Intro
Explore Russias debt to GDP ratio, economic stability, and fiscal policy, including public debt, government spending, and economic growth implications.
The debt-to-GDP ratio is a widely used indicator to assess a country's fiscal health and sustainability. It represents the ratio of a country's total debt to its gross domestic product (GDP). A high debt-to-GDP ratio can indicate a higher risk of default and may lead to a decrease in investor confidence, while a low ratio suggests a more stable fiscal situation. Russia, being one of the world's major economies, has experienced fluctuations in its debt-to-GDP ratio over the years. Understanding the trends and factors influencing this ratio is crucial for evaluating Russia's economic stability and potential for growth.
Russia's economy has faced numerous challenges, including fluctuations in global commodity prices, particularly oil, which is a significant contributor to the country's revenue. The impact of economic sanctions imposed by Western countries following the annexation of Crimea in 2014 has also been a factor affecting Russia's economic performance. Despite these challenges, Russia has managed to maintain a relatively low debt-to-GDP ratio compared to other major economies. This is partly due to the country's fiscal policy, which has aimed at reducing budget deficits and accumulating reserves.
The Russian government has implemented various measures to manage its debt and improve its fiscal position. These include the establishment of the National Wealth Fund (NWF), which is designed to accumulate surplus revenues from oil exports and use them for debt repayment and investment in strategic projects. Additionally, Russia has focused on diversifying its economy, aiming to reduce dependence on oil and gas exports, which are subject to price volatility. Efforts to stimulate non-oil sectors, such as manufacturing and agriculture, have been part of this diversification strategy.
Russia's Economic Performance and Debt Management
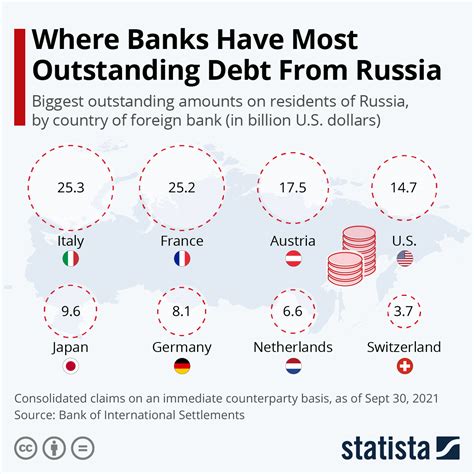
Russia's economic performance and debt management have been closely monitored by international financial institutions and rating agencies. The country's ability to navigate through economic challenges, including the COVID-19 pandemic, has been a subject of interest. The pandemic posed significant risks to Russia's economy, including a decline in oil prices and a reduction in domestic demand. However, the government's response, which included fiscal support measures and monetary policy easing, helped mitigate the impact of the pandemic on the economy.
Factors Influencing Russia's Debt-to-GDP Ratio
Several factors influence Russia's debt-to-GDP ratio, including government spending, revenue collection, and the overall performance of the economy. The price of oil is a critical factor, as it directly affects government revenues. A significant decline in oil prices can lead to a decrease in revenue, potentially increasing the debt-to-GDP ratio if not offset by spending cuts or other revenue sources. Additionally, the impact of sanctions and geopolitical tensions on investor confidence and capital flows can also affect Russia's ability to manage its debt.
Debt Structure and Management
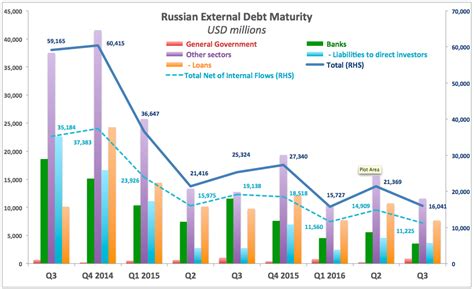
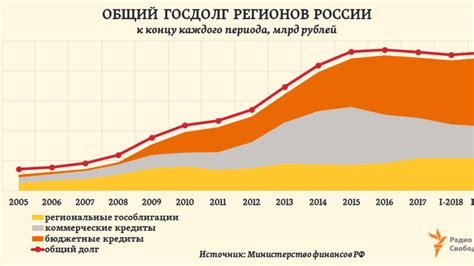
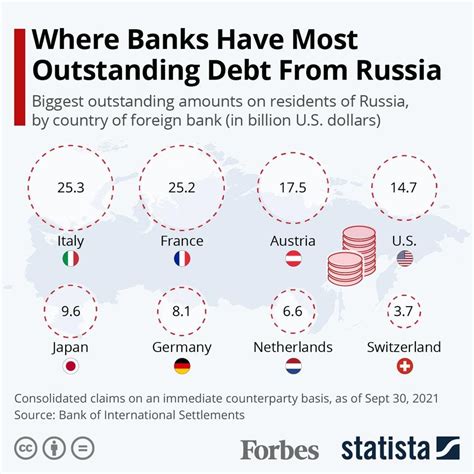
Understanding Russia's debt structure is essential for assessing its debt management strategies. The country's debt is primarily denominated in local currency, the ruble, which reduces the risk associated with foreign exchange fluctuations. However, a significant portion of Russia's debt is held by non-resident investors, which can make the country vulnerable to changes in global market conditions and investor sentiment. The Russian government has been working to reduce its dependence on foreign capital by developing the domestic bond market and encouraging long-term investments.
Economic Diversification and Growth

Economic diversification is a key strategy for Russia to achieve sustainable growth and reduce its vulnerability to external shocks. The government has identified several sectors for development, including technology, agriculture, and manufacturing. Initiatives such as the "National Projects" aim to stimulate investment in these areas through infrastructure development, innovation support, and human capital development. Success in diversification efforts can lead to a more balanced economy, improved fiscal resilience, and a lower debt-to-GDP ratio over time.
Fiscal Policy and Budget Management

Russia's fiscal policy plays a crucial role in managing the country's debt and achieving economic stability. The government has implemented a fiscal rule that links budget expenditures to the long-term price of oil, aiming to smooth out the impact of price volatility on revenues. This approach helps in maintaining a stable fiscal position and reduces the risk of sharp increases in the debt-to-GDP ratio during periods of low oil prices. Additionally, efforts to improve tax administration and broaden the tax base are underway to enhance revenue collection and reduce dependence on oil revenues.
International Cooperation and Investment

International cooperation and investment are essential for Russia's economic growth and debt management. The country has been actively engaged in regional and global economic organizations, such as the Eurasian Economic Union (EEU) and the BRICS grouping, to promote trade, investment, and economic integration. Attracting foreign investment, particularly in strategic sectors, can help in diversifying the economy and improving its growth prospects. However, geopolitical tensions and sanctions have posed challenges to Russia's ability to attract significant foreign investment, underscoring the need for a stable and predictable investment climate.
Gallery of Russia Debt Management
Russia Debt Management Image Gallery

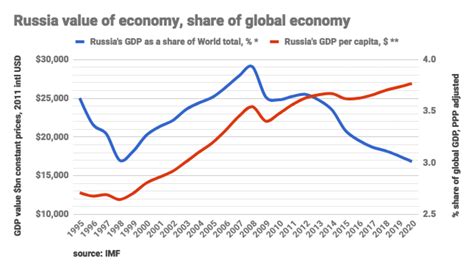





What is the current debt-to-GDP ratio of Russia?
+Russia's debt-to-GDP ratio has fluctuated over the years but remains relatively low compared to other major economies. As of the latest available data, the ratio stands at around 15%, which is considered manageable.
How does the price of oil affect Russia's debt-to-GDP ratio?
+The price of oil has a significant impact on Russia's debt-to-GDP ratio. A decline in oil prices can lead to a decrease in government revenues, potentially increasing the debt-to-GDP ratio if not offset by spending cuts or other revenue sources.
What measures has the Russian government taken to manage its debt?
+The Russian government has implemented several measures to manage its debt, including the establishment of the National Wealth Fund, diversification of the economy, and improvement of tax administration. These efforts aim to reduce dependence on oil revenues and enhance fiscal resilience.
How does economic diversification impact Russia's debt-to-GDP ratio?
+Economic diversification can lead to a more balanced economy, improved fiscal resilience, and a lower debt-to-GDP ratio over time. By reducing dependence on oil and gas exports, Russia can mitigate the impact of price volatility on its revenues and achieve more sustainable economic growth.
What role does international cooperation play in Russia's debt management?
+International cooperation is essential for Russia's economic growth and debt management. Engaging in regional and global economic organizations and attracting foreign investment can help diversify the economy and improve its growth prospects, thereby supporting debt management efforts.
In conclusion, Russia's debt-to-GDP ratio is a critical indicator of the country's fiscal health and sustainability. The government's efforts to manage debt, diversify the economy, and improve fiscal policy have been crucial in maintaining a relatively stable fiscal position. However, challenges such as the impact of oil price volatility, geopolitical tensions, and the need for further economic diversification remain. As Russia continues to navigate these challenges, its ability to adapt and implement effective economic strategies will be key to achieving long-term fiscal stability and growth. We invite readers to share their insights and thoughts on Russia's economic prospects and debt management strategies, and we look forward to continuing the discussion on this critical topic.
