Intro
Discover 7 synonyms for pump including boost, lift, and propel, to enhance vocabulary and improve fluid dynamics, hydraulic systems, and energy transfer understanding.
The term "pump" can have various meanings depending on the context, ranging from a device that raises or transfers fluids to an exercise move. Here are 7 synonyms for "pump" across different contexts:
-
Compressor: This term is often used in the context of machinery or devices that increase the pressure of gases or fluids. For example, an air compressor is used to pump air into tires or power pneumatic tools.
-
Lift: In the context of moving fluids or gases, "lift" can be used interchangeably with "pump" to describe the action of raising something to a higher position or level. For instance, a lift pump is used to raise water from a lower to a higher level.
-
Push: While more general, "push" can sometimes be used as a synonym for "pump" when describing the action of exerting force to move something forward or upward. For example, in the context of exercising, doing push-ups involves pushing one's body upward.
-
Impeller: This is a part of a pump that imparts energy to a fluid, such as water or air, by rotating and thus "pumping" it through a system. It's a key component in many types of pumps.
-
Blower: A blower is a device that generates a large volume of air at moderate pressure, which can be considered a form of pumping air. It's commonly used in heating and cooling systems, as well as in leaf blowers for gardening.
-
Injector: In certain contexts, especially regarding fuel systems in vehicles, an injector can be thought of as a type of pump. It pumps fuel into the engine's cylinders at the right moment to ensure efficient combustion.
-
Siphon: While not a direct synonym in all contexts, a siphon can be used to pump liquids without the need for mechanical energy, relying on gravity and pressure differences. It's a tool used to transfer liquids from one container to another.
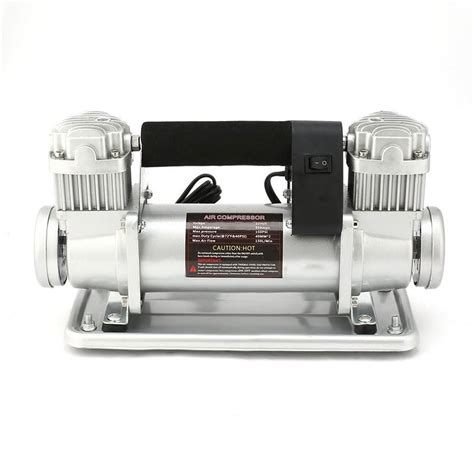

These synonyms highlight the diverse applications and meanings of the term "pump," from mechanical devices to physical actions, each serving to move, raise, or transfer substances or objects from one place to another.
Understanding Pump Mechanisms
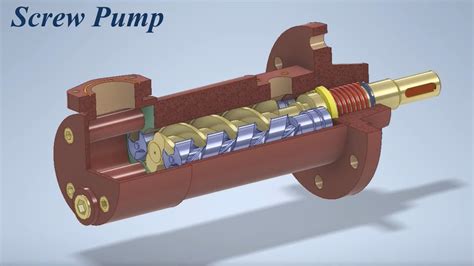
Pumps operate on a variety of principles, including centrifugal force, positive displacement, and gravity. Centrifugal pumps, for example, use an impeller to accelerate fluids outward, creating a pressure difference that draws more fluid into the pump. Positive displacement pumps, on the other hand, trap a fixed amount of fluid and then force it out, creating pressure.
Types of Pumps
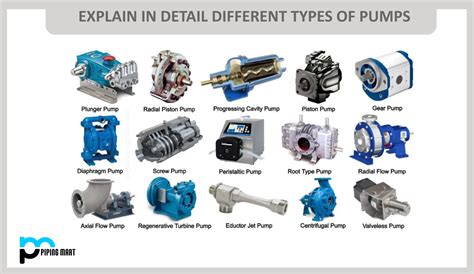
There are numerous types of pumps, each designed for specific applications:
- Centrifugal pumps for large volumes of fluid at moderate pressures.
- Positive displacement pumps for high pressures and precise flow rates.
- Diaphragm pumps for handling corrosive or abrasive fluids.
- Rotary pumps for high-viscosity fluids.
Pump Applications
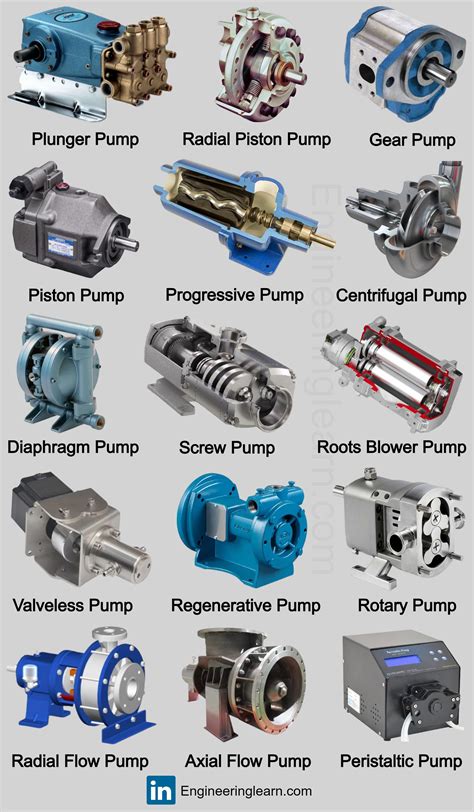
Pumps find applications in virtually every industry, from agriculture to aerospace. In agriculture, pumps are used for irrigation and drainage. In the oil and gas industry, they are crucial for extraction, refining, and distribution. In medical settings, pumps are used in equipment such as ventilators and dialysis machines.
Pump Efficiency and Maintenance
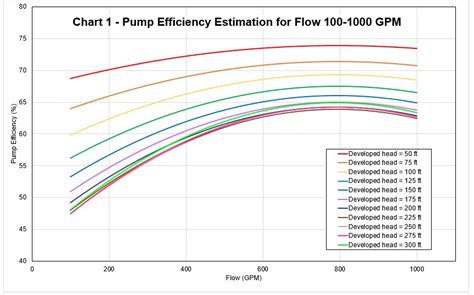
The efficiency of a pump is determined by its ability to convert input energy into useful pump work. Regular maintenance is key to ensuring that a pump operates at its best efficiency point. This includes monitoring performance, checking for leaks, and replacing worn parts.
Pump Safety Considerations

Safety is a critical aspect of pump operation. Pumps can pose hazards such as entrapment, electrical shock, and chemical exposure. Proper training, adherence to safety protocols, and regular inspection of equipment are essential for minimizing risks.
Future of Pump Technology

Advancements in materials science, computer simulations, and renewable energy are driving innovations in pump technology. More efficient, quieter, and environmentally friendly pumps are being developed to meet the demands of a rapidly changing world.
Gallery of Pump Images
Pump Image Gallery




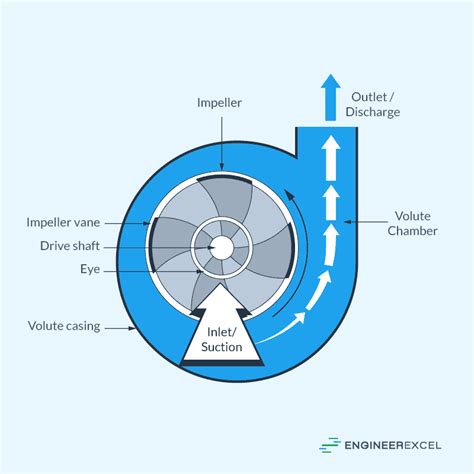
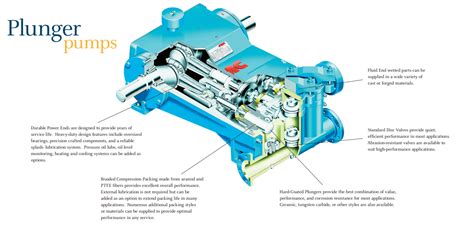
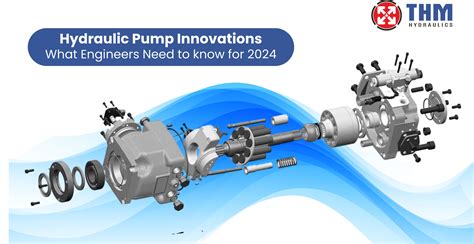



What are the main types of pumps?
+The main types of pumps include centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps, and rotary pumps, each suited for different applications and fluid properties.
How do I choose the right pump for my application?
+Choosing the right pump involves considering factors such as the type of fluid, flow rate, pressure requirements, and operational conditions. It's also important to consider efficiency, maintenance needs, and safety features.
What are some common issues with pumps and how can they be resolved?
+Common issues with pumps include low flow rates, high energy consumption, and leakage. These can often be resolved through proper maintenance, such as cleaning or replacing worn parts, adjusting operational settings, and ensuring the pump is appropriately sized for the application.
In conclusion, understanding pumps and their applications is crucial for a wide range of industries and everyday life. From the mechanisms that drive them to the diverse applications they serve, pumps are a cornerstone of modern technology. As technology advances, we can expect even more efficient, safe, and innovative pump solutions to emerge. We invite you to share your thoughts on the importance of pumps and any experiences you may have with them. Whether you're a professional in the field or simply someone interested in how things work, your insights are valuable. Please feel free to comment below or share this article with others who might find it informative. Together, let's explore the fascinating world of pumps and their role in shaping our world.
