Intro
Discover the cultural and economic differences between Northern China and Southern China, exploring regional variations in climate, cuisine, and lifestyle, and uncovering the unique charms of each area.
The vast and diverse country of China is often divided into two distinct regions: Northern China and Southern China. These two areas have been shaped by their unique histories, cultures, and geographical characteristics, resulting in distinct differences in cuisine, language, customs, and ways of life. Understanding the differences between Northern and Southern China can provide valuable insights into the complexities of this fascinating country.
The division between Northern and Southern China is not just a matter of geography, but also of culture, economy, and history. The two regions have developed separately, with Northern China being influenced by its proximity to Mongolia and the Soviet Union, while Southern China has been shaped by its maritime trade and cultural exchange with Southeast Asia and the West. This has resulted in distinct differences in the way people live, work, and interact with one another.
The cuisine in Northern and Southern China is a prime example of these differences. Northern Chinese cuisine is known for its hearty and savory dishes, such as Beijing roast duck, noodles, and dumplings. The use of wheat, meat, and vegetables is prevalent in Northern Chinese cooking, reflecting the region's agricultural traditions. In contrast, Southern Chinese cuisine is characterized by its use of rice, seafood, and tropical fruits, with popular dishes like Cantonese roast pork, dim sum, and congee. The differences in cuisine are not just a matter of taste, but also reflect the unique cultural and historical contexts of each region.
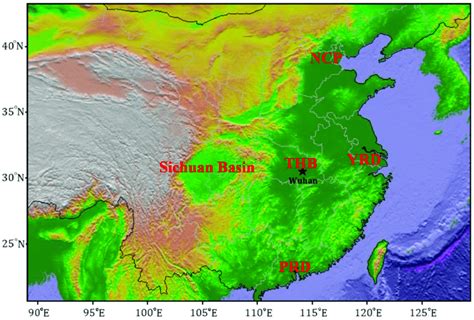
Geography and Climate

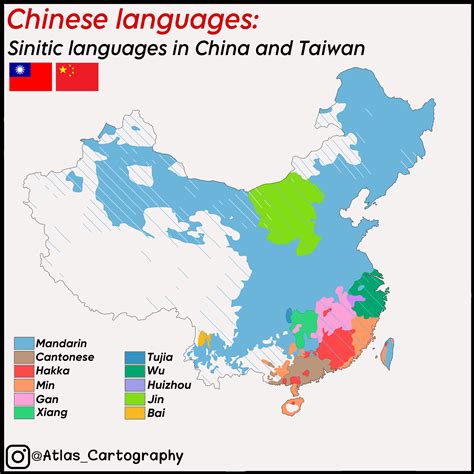
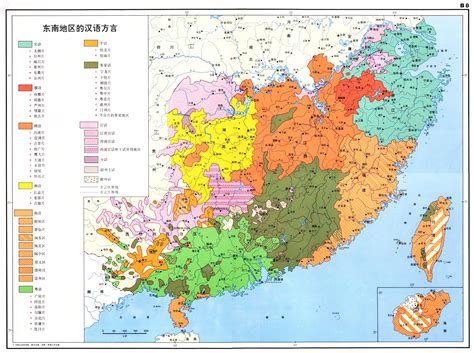
Language and Culture
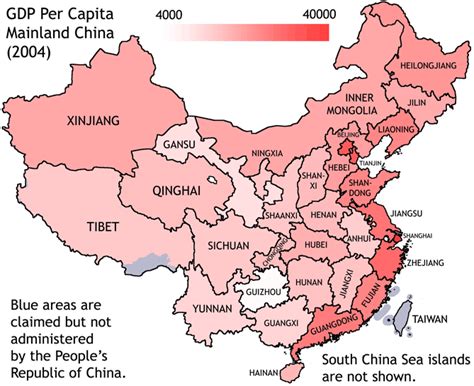
Economy and Development

Key Differences
The key differences between Northern and Southern China can be summarized as follows: * Cuisine: Northern Chinese cuisine is hearty and savory, while Southern Chinese cuisine is light and sweet. * Geography: Northern China is characterized by its vast plains and mountains, while Southern China is marked by its rugged terrain and coastal plains. * Language: Mandarin Chinese is dominant in Northern China, while Cantonese and other dialects are spoken in Southern China. * Culture: Northern China is known for its traditional opera and acrobatics, while Southern China is famous for its Cantonese opera and martial arts. * Economy: Northern China is a major center for industry and technology, while Southern China is a major center for trade, finance, and services.History and Politics

Regional Identity
The regional identity of Northern and Southern China is complex and multifaceted. Northerners are often seen as being more straightforward and direct, while Southerners are often viewed as being more cunning and entrepreneurial. These stereotypes reflect the unique cultural and historical contexts of each region, with Northerners being shaped by their proximity to the Mongolian and Soviet borders, and Southerners being influenced by their maritime trade and cultural exchange with Southeast Asia and the West.Social and Economic Challenges

Possible Solutions
The possible solutions to these challenges are complex and multifaceted. For Northern China, possible solutions include: * Investing in renewable energy and reducing dependence on coal and other fossil fuels. * Implementing sustainable agricultural practices and reducing water pollution. * Promoting urban planning and development that is sustainable and equitable. For Southern China, possible solutions include: * Investing in education and training programs to develop a more skilled and competitive workforce. * Promoting innovation and entrepreneurship, particularly in the technology and services sectors. * Implementing policies to reduce inequality and promote social mobility.China Image Gallery





What are the main differences between Northern and Southern China?
+The main differences between Northern and Southern China include cuisine, geography, language, culture, and economy. Northern China is known for its hearty and savory dishes, vast plains and mountains, Mandarin Chinese, traditional opera and acrobatics, and industrial economy. Southern China, on the other hand, is famous for its light and sweet dishes, rugged terrain and coastal plains, Cantonese and other dialects, Cantonese opera and martial arts, and export-oriented economy.
What are the key challenges facing Northern and Southern China?
+Northern China is facing significant environmental challenges, including air and water pollution, soil degradation, and desertification. The region is also experiencing significant urbanization, with many rural residents moving to cities in search of work and better living standards. Southern China, on the other hand, is facing significant economic challenges, including rising labor costs, declining competitiveness, and increasing inequality. The region is also experiencing significant social challenges, including a rapidly aging population, a shortage of skilled workers, and a growing wealth gap.
What are the possible solutions to these challenges?
+For Northern China, possible solutions include investing in renewable energy and reducing dependence on coal and other fossil fuels, implementing sustainable agricultural practices and reducing water pollution, and promoting urban planning and development that is sustainable and equitable. For Southern China, possible solutions include investing in education and training programs to develop a more skilled and competitive workforce, promoting innovation and entrepreneurship, particularly in the technology and services sectors, and implementing policies to reduce inequality and promote social mobility.
What is the significance of the regional identity of Northern and Southern China?
+The regional identity of Northern and Southern China is complex and multifaceted, reflecting the unique cultural and historical contexts of each region. Northerners are often seen as being more straightforward and direct, while Southerners are often viewed as being more cunning and entrepreneurial. These stereotypes reflect the distinct cultural and historical traditions of each region, with Northerners being shaped by their proximity to the Mongolian and Soviet borders, and Southerners being influenced by their maritime trade and cultural exchange with Southeast Asia and the West.
How do the differences between Northern and Southern China impact the country's development and growth?
+The differences between Northern and Southern China have significant implications for the country's development and growth. The distinct cultural, economic, and geographical characteristics of each region require tailored policies and strategies to promote sustainable and equitable development. Understanding these differences is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals seeking to navigate the complexities of the Chinese market and contribute to the country's continued growth and prosperity.
In conclusion, the differences between Northern and Southern China are complex and multifaceted, reflecting the unique cultural, historical, and geographical contexts of each region. Understanding these differences is essential for navigating the complexities of the Chinese market and contributing to the country's continued growth and prosperity. By recognizing the distinct characteristics of each region, policymakers, businesses, and individuals can develop tailored strategies to promote sustainable and equitable development, address social and economic challenges, and foster greater cooperation and understanding between the two regions. We invite you to share your thoughts and insights on the differences between Northern and Southern China, and to explore the many opportunities and challenges that this fascinating country has to offer.
