Intro
Identify and fix common welding defects with our guide to 5 faulty weld issues, including porosity, cracking, and lack of fusion, to improve weld quality and strength.
Welding is a complex process that requires precision, skill, and attention to detail. Even with the best equipment and techniques, faulty welds can occur, leading to structural weaknesses, safety hazards, and costly repairs. In this article, we will explore five common faulty weld issues, their causes, and prevention methods. Whether you are a seasoned welder or a beginner, understanding these issues is crucial for producing high-quality welds.
The importance of identifying and addressing faulty weld issues cannot be overstated. A single weak weld can compromise the entire structure, leading to catastrophic failures and accidents. Moreover, faulty welds can result in significant economic losses, as repairs and replacements can be time-consuming and expensive. By recognizing the signs of faulty welds and taking proactive measures to prevent them, welders can ensure the integrity and safety of their work.
Welding is a critical process in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and transportation. The demand for skilled welders is high, and the profession requires a deep understanding of welding techniques, materials, and safety protocols. As the industry continues to evolve, new technologies and methods are being developed to improve welding quality and efficiency. However, despite these advances, faulty weld issues remain a persistent problem, highlighting the need for ongoing education and training.
Introduction to Faulty Weld Issues

Porosity in Welds

Causes of Porosity
The causes of porosity in welds can be summarized as follows: * Poor shielding gas coverage * High welding speeds * Contamination of the weld area * Incorrect welding technique * Insufficient weld pool protectionLack of Fusion
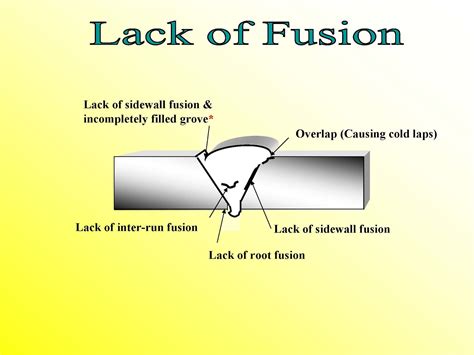
Prevention Methods for Lack of Fusion
The prevention methods for lack of fusion can be summarized as follows: * Ensure adequate heat input * Maintain a clean weld area * Adjust welding parameters to optimize fusion * Use proper welding technique * Inspect welds regularly to detect lack of fusionLack of Penetration

Causes of Lack of Penetration
The causes of lack of penetration can be summarized as follows: * Inadequate heat input * Poor welding technique * Incorrect weld joint design * Insufficient weld pool protection * Contamination of the weld areaCracking in Welds

Prevention Methods for Cracking
The prevention methods for cracking can be summarized as follows: * Control welding parameters to minimize thermal stresses * Maintain a clean weld area to prevent contamination * Use proper welding techniques to minimize mechanical stresses * Inspect welds regularly to detect cracking * Use weld joints and designs that minimize stress concentrationsWeld Distortion
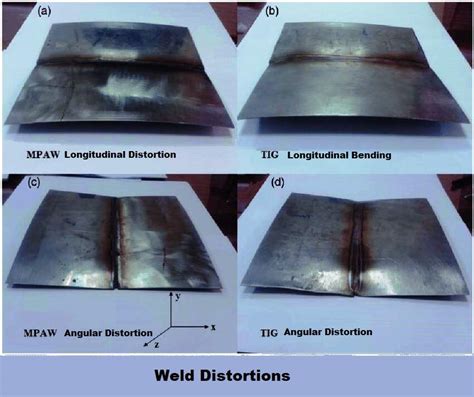
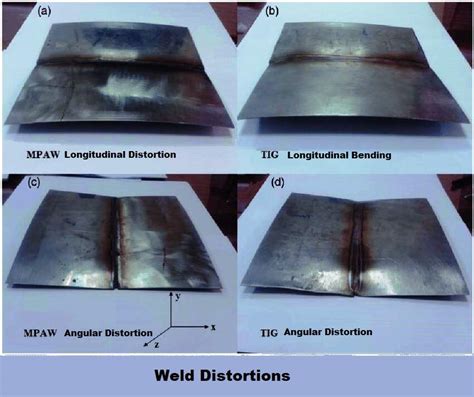
Causes of Weld Distortion
The causes of weld distortion can be summarized as follows: * Thermal stresses and contraction * Mechanical stresses and loading * Material incompatibility and properties * Poor welding technique and parameters * Insufficient weld pool protection and controlFaulty Weld Issues Image Gallery
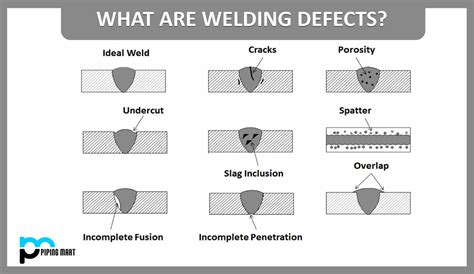



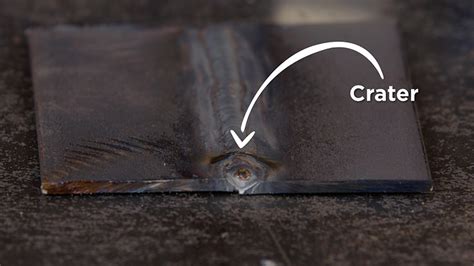


What are the most common faulty weld issues?
+The most common faulty weld issues are porosity, lack of fusion, lack of penetration, cracking, and weld distortion.
How can I prevent porosity in welds?
+To prevent porosity, ensure adequate shielding gas coverage, maintain a clean weld area, and adjust welding parameters to minimize gas entrapment.
What are the causes of lack of fusion in welds?
+The causes of lack of fusion include inadequate heat input, poor welding technique, and contamination of the weld area.
How can I prevent cracking in welds?
+To prevent cracking, control welding parameters to minimize thermal stresses, maintain a clean weld area, and use proper welding techniques to minimize mechanical stresses.
What are the consequences of weld distortion?
+The consequences of weld distortion include a weakened and unsightly weld, prone to cracking and failure, and potential safety hazards.
In conclusion, faulty weld issues are a persistent problem in the welding industry, requiring ongoing education and training to prevent. By understanding the causes and prevention methods for each type of faulty weld, welders can minimize the risk of errors and produce high-quality welds. We encourage readers to share their experiences and insights on faulty weld issues, and to take proactive measures to improve their welding skills and knowledge. Whether you are a seasoned welder or a beginner, recognizing the importance of faulty weld issues is crucial for producing safe and reliable welds.
