Intro
Discover Military Officers Ranks And Roles, including commissioned and non-commissioned officer ranks, military hierarchy, and career paths, to understand the structure and responsibilities of armed forces personnel.
The hierarchy of military officers is a complex and fascinating system, with various ranks and roles that define the structure and functioning of armed forces around the world. Understanding the different ranks and roles of military officers is essential for appreciating the organization, discipline, and effectiveness of modern militaries. In this article, we will delve into the world of military officers, exploring their ranks, responsibilities, and the significance of their roles in maintaining national security and defending against threats.
The rank structure of military officers varies across countries, but most nations follow a similar pattern, with officers progressing through a series of ranks as they gain experience, training, and responsibilities. The ranks of military officers are typically divided into several categories, including junior officers, field-grade officers, senior officers, and general officers. Each rank has its unique set of responsibilities, challenges, and opportunities, shaping the career paths and contributions of military officers.
As we explore the ranks and roles of military officers, it becomes clear that their work is not only about combat and warfare but also about leadership, strategy, and diplomacy. Military officers are responsible for making critical decisions, often under intense pressure, that can have far-reaching consequences for their units, their countries, and the global community. Their roles require a unique blend of physical and mental toughness, intellectual curiosity, and emotional intelligence, making them some of the most skilled and dedicated professionals in the world.
Introduction to Military Officers Ranks
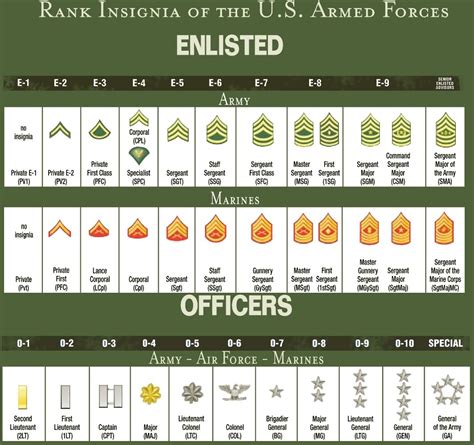
The ranks of military officers are designed to reflect their level of experience, expertise, and responsibility. Junior officers, typically holding the ranks of second lieutenant or ensign, are at the beginning of their careers, learning the fundamentals of leadership and military operations. As they progress through the ranks, they take on more significant responsibilities, such as commanding units, developing strategies, and making key decisions.
Field-grade officers, including captains, majors, and lieutenant colonels, have gained significant experience and expertise, often specializing in specific areas like infantry, artillery, or logistics. Senior officers, such as colonels and brigadier generals, have reached the pinnacle of their careers, providing strategic leadership and guidance to their units and organizations.
Junior Officers Ranks and Roles

Junior officers are the backbone of any military organization, responsible for leading small units and executing tactical operations. Their ranks and roles are critical to the success of military missions, as they provide the foundation for more senior officers to build upon. The junior officer ranks include:
- Second Lieutenant (2nd Lt): The most junior officer rank, typically serving as a platoon leader or executive officer.
- First Lieutenant (1st Lt): A more experienced junior officer, often serving as a company executive officer or battalion staff officer.
- Captain (Cpt): A field-grade officer, typically commanding a company or serving as a battalion staff officer.
These junior officers are responsible for:
- Leading small units, such as platoons or companies
- Developing and executing tactical plans
- Mentoring and training enlisted personnel
- Coordinating with other units and organizations
Field-Grade Officers Ranks and Roles

Field-grade officers have gained significant experience and expertise, often specializing in specific areas of military operations. Their ranks and roles are critical to the success of military missions, as they provide strategic leadership and guidance to their units and organizations. The field-grade officer ranks include:
- Major (Maj): A senior field-grade officer, typically serving as a battalion executive officer or brigade staff officer.
- Lieutenant Colonel (Lt Col): A senior field-grade officer, often commanding a battalion or serving as a brigade staff officer.
- Colonel (Col): A senior officer, typically commanding a brigade or serving as a division staff officer.
These field-grade officers are responsible for:
- Leading larger units, such as battalions or brigades
- Developing and executing operational plans
- Providing strategic guidance and mentorship to junior officers
- Coordinating with other units and organizations
Senior Officers Ranks and Roles

Senior officers have reached the pinnacle of their careers, providing strategic leadership and guidance to their units and organizations. Their ranks and roles are critical to the success of military missions, as they make key decisions and provide direction to their subordinates. The senior officer ranks include:
- Brigadier General (BG): A one-star general officer, typically commanding a brigade or serving as a division staff officer.
- Major General (MG): A two-star general officer, often commanding a division or serving as a corps staff officer.
- Lieutenant General (LTG): A three-star general officer, typically commanding a corps or serving as a army staff officer.
These senior officers are responsible for:
- Providing strategic leadership and guidance to their units and organizations
- Making key decisions and providing direction to their subordinates
- Coordinating with other units and organizations
- Developing and executing strategic plans
General Officers Ranks and Roles

General officers are the most senior officers in the military, responsible for providing strategic leadership and guidance to their units and organizations. Their ranks and roles are critical to the success of military missions, as they make key decisions and provide direction to their subordinates. The general officer ranks include:
- General (GEN): A four-star general officer, typically serving as the Chief of Staff of the Army or the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff.
- Admiral (ADM): A four-star admiral, typically serving as the Chief of Naval Operations or the Commander of the Joint Chiefs of Staff.
These general officers are responsible for:
- Providing strategic leadership and guidance to their units and organizations
- Making key decisions and providing direction to their subordinates
- Coordinating with other units and organizations
- Developing and executing strategic plans
Gallery of Military Officers Ranks
Military Officers Ranks Image Gallery
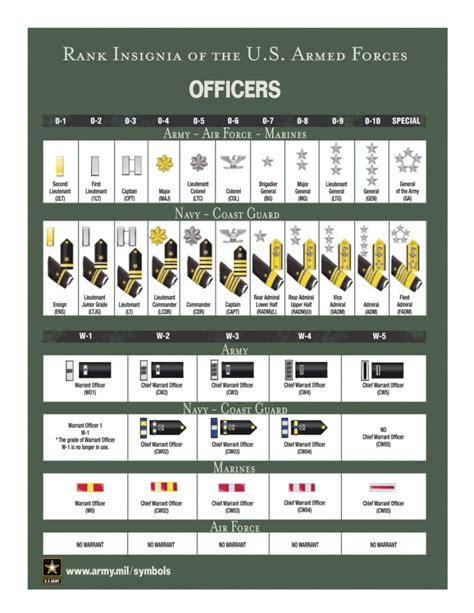






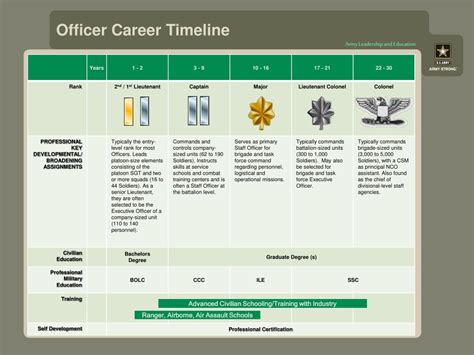


What are the different ranks of military officers?
+The ranks of military officers include junior officers, field-grade officers, senior officers, and general officers. Each rank has its unique set of responsibilities and challenges.
What are the responsibilities of junior officers?
+Junior officers are responsible for leading small units, developing and executing tactical plans, mentoring and training enlisted personnel, and coordinating with other units and organizations.
What are the responsibilities of field-grade officers?
+Field-grade officers are responsible for leading larger units, developing and executing operational plans, providing strategic guidance and mentorship to junior officers, and coordinating with other units and organizations.
What are the responsibilities of senior officers?
+Senior officers are responsible for providing strategic leadership and guidance to their units and organizations, making key decisions and providing direction to their subordinates, and coordinating with other units and organizations.
What are the responsibilities of general officers?
+General officers are responsible for providing strategic leadership and guidance to their units and organizations, making key decisions and providing direction to their subordinates, and coordinating with other units and organizations.
As we conclude our exploration of military officers ranks and roles, it is clear that their work is essential to the success of military missions and the defense of nations. Their ranks and roles are critical to the functioning of modern militaries, providing a framework for leadership, strategy, and decision-making. We hope that this article has provided a comprehensive and informative overview of the ranks and roles of military officers, and we invite readers to share their thoughts and comments on this important topic. Whether you are a military professional, a student of military history, or simply someone interested in learning more about the world of military officers, we encourage you to engage with this topic and explore the many fascinating aspects of military leadership and strategy.

