a World War I hero who received the Medal of Honor for his actions during the Meuse-Argonne Offensive
- Sergeant Audie Murphy, a World War II hero who received the Medal of Honor for his actions during the Battle of Colmar Pocket
- Sergeant First Class Randall Shugart, a Medal of Honor recipient who was killed in action during the Battle of Mogadishu in 1993
- Master Sergeant Gary I. Gordon, a Medal of Honor recipient who was killed in action during the Battle of Mogadishu in 1993
Notable Army Sergeants

Other notable Army Sergeants include:
- Sergeant Major of the Army Daniel A. Dailey, the 15th Sergeant Major of the Army
- Sergeant First Class Darius T. Fuller, a Medal of Honor recipient who served in World War II
- Master Sergeant Joshua Wheeler, a Medal of Honor recipient who was killed in action during the Iraq War
- Sergeant First Class Paul R. Smith, a Medal of Honor recipient who was killed in action during the Iraq War
Army Sergeant Ranks
The Army Sergeant rank is divided into several categories, each with its unique responsibilities and requirements. The ranks are:- Sergeant (E-5)
- Staff Sergeant (E-6)
- Sergeant First Class (E-7)
- Master Sergeant (E-8)
- First Sergeant (E-8)
Army Sergeant Specializations
Army Sergeants can specialize in various fields, including:
- Infantry
- Artillery
- Engineering
- Communications
- Intelligence
- Logistics
Each specialization requires unique skills and knowledge, and Army Sergeants must complete specialized training to become qualified in their field.
Army Sergeant Training

Army Sergeant training is rigorous and challenging. Sergeants must complete advanced individual training, non-commissioned officer (NCO) education, and specialized training in their field. They must also demonstrate exceptional leadership and character to become qualified as a Sergeant.
Army Sergeant Leadership
Army Sergeants are expected to demonstrate exceptional leadership and character. They must be able to lead and mentor junior soldiers, make critical decisions, and maintain discipline and order within their unit.Army Sergeant Career Progression

The Army Sergeant career progression is as follows:
- Sergeant (E-5): Typically serves as a team leader or squad leader
- Staff Sergeant (E-6): Typically serves as a platoon sergeant or section leader
- Sergeant First Class (E-7): Typically serves as a platoon sergeant or first sergeant
- Master Sergeant (E-8): Typically serves as a senior enlisted advisor or first sergeant
- First Sergeant (E-8): Typically serves as a senior enlisted advisor or command sergeant major
Gallery of Army Sergeants
Army Sergeant Image Gallery










Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of an Army Sergeant?
+An Army Sergeant is a non-commissioned officer who serves as a team leader, squad leader, or platoon sergeant. They are responsible for leading and mentoring junior soldiers, developing and implementing training programs, and conducting missions and operations.
What are the different types of Army Sergeants?
+There are several types of Army Sergeants, including Sergeant (E-5), Staff Sergeant (E-6), Sergeant First Class (E-7), Master Sergeant (E-8), and First Sergeant (E-8). Each type has its unique responsibilities and requirements.
What is the career progression for an Army Sergeant?
+The career progression for an Army Sergeant typically begins as a Sergeant (E-5) and can progress to Staff Sergeant (E-6), Sergeant First Class (E-7), Master Sergeant (E-8), and First Sergeant (E-8). Each rank requires additional training, experience, and leadership responsibilities.
In conclusion, Army Sergeants play a vital role in the United States Army. They are exceptional leaders, mentors, and soldiers who have demonstrated exceptional skills, knowledge, and character. From Sergeant to First Sergeant, each rank requires unique responsibilities and requirements. We hope this article has provided valuable information about Army Sergeants and their importance in the military. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
