Intro
Discover the US Militarys oldest branch, exploring its rich history, founding, and evolution, with key milestones and legacy as the foundation of American defense and security forces.
The history of the US military is rich and complex, with each branch having its own unique story and significance. Among the five branches of the US military, one stands out as the oldest, with a legacy dating back to the earliest days of the American nation. This branch has played a crucial role in shaping the country's defense and security, and its contributions continue to be felt to this day.
The US Army is the oldest branch of the US military, with its roots tracing back to June 3, 1784, when the Continental Congress established the United States Army as a permanent institution. However, the Army's precursor, the Continental Army, was formed on June 14, 1775, during the American Revolutionary War. This makes the Army the oldest of all the US military branches, with a history spanning over two centuries.
The Army's long history is a testament to its enduring importance in the nation's defense. From the Revolutionary War to the present day, the Army has been involved in numerous conflicts, including the War of 1812, the Mexican-American War, the Civil War, World War I, World War II, the Korean War, the Vietnam War, and the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq. Throughout its history, the Army has demonstrated its ability to adapt and evolve, embracing new technologies and strategies while remaining committed to its core values of loyalty, duty, respect, selfless service, honor, integrity, and personal courage.
Early History of the US Army

The early history of the US Army is marked by significant milestones, including the establishment of the Continental Army in 1775 and the creation of the United States Army as a permanent institution in 1784. The Army played a crucial role in the American Revolutionary War, fighting against the British Army and its allies. The war saw the emergence of notable military leaders, including George Washington, who would later become the first President of the United States.
The Army's early years were also marked by challenges, including a lack of resources, inadequate training, and poor equipment. Despite these challenges, the Army persevered, and by the end of the 18th century, it had established itself as a professional and effective fighting force. The Army's growth and development during this period laid the foundation for its future success, enabling it to respond to the changing needs of the nation and to adapt to new threats and challenges.
Key Events in US Army History
The US Army has been involved in numerous significant events throughout its history, including: * The American Revolutionary War (1775-1783) * The War of 1812 (1812-1815) * The Mexican-American War (1846-1848) * The Civil War (1861-1865) * World War I (1917-1918) * World War II (1941-1945) * The Korean War (1950-1953) * The Vietnam War (1955-1975) * The Gulf War (1990-1991) * The wars in Afghanistan (2001-present) and Iraq (2003-2011)These events have shaped the Army's development, influencing its doctrine, organization, and equipment. The Army has learned from its experiences, using them to improve its performance and to prepare for future challenges.
US Army Structure and Organization
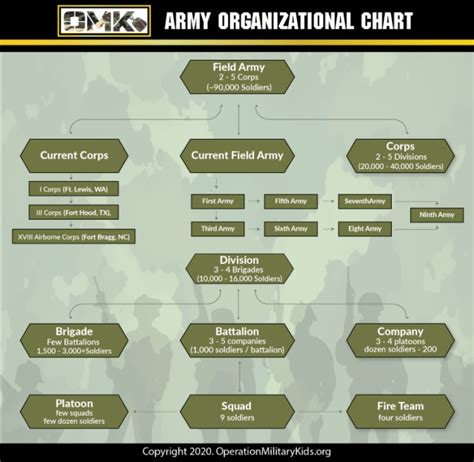
The US Army is a complex organization, with a hierarchical structure that includes several key components. The Army is divided into several branches, including the Infantry, Armor, Artillery, Engineers, and Signal Corps, among others. Each branch has its own unique role and responsibilities, contributing to the Army's overall mission and objectives.
The Army is also organized into several types of units, including brigades, divisions, and corps. These units are designed to be flexible and adaptable, enabling the Army to respond to a wide range of scenarios and challenges. The Army's structure and organization are designed to support its core functions, including combat, peacekeeping, and humanitarian assistance.
US Army Ranks and Insignia
The US Army uses a system of ranks and insignia to identify an individual's position and level of responsibility. The Army's rank structure includes: * Enlisted ranks: Private (PVT), Private First Class (PFC), Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL), Sergeant (SGT), Staff Sergeant (SSG), Sergeant First Class (SFC), Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG), Sergeant Major (SGM) * Warrant officer ranks: Warrant Officer 1 (WO1), Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2), Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3), Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4), Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5) * Officer ranks: Second Lieutenant (2LT), First Lieutenant (1LT), Captain (CPT), Major (MAJ), Lieutenant Colonel (LTC), Colonel (COL), Brigadier General (BG), Major General (MG), Lieutenant General (LTG), General (GEN)The Army's rank structure is designed to provide a clear chain of command, enabling effective communication and decision-making. The use of insignia, including chevrons, bars, and stars, helps to identify an individual's rank and branch, facilitating recognition and respect.
US Army Equipment and Technology

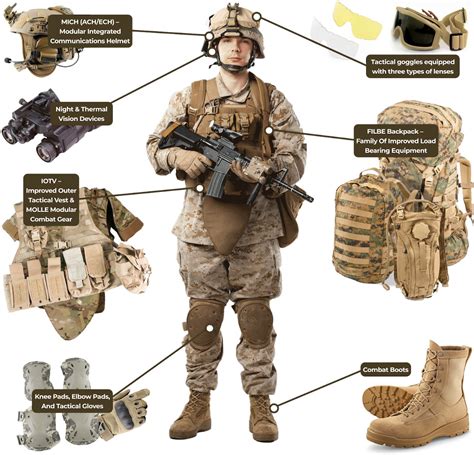
The US Army has a wide range of equipment and technology at its disposal, including:
- Small arms: M4 carbine, M9 pistol, M249 machine gun
- Vehicles: M1 Abrams tank, M2 Bradley infantry fighting vehicle, HMMWV (Humvee)
- Aircraft: UH-60 Black Hawk helicopter, AH-64 Apache helicopter, CH-47 Chinook helicopter
- Artillery: M109 howitzer, M270 multiple launch rocket system
- Communications: satellite communications, radio systems, computer networks
The Army's equipment and technology are designed to support its core functions, including combat, peacekeeping, and humanitarian assistance. The Army is continually updating and modernizing its equipment, embracing new technologies and innovations to enhance its performance and effectiveness.
US Army Training and Doctrine
The US Army has a comprehensive system of training and doctrine, designed to prepare soldiers for a wide range of scenarios and challenges. The Army's training includes: * Basic Combat Training (BCT) * Advanced Individual Training (AIT) * Officer Candidate School (OCS) * Ranger School * Special Forces Qualification CourseThe Army's doctrine includes:
- Army Doctrine Publication (ADP) 1: The Army
- ADP 3-0: Operations
- ADP 5-0: The Operations Process
- ADP 6-0: Mission Command
The Army's training and doctrine are designed to support its core functions, including combat, peacekeeping, and humanitarian assistance. The Army is continually updating and refining its training and doctrine, embracing new ideas and innovations to enhance its performance and effectiveness.
US Army Missions and Operations

The US Army has a wide range of missions and operations, including:
- Combat operations: the Army is trained to fight and win in a variety of environments, from urban warfare to desert warfare
- Peacekeeping operations: the Army has been involved in numerous peacekeeping missions, including in Bosnia, Kosovo, and Afghanistan
- Humanitarian assistance: the Army provides humanitarian assistance in response to natural disasters and other crises
The Army's missions and operations are designed to support its core functions, including combat, peacekeeping, and humanitarian assistance. The Army is continually updating and refining its missions and operations, embracing new challenges and opportunities to enhance its performance and effectiveness.
US Army Budget and Resources
The US Army has a significant budget and resources, including: * Personnel: the Army has approximately 475,000 active-duty soldiers, 336,000 reserve soldiers, and 206,000 civilian employees * Equipment: the Army has a wide range of equipment, including tanks, infantry fighting vehicles, artillery, and aircraft * Facilities: the Army has numerous facilities, including bases, forts, and training areasThe Army's budget and resources are designed to support its core functions, including combat, peacekeeping, and humanitarian assistance. The Army is continually updating and refining its budget and resources, embracing new challenges and opportunities to enhance its performance and effectiveness.
US Army Culture and Traditions

The US Army has a rich culture and traditions, including:
- The Army Song: "The Army Goes Rolling Along"
- The Army Crest: the Army crest features a eagle, a shield, and a motto, "This We'll Defend"
- The Army Uniform: the Army uniform includes the Army Combat Uniform (ACU), the Army Service Uniform (ASU), and the Dress Uniform
The Army's culture and traditions are designed to promote esprit de corps, unit cohesion, and a sense of pride and identity. The Army is continually updating and refining its culture and traditions, embracing new ideas and innovations to enhance its performance and effectiveness.
US Army Community and Support
The US Army has a strong community and support system, including: * Army families: the Army provides numerous resources and support for Army families, including housing, healthcare, and education * Army veterans: the Army provides numerous resources and support for Army veterans, including healthcare, education, and employment assistance * Army civilian employees: the Army provides numerous resources and support for Army civilian employees, including training, education, and career developmentThe Army's community and support system is designed to promote a sense of belonging and connection among Army personnel, families, and civilians. The Army is continually updating and refining its community and support system, embracing new challenges and opportunities to enhance its performance and effectiveness.
US Army Image Gallery










What is the oldest branch of the US military?
+The US Army is the oldest branch of the US military, with its roots tracing back to June 3, 1784.
What is the mission of the US Army?
+The mission of the US Army is to protect the American people and the nation by fighting and winning wars, and by providing humanitarian assistance and disaster relief.
What are the core values of the US Army?
+The core values of the US Army are loyalty, duty, respect, selfless service, honor, integrity, and personal courage.
What is the structure of the US Army?
+The US Army is divided into several branches, including the Infantry, Armor, Artillery, Engineers, and Signal Corps, among others. The Army is also organized into several types of units, including brigades, divisions, and corps.
What is the role of the US Army in modern warfare?
+The US Army plays a critical role in modern warfare, providing ground forces for combat operations, peacekeeping, and humanitarian assistance. The Army is also responsible for providing security and stability in regions around the world.
As we reflect on the history and significance of the US Army, we are reminded of the importance of this institution in protecting the American people and the nation. The Army's legacy is a testament to the bravery, sacrifice, and dedication of its soldiers, who have served with honor and distinction throughout the centuries. As we look to the future, we can be confident that the US Army will continue to play a vital role in defending the nation and promoting peace and stability around the world. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on the US Army and its significance, and to explore the many resources and opportunities available to those who serve in this noble institution.
