Intro
Discover 5 Navy Reserve age tips, including eligibility requirements, age limits, and enlistment options, to help you navigate the enlistment process and join the Navy Reserve with confidence, considering factors like prior service, citizenship, and physical fitness.
Joining the Navy Reserve can be a rewarding and challenging experience, offering individuals the opportunity to serve their country while also pursuing civilian careers. For those considering this path, understanding the age requirements and how they impact eligibility is crucial. The Navy Reserve, like other branches of the military, has specific age limits for enlistment and commissioning, which can vary based on the role, education level, and prior service. Here are five key tips regarding age and the Navy Reserve:
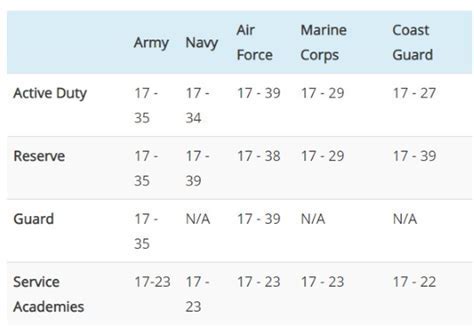
The first consideration for anyone looking to join the Navy Reserve is the basic age requirement. Generally, to enlist in the Navy Reserve, you must be between the ages of 18 and 35. However, the maximum age limit can be waived in certain circumstances, such as for those with prior military service or for critical skills. It's also worth noting that the age requirements can vary slightly depending on whether you're looking to enlist or become an officer. Officers typically have different age requirements, often with a higher maximum age limit, especially for those with advanced degrees or specialized skills.
For individuals who are nearing or have passed the typical age limit, there are still opportunities to serve. The Navy Reserve has programs in place for older recruits, recognizing the value of life experience and skills that older individuals can bring to the table. These programs may have different physical fitness standards and can offer a more flexible service commitment, which can be appealing to those who want to serve but also have established civilian careers or family commitments.
Another aspect to consider is the impact of age on the type of role you can pursue within the Navy Reserve. Certain specialties or ratings may have age restrictions due to the physical demands or the time required for training. For example, special operations roles like the Navy SEALs have younger age limits due to the extreme physical and mental demands of the training and the job itself. In contrast, roles that are more administrative or technical may have less stringent age requirements, making them more accessible to older recruits.
The process of joining the Navy Reserve involves several steps, including taking the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test, passing a physical fitness test, and undergoing a medical examination. Age can be a factor in how one prepares for and performs on these tests. For instance, older recruits may need to focus more on their physical conditioning to meet the fitness standards, while their life experience can be an advantage in terms of maturity and discipline, which are valued in the military.
Lastly, for those who are considering joining the Navy Reserve later in life, it's essential to understand the benefits and challenges. Serving in the Navy Reserve can provide a sense of purpose, camaraderie, and personal growth, along with financial benefits like education assistance and retirement benefits. However, it also requires a significant time commitment, including drills one weekend a month and two weeks of annual training, which can impact family and work life. Older recruits may find that their age gives them a unique perspective and advantage in balancing these commitments, as they often have more established support systems and time management skills.
Understanding Navy Reserve Eligibility
Age and Physical Fitness
Physical fitness is a critical component of Navy Reserve service, and age can play a role in how one approaches the physical demands of service. The Navy uses the Physical Readiness Test (PRT) to assess fitness, which includes a 1.5-mile run, push-ups, and sit-ups. Older recruits may need to work harder to meet these standards, focusing on cardiovascular health, strength, and flexibility. However, with a consistent training program, many find that they can achieve and maintain the required level of fitness.Navy Reserve Careers and Age

Benefits of Serving in the Navy Reserve
Serving in the Navy Reserve comes with numerous benefits, including education assistance, retirement benefits, and access to military facilities and services. For older recruits, the educational benefits can be particularly appealing, offering a chance to pursue higher education or vocational training with financial assistance. The experience and skills gained through Navy Reserve service can also enhance civilian career prospects, demonstrating discipline, leadership, and a strong work ethic.Preparing for Navy Reserve Service
Age Considerations for Officers
For those interested in becoming officers in the Navy Reserve, the age requirements can be different. Typically, officer candidates must have a bachelor's degree and meet specific age limits, which can vary depending on the commissioning program. The age limit for officer commissioning is often higher than for enlisted personnel, reflecting the value placed on education and life experience. However, certain programs, like the Navy's Officer Candidate School, may have stricter age limits, usually not exceeding 35 years of age for most candidates.Navy Reserve Training and Age

Life as a Navy Reserve Member
Life as a Navy Reserve member involves a unique balance between military service and civilian life. Members are required to attend drills one weekend a month and complete two weeks of annual training, which can be a significant commitment. However, the sense of service, camaraderie, and personal growth can be highly rewarding. For older members, the Navy Reserve can offer a way to give back, stay engaged, and be part of a community with shared values and experiences.Gallery of Navy Reserve Images
Navy Reserve Image Gallery









Frequently Asked Questions
What is the age limit to join the Navy Reserve?
+The general age limit to join the Navy Reserve is between 18 and 35 years old. However, the maximum age limit can be waived for certain roles or for those with prior military service.
Can I join the Navy Reserve if I am over 35?
+Yes, it is possible to join the Navy Reserve if you are over 35, but this typically requires a waiver. The likelihood of receiving a waiver can depend on the role you're applying for, your prior service experience, and other factors.
What are the physical fitness requirements for the Navy Reserve?
+The Navy Reserve uses the Physical Readiness Test (PRT) to assess fitness, which includes a 1.5-mile run, push-ups, and sit-ups. The standards can vary based on age and gender.
How long do I have to serve in the Navy Reserve?
+The service commitment for the Navy Reserve typically involves attending drills one weekend a month and completing two weeks of annual training. The total length of service can vary based on the role and the terms of your enlistment or commission.
What benefits does the Navy Reserve offer?
+The Navy Reserve offers a range of benefits, including education assistance, retirement benefits, access to military facilities, and the opportunity to serve and be part of a community with shared values.
In conclusion, joining the Navy Reserve can be a fulfilling way to serve one's country, develop new skills, and enhance one's career prospects. Understanding the age requirements and how they impact eligibility is a crucial first step. Whether you're considering enlistment or becoming an officer, the Navy Reserve offers a variety of roles and opportunities for individuals of different ages and backgrounds. If you're interested in learning more or have questions about the process, we invite you to share your thoughts, ask questions, or explore the resources available to help you get started on this rewarding path.
