Intro
Discover the 5 Key Marine Differences, exploring naval variations, maritime distinctions, and oceanic divergences that impact marine ecosystems, marine life, and maritime industries, highlighting crucial marine biology and marine conservation aspects.
The marine world is a diverse and complex ecosystem, comprising various species, habitats, and processes that are interconnected and interdependent. Understanding the key differences between various marine components is essential for appreciating the intricacies of this ecosystem and addressing the challenges it faces. In this article, we will delve into five key marine differences that are crucial for maintaining the health and resilience of marine ecosystems.
Marine ecosystems are vital for the planet, providing numerous benefits, including food, livelihoods, and climate regulation. However, these ecosystems are facing unprecedented threats, such as overfishing, pollution, and climate change, which can have far-reaching consequences for the health of our planet. By exploring the key differences between various marine components, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complex relationships within marine ecosystems and develop effective strategies for conservation and management.
The importance of understanding marine differences cannot be overstated. Marine ecosystems are dynamic and constantly evolving, with species interacting and adapting to their environments in complex ways. By recognizing and appreciating these differences, we can better manage marine resources, mitigate the impacts of human activities, and promote the long-term sustainability of marine ecosystems. In the following sections, we will examine five key marine differences that are critical for maintaining the health and resilience of marine ecosystems.
Introduction to Marine Ecosystems
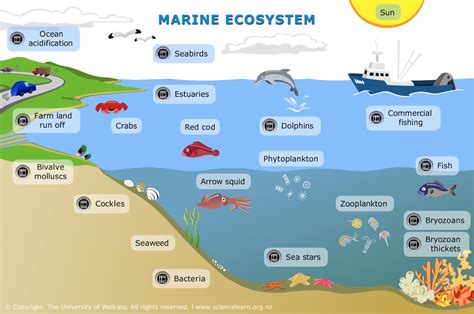
Marine ecosystems are complex and diverse, comprising various habitats, such as coral reefs, estuaries, and open ocean. Each of these habitats supports a unique array of species, from tiny plankton to massive blue whales. Understanding the differences between these habitats and the species they support is essential for managing marine resources effectively and promoting the long-term sustainability of marine ecosystems.
Key Components of Marine Ecosystems
Marine ecosystems are composed of various components, including phytoplankton, zooplankton, fish, and marine mammals. Each of these components plays a critical role in the functioning of marine ecosystems, and changes to one component can have far-reaching consequences for the entire ecosystem. By recognizing and appreciating the differences between these components, we can better understand the complex relationships within marine ecosystems and develop effective strategies for conservation and management.Marine Habitat Differences
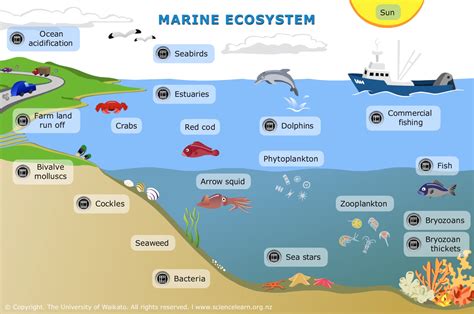
Marine habitats are diverse and complex, with different habitats supporting unique arrays of species. Coral reefs, for example, are some of the most biodiverse ecosystems on the planet, with thousands of species interacting and adapting to their environments in complex ways. In contrast, open ocean habitats are characterized by vast expanses of water, with species such as blue whales and tuna migrating across entire ocean basins. Understanding the differences between these habitats is essential for managing marine resources effectively and promoting the long-term sustainability of marine ecosystems.
Types of Marine Habitats
There are several types of marine habitats, including coral reefs, estuaries, mangroves, and open ocean. Each of these habitats supports a unique array of species and plays a critical role in the functioning of marine ecosystems. Coral reefs, for example, provide important habitat for numerous species of fish and invertebrates, while estuaries and mangroves provide critical nursery habitats for many marine species.Species Differences in Marine Ecosystems

Species differences are a critical component of marine ecosystems, with different species interacting and adapting to their environments in complex ways. Phytoplankton, for example, are the base of many marine food webs, providing important food sources for zooplankton and other marine species. In contrast, apex predators such as sharks and tuna play critical roles in regulating the populations of other marine species. Understanding the differences between these species is essential for managing marine resources effectively and promoting the long-term sustainability of marine ecosystems.
Importance of Species Diversity
Species diversity is critical for maintaining the health and resilience of marine ecosystems. When species diversity is high, ecosystems are better able to withstand disturbances and recover from setbacks. In contrast, low species diversity can make ecosystems more vulnerable to disturbances and less resilient to change. By recognizing and appreciating the differences between species, we can better understand the complex relationships within marine ecosystems and develop effective strategies for conservation and management.Marine Food Web Differences
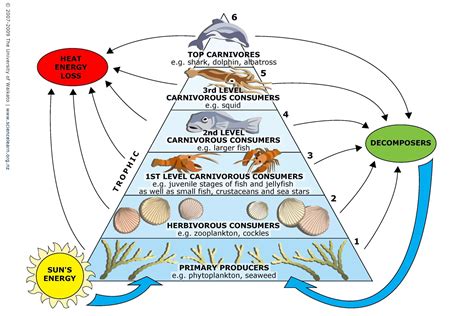
Marine food webs are complex and dynamic, with different species interacting and adapting to their environments in complex ways. Phytoplankton, for example, are the base of many marine food webs, providing important food sources for zooplankton and other marine species. In contrast, apex predators such as sharks and tuna play critical roles in regulating the populations of other marine species. Understanding the differences between these food webs is essential for managing marine resources effectively and promoting the long-term sustainability of marine ecosystems.
Types of Marine Food Webs
There are several types of marine food webs, including phytoplankton-based food webs, zooplankton-based food webs, and benthic food webs. Each of these food webs plays a critical role in the functioning of marine ecosystems, and changes to one food web can have far-reaching consequences for the entire ecosystem. By recognizing and appreciating the differences between these food webs, we can better understand the complex relationships within marine ecosystems and develop effective strategies for conservation and management.Marine Conservation Differences

Marine conservation is critical for maintaining the health and resilience of marine ecosystems. Different conservation strategies are needed for different marine habitats and species, and understanding the differences between these strategies is essential for effective conservation. Marine protected areas, for example, can provide important habitat for numerous species of fish and invertebrates, while sustainable fishing practices can help to maintain the long-term sustainability of marine fisheries.
Importance of Marine Conservation
Marine conservation is essential for maintaining the health and resilience of marine ecosystems. When marine ecosystems are healthy and resilient, they are better able to withstand disturbances and recover from setbacks. In contrast, degraded marine ecosystems can be more vulnerable to disturbances and less resilient to change. By recognizing and appreciating the differences between conservation strategies, we can better understand the complex relationships within marine ecosystems and develop effective strategies for conservation and management.Marine Ecosystems Image Gallery










What are the key differences between marine habitats?
+Marine habitats are diverse and complex, with different habitats supporting unique arrays of species. Coral reefs, for example, are some of the most biodiverse ecosystems on the planet, while open ocean habitats are characterized by vast expanses of water.
Why is species diversity important in marine ecosystems?
+Species diversity is critical for maintaining the health and resilience of marine ecosystems. When species diversity is high, ecosystems are better able to withstand disturbances and recover from setbacks.
What are the benefits of marine conservation?
+Marine conservation is essential for maintaining the health and resilience of marine ecosystems. When marine ecosystems are healthy and resilient, they are better able to withstand disturbances and recover from setbacks.
How can we promote the long-term sustainability of marine ecosystems?
+We can promote the long-term sustainability of marine ecosystems by recognizing and appreciating the differences between marine habitats, species, and food webs, and by developing effective strategies for conservation and management.
What are some of the key challenges facing marine ecosystems?
+Marine ecosystems are facing numerous challenges, including overfishing, pollution, and climate change. These challenges can have far-reaching consequences for the health of marine ecosystems and the planet as a whole.
In conclusion, understanding the key differences between various marine components is essential for appreciating the intricacies of marine ecosystems and addressing the challenges they face. By recognizing and appreciating these differences, we can develop effective strategies for conservation and management, promote the long-term sustainability of marine ecosystems, and ensure the health and resilience of our planet. We encourage you to share your thoughts and ideas on this topic, and to take action to promote the conservation and sustainability of marine ecosystems. Together, we can make a difference and ensure a healthy and thriving planet for future generations.
