Intro
Discover the US Military Ranking System, including officer and enlisted ranks, pay grades, and insignia, to understand the hierarchical structure and promotions within the Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps.
The US military ranking system is a complex and hierarchical structure that defines the roles, responsibilities, and levels of authority for members of the US Armed Forces. Understanding the ranking system is essential for navigating the military's organizational framework and recognizing the accomplishments and qualifications of its personnel. The ranking system is used across all branches of the US military, including the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard.
The US military ranking system is divided into three main categories: enlisted, warrant officer, and officer. Each category has its own set of ranks, with increasing levels of responsibility and authority. The ranking system is designed to provide a clear chain of command and to recognize individual achievements and contributions to the military. The system also provides a framework for career advancement and professional development.
The history of the US military ranking system dates back to the American Revolution, when the Continental Army was formed. The first ranking system was based on the British military model, with modifications to reflect the unique needs and circumstances of the American colonies. Over time, the ranking system has evolved to reflect changes in military technology, tactics, and organizational structure. Today, the US military ranking system is one of the most complex and sophisticated in the world, with a wide range of ranks and specialties.
Enlisted Ranks
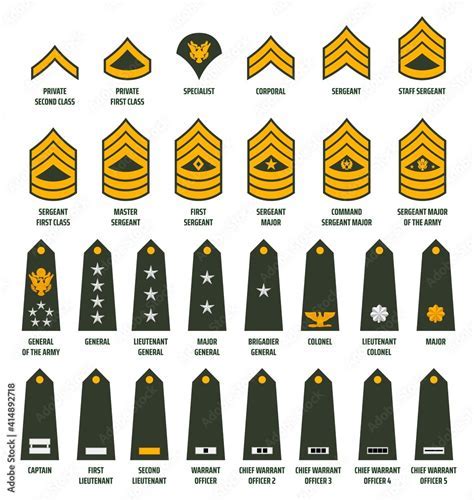

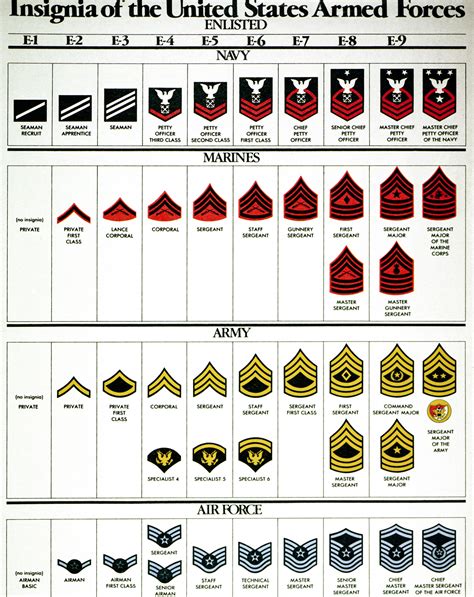
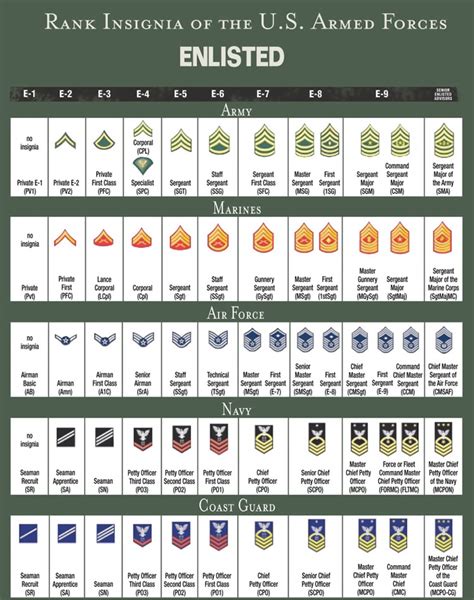
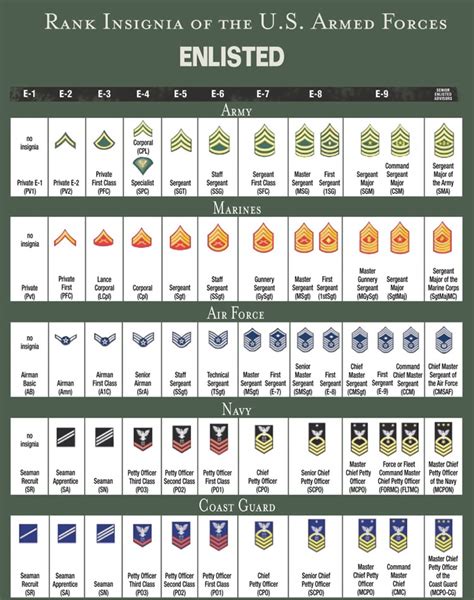
Some of the key enlisted ranks in the US military include:
- Private (PVT)
- Private First Class (PFC)
- Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL)
- Sergeant (SGT)
- Staff Sergeant (SSG)
- Sergeant First Class (SFC)
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG)
- Sergeant Major (SGM)
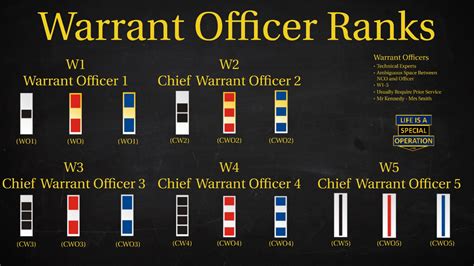
Warrant Officer Ranks
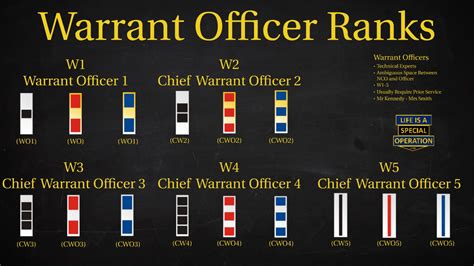
Some of the key warrant officer ranks in the US military include:
- Warrant Officer 1 (WO1)
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2)
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3)
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4)
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5)
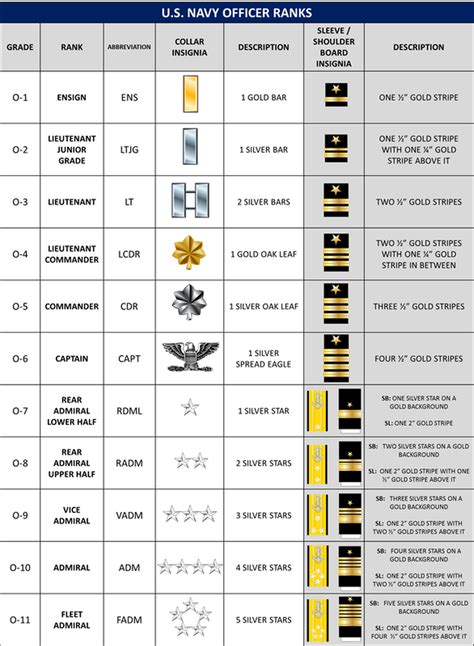
Officer Ranks

Some of the key officer ranks in the US military include:
- Second Lieutenant (2LT)
- First Lieutenant (1LT)
- Captain (CPT)
- Major (MAJ)
- Lieutenant Colonel (LTC)
- Colonel (COL)
- Brigadier General (BG)
- Major General (MG)
- Lieutenant General (LTG)
- General (GEN)
Officer Specialties
Officers in the US military can specialize in a wide range of fields, including: * Infantry * Armor * Artillery * Engineering * Signal Corps * Intelligence * Logistics * Medical Corps * Judge Advocate General (JAG)Each specialty has its own set of requirements and qualifications, and officers may be required to complete additional training or education to become certified in their field.
Military Rank Insignia
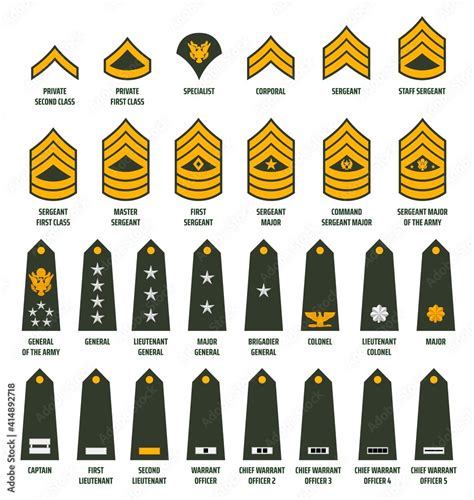

Ranking System by Branch
For example, the Navy and Coast Guard use a combination of officer and enlisted ranks, while the Marine Corps uses a unique set of ranks that are distinct from the other branches. The Air Force uses a similar ranking system to the Army, but with some differences in terminology and insignia.
Benefits of the Ranking System
Challenges of the Ranking System
Despite its benefits, the US military ranking system also faces some challenges, including: * Complexity: The ranking system can be complex and difficult to navigate, particularly for new recruits or those who are not familiar with military terminology and protocols. * Inequities: The ranking system can be subject to inequities and biases, with some individuals or groups being promoted or recognized more quickly than others. * Limited opportunities: The ranking system can limit opportunities for advancement, particularly for those who are not in a traditional leadership role or who do not have the right skills or experience.US Military Ranking System Image Gallery


What is the highest rank in the US military?
+The highest rank in the US military is General (GEN) in the Army, Air Force, and Marine Corps, and Admiral (ADM) in the Navy and Coast Guard.
How do I get promoted in the US military?
+Promotions in the US military are typically based on a combination of factors, including time in service, performance evaluations, and completion of required training and education.
What is the difference between an officer and an enlisted person?
+Officers are the leaders of the US military, responsible for planning, directing, and executing military operations. Enlisted personnel are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day tasks and operations of the military.
How long does it take to become a general in the US military?
+Becoming a general in the US military typically requires 20-30 years of service, as well as completion of advanced education and training, and a strong record of performance and leadership.
What are the benefits of serving in the US military?
+The benefits of serving in the US military include education and training opportunities, career advancement, and a sense of pride and purpose. Military personnel also receive a range of benefits, including healthcare, housing, and food allowances.
In conclusion, the US military ranking system is a complex and hierarchical structure that defines the roles, responsibilities, and levels of authority for members of the US Armed Forces. Understanding the ranking system is essential for navigating the military's organizational framework and recognizing the accomplishments and qualifications of its personnel. Whether you are a new recruit or a seasoned veteran, the US military ranking system provides a framework for career advancement, recognition of achievement, and standardization across different branches and units. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the US military ranking system in the comments below, and to explore the many resources and opportunities available to military personnel and their families.
