Intro
Discover 5 ways to join the army, including enlistment, officer programs, and special forces recruitment, to start your military career and serve your country with honor and patriotism.
Joining the army can be a life-changing decision that offers a unique blend of challenges, opportunities, and personal growth. For those who are considering a career in the military, there are several paths to explore. The army is not just about combat; it encompasses a wide range of roles and specialties, from medical and engineering fields to communications and intelligence. Whether you're driven by a sense of patriotism, a desire for education and training, or the appeal of a structured and disciplined lifestyle, the army has something to offer. In this article, we will delve into the various ways to join the army, highlighting the benefits, requirements, and what to expect from each path.
The decision to join the army is significant, and it's essential to understand the different entry points and career trajectories available. From enlisted personnel to officers, each role comes with its own set of responsibilities, challenges, and rewards. The army provides comprehensive training, education opportunities, and a sense of camaraderie that is hard to find in civilian life. However, it also demands sacrifice, resilience, and a commitment to serving one's country. For those who are unsure about which path to take, exploring the different ways to join the army can help clarify their options and make an informed decision.
For individuals who are considering a military career, it's crucial to weigh the pros and cons, understand the recruitment process, and prepare themselves physically and mentally for the challenges ahead. The army offers a structured environment that fosters personal development, teamwork, and leadership skills. It also provides opportunities for education, travel, and career advancement that might not be available in the civilian sector. As we explore the different ways to join the army, we will discuss the eligibility criteria, the application process, and what new recruits can expect during their initial training and beyond.
Enlisting as a Soldier

Benefits of Enlisting
The benefits of enlisting include the opportunity to serve your country, develop new skills, and gain experience in a variety of fields. The army also offers comprehensive education benefits, including the GI Bill, which can help you pay for college or vocational training after your service. Additionally, enlisting provides a steady income, access to healthcare, and a sense of camaraderie and belonging that is unique to the military experience.Commissioning as an Officer
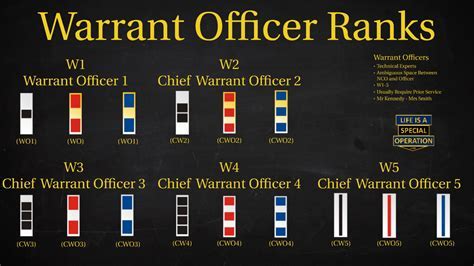
Officer Career Paths
Officer career paths are diverse, ranging from combat arms to support and technical fields. Officers can specialize in areas such as aviation, engineering, intelligence, or medicine, among others. The role of an officer is demanding, requiring strong leadership, communication, and problem-solving skills. However, it also offers a high level of responsibility, the opportunity to mentor and lead soldiers, and a competitive salary and benefits package.Joining the Army Reserves

Benefits of the Reserves
The benefits of joining the army reserves include the opportunity to serve part-time, receive training and education benefits, and have access to healthcare and other military benefits. Reservists also earn a steady income for their service and can qualify for retirement benefits after 20 years of service. Additionally, the experience and skills gained in the reserves can be highly transferable to civilian careers, making reservists more competitive in the job market.Attending a Military Academy

Academy Life
Life at a military academy is rigorous, with a focus on academic excellence, physical fitness, and military training. Cadets follow a structured schedule that includes classes, training exercises, and leadership development activities. The experience is challenging but rewarding, offering a unique blend of personal growth, education, and service to one's country. Graduates are well-prepared for the demands of military life and go on to serve in a variety of roles, from combat leadership to technical specialties.Enlisting in the National Guard

National Guard Missions
The National Guard has a dual mission, serving both state and federal governments. In times of natural disasters or civil unrest, the National Guard can be called upon by the state to assist with relief efforts and maintain order. Additionally, the National Guard can be deployed overseas in support of military operations. This dual role makes the National Guard a unique and vital component of the army, offering members the opportunity to serve in a variety of contexts and make a difference in their communities.Army Service Image Gallery










What are the basic requirements to join the army?
+The basic requirements include being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35, having a high school diploma or equivalent, and meeting physical fitness standards.
How long does the enlistment process take?
+The enlistment process can take several weeks to several months, depending on factors such as the time of year, the number of applicants, and the individual's qualifications and preferences.
What kind of training will I receive in the army?
+Training in the army includes Basic Combat Training (BCT), Advanced Individual Training (AIT), and ongoing professional development and leadership training, depending on your role and specialty.
Can I choose my job in the army?
+While the army considers your preferences and aptitudes, job assignments are based on the needs of the service. However, there are many different careers and specialties to choose from, and the army provides training and education to help you succeed in your role.
How does the army support education and career advancement?
+The army offers a range of education benefits, including the GI Bill, tuition assistance, and on-duty education programs. Additionally, the army provides opportunities for career advancement through training, mentorship, and leadership development programs.
In conclusion, joining the army is a significant decision that can offer a wide range of benefits, from education and career opportunities to personal growth and a sense of service. Whether you choose to enlist as a soldier, commission as an officer, join the reserves, attend a military academy, or enlist in the National Guard, there are many paths to explore. Each option has its own set of requirements, challenges, and rewards, and understanding these differences is key to making an informed decision. As you consider your options, remember to weigh the pros and cons carefully, prepare yourself physically and mentally, and seek out resources and support to help you navigate the recruitment and training process. By doing so, you can set yourself up for success and embark on a rewarding and challenging career in the army. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about joining the army, and we hope this article has provided you with valuable insights and information to consider as you explore your options.

