Intro
Discover 5 key security differences, including threat detection, encryption, and access control, to enhance your cybersecurity measures and protect against vulnerabilities, breaches, and malware attacks.
The world of technology is constantly evolving, and with it, the need for robust security measures has become more pressing than ever. As we navigate the complex landscape of digital threats, it's essential to understand the nuances of security differences that can make or break our defenses. In this article, we'll delve into the top 5 security differences that can significantly impact our online safety and explore the importance of each in protecting our digital assets.
The security of our personal and professional data is a top priority, and the differences in security measures can be the deciding factor between a secure and a compromised system. From encryption methods to access control, each security difference plays a vital role in safeguarding our information from unauthorized access. As we move forward in this digital age, it's crucial to recognize the significance of these security differences and implement them effectively to ensure the integrity of our online presence.
The ever-increasing threat of cyberattacks has made it imperative to understand the security differences that can protect us from these malicious attempts. By grasping the concepts of security differences, we can better equip ourselves to combat the evolving threats and maintain a secure online environment. Whether it's a personal computer or a large-scale enterprise, the importance of security differences cannot be overstated, and it's essential to acknowledge their role in maintaining our digital security.
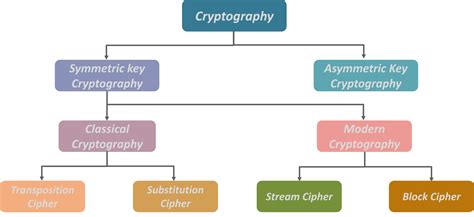
Encryption Methods
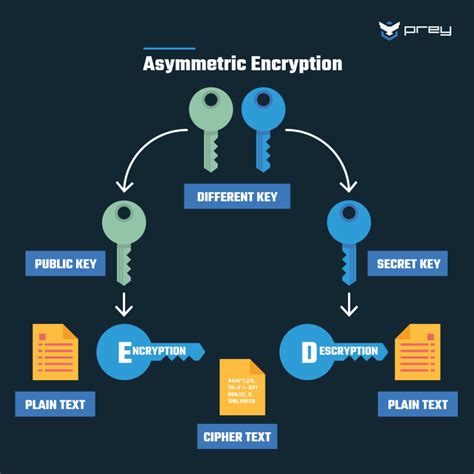
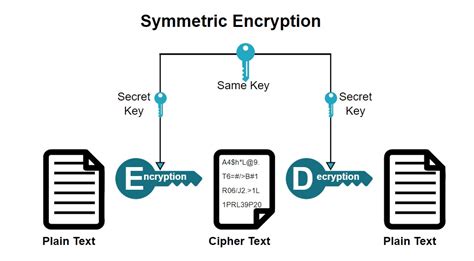
Types of Encryption
There are several types of encryption, including: * Symmetric encryption: Uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. * Asymmetric encryption: Uses a pair of keys: one for encryption and another for decryption. * Hashing: A one-way encryption method that produces a fixed-size string of characters. * Block cipher: Divides the data into fixed-size blocks and encrypts each block independently. Each type of encryption has its unique characteristics, and selecting the right one depends on the specific use case and security requirements.Access Control
Access Control Models
There are several access control models, including: * Discretionary access control (DAC): Grants access based on user identity. * Mandatory access control (MAC): Grants access based on user clearance. * Role-based access control (RBAC): Grants access based on user role. * Attribute-based access control (ABAC): Grants access based on user attributes. Each access control model has its strengths and weaknesses, and selecting the right one depends on the specific security requirements and use case.Network Security

Network Security Threats
There are several network security threats, including: * Malware: Software designed to harm or exploit our system. * Phishing: Attempting to obtain sensitive information by disguising as a trustworthy entity. * Denial of service (DoS): Overwhelming our system with traffic to make it unavailable. * Man-in-the-middle (MitM): Intercepting and altering our communication to steal sensitive information. Each network security threat has its unique characteristics, and understanding the differences between them is essential in protecting our network from these threats.Cryptography
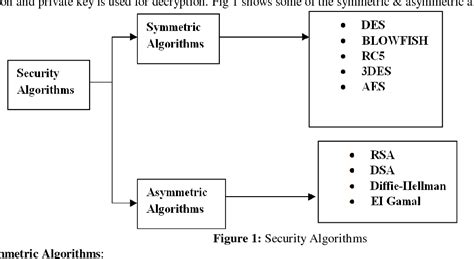
Cryptographic Algorithms
There are several cryptographic algorithms, including: * Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): A symmetric encryption algorithm. * Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA): An asymmetric encryption algorithm. * Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA): A hashing algorithm. * Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC): An asymmetric encryption algorithm. Each cryptographic algorithm has its unique characteristics, and selecting the right one depends on the specific security requirements and use case.Secure Communication
Secure Communication Protocols
There are several secure communication protocols, including: * Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS): Encrypts our internet traffic to protect our data. * Internet Protocol Security (IPSec): Encrypts our internet traffic to protect our data. * Secure Shell (SSH): A secure remote access protocol. * Pretty Good Privacy (PGP): A secure email protocol. Each secure communication protocol has its unique characteristics, and selecting the right one depends on the specific security requirements and use case.Security Image Gallery







What is encryption, and how does it work?
+Encryption is the process of converting plaintext into unreadable ciphertext to protect our data from unauthorized access. It works by using an encryption algorithm and a key to transform the plaintext into ciphertext.
What is access control, and why is it important?
+Access control is the process of granting or denying access to our digital assets based on user identity, role, or permissions. It's essential in protecting our data from unauthorized access and ensuring that only authorized users can access our digital assets.
What is network security, and how does it work?
+Network security is the process of protecting our network from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. It works by using various network security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and virtual private networks, to protect our network from security threats.
What is cryptography, and why is it important?
+Cryptography is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of third-party adversaries. It's essential in protecting our data from unauthorized access and ensuring that our communication remains confidential and secure.
What is secure communication, and how does it work?
+Secure communication is the process of protecting our communication from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. It works by using various secure communication protocols, such as SSL/TLS and IPSec, to encrypt our internet traffic and protect our data.
In conclusion, the 5 security differences discussed in this article are crucial in protecting our online safety and security. By understanding the importance of encryption methods, access control, network security, cryptography, and secure communication, we can better equip ourselves to combat the evolving threats and maintain a secure online environment. Whether it's a personal computer or a large-scale enterprise, the implementation of these security differences can significantly impact our digital security and protect our sensitive information from unauthorized access. We encourage you to share this article with others, comment on your experiences with security differences, and take the necessary steps to implement these security measures in your own online presence.
