Intro
Compare naval ranks to army ranks, understanding officer hierarchies, enlisted personnel, and rank structures in military organizations, including commissioned officers and non-commissioned officers.
The world of military ranks can be complex and fascinating, with different branches having their own unique hierarchies and systems. Two of the most well-known branches are the Navy and the Army, each with its own set of ranks that reflect the specific needs and traditions of the service. In this article, we'll delve into the world of naval ranks vs army ranks, exploring the similarities and differences between these two branches.
The importance of understanding military ranks cannot be overstated. Not only do ranks reflect an individual's level of responsibility and expertise, but they also play a crucial role in maintaining order and discipline within the military. Whether you're a seasoned veteran or just starting out, knowing the ins and outs of naval and army ranks can help you navigate the complexities of military life. From the enlisted ranks to the highest levels of command, each rank has its own unique set of challenges and opportunities.
As we explore the world of naval ranks vs army ranks, it's essential to keep in mind that both branches have their own distinct cultures and traditions. The Navy, with its emphasis on maritime operations and shipboard life, has developed a unique set of ranks that reflect the specialized skills and knowledge required to operate at sea. The Army, on the other hand, has a more traditional rank structure that emphasizes leadership and command on land. By understanding these differences, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and nuances of military life.
Introduction to Naval Ranks
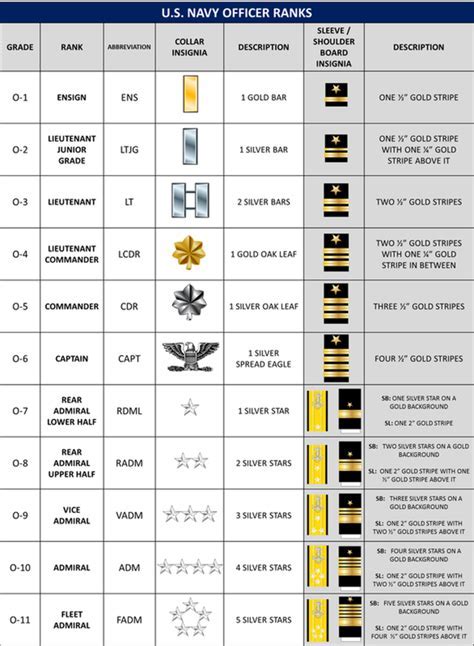
Naval ranks are designed to reflect the unique challenges and responsibilities of life at sea. From the lowest enlisted ranks to the highest levels of command, naval personnel must be able to adapt to a wide range of situations, from combat operations to humanitarian missions. The Navy's rank structure is divided into several categories, including enlisted, warrant officer, and commissioned officer ranks. Each category has its own set of ranks, with corresponding levels of responsibility and authority.
Some of the key naval ranks include:
- Seaman Recruit (E-1): The lowest enlisted rank in the Navy, responsible for basic tasks and duties.
- Petty Officer Third Class (E-4): A junior enlisted rank that requires specialized skills and knowledge.
- Chief Petty Officer (E-7): A senior enlisted rank that reflects a high level of expertise and leadership.
- Ensign (O-1): The lowest commissioned officer rank in the Navy, responsible for leading and commanding junior personnel.
- Captain (O-6): A senior commissioned officer rank that reflects a high level of command authority and responsibility.
Introduction to Army Ranks

Army ranks, on the other hand, are designed to reflect the unique challenges and responsibilities of life on land. From the lowest enlisted ranks to the highest levels of command, Army personnel must be able to adapt to a wide range of situations, from combat operations to peacekeeping missions. The Army's rank structure is also divided into several categories, including enlisted, warrant officer, and commissioned officer ranks. Each category has its own set of ranks, with corresponding levels of responsibility and authority.
Some of the key Army ranks include:
- Private (E-1): The lowest enlisted rank in the Army, responsible for basic tasks and duties.
- Sergeant (E-5): A junior enlisted rank that requires specialized skills and knowledge.
- Sergeant Major (E-9): A senior enlisted rank that reflects a high level of expertise and leadership.
- Second Lieutenant (O-1): The lowest commissioned officer rank in the Army, responsible for leading and commanding junior personnel.
- Colonel (O-6): A senior commissioned officer rank that reflects a high level of command authority and responsibility.
Comparing Naval and Army Ranks
When comparing naval and army ranks, it's essential to keep in mind that both branches have their own unique cultures and traditions. While there are some similarities between the two rank structures, there are also some key differences. For example, the Navy's emphasis on maritime operations means that its ranks are often more specialized, with a focus on skills such as navigation and engineering. The Army, on the other hand, has a more traditional rank structure that emphasizes leadership and command on land.
Some of the key similarities between naval and army ranks include:
- Both branches have a clear hierarchy, with higher ranks reflecting greater levels of responsibility and authority.
- Both branches have a system of promotion, with personnel advancing through the ranks based on merit and performance.
- Both branches have a strong emphasis on leadership and command, with senior personnel responsible for guiding and directing junior personnel.
Some of the key differences between naval and army ranks include:
- The Navy's emphasis on maritime operations means that its ranks are often more specialized, with a focus on skills such as navigation and engineering.
- The Army's traditional rank structure emphasizes leadership and command on land, with a focus on skills such as tactics and strategy.
- The Navy's rank structure is often more fluid, with personnel advancing through the ranks based on a combination of merit, performance, and time in service.
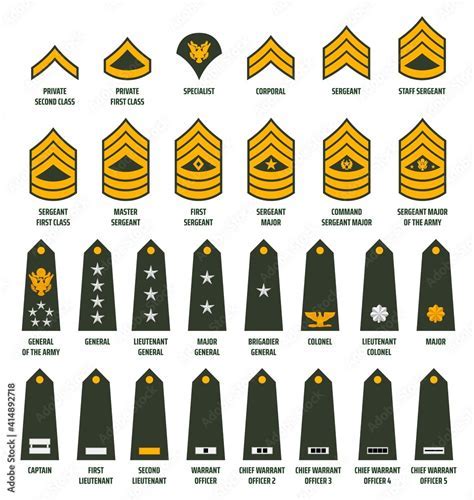
Enlisted Ranks

Enlisted ranks are the backbone of both the Navy and the Army, providing the manpower and expertise needed to carry out a wide range of missions. In both branches, enlisted personnel are responsible for performing specific tasks and duties, with higher ranks reflecting greater levels of responsibility and authority.
Some of the key enlisted ranks in the Navy include:
- Seaman Recruit (E-1)
- Seaman Apprentice (E-2)
- Seaman (E-3)
- Petty Officer Third Class (E-4)
- Petty Officer Second Class (E-5)
Some of the key enlisted ranks in the Army include:
- Private (E-1)
- Private Second Class (E-2)
- Private First Class (E-3)
- Specialist/Corporal (E-4)
- Sergeant (E-5)
Warrant Officer Ranks
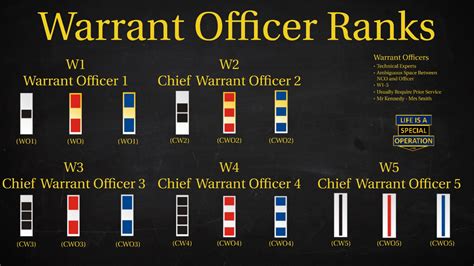
Warrant officer ranks are a unique category of ranks that exist in both the Navy and the Army. Warrant officers are technical experts who have advanced knowledge and skills in a specific area, such as aviation or engineering. They are responsible for providing guidance and expertise to junior personnel, and for carrying out specialized tasks and duties.
Some of the key warrant officer ranks in the Navy include:
- Warrant Officer 1 (W-1)
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2)
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (W-3)
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (W-4)
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5)
Some of the key warrant officer ranks in the Army include:
- Warrant Officer 1 (W-1)
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2)
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (W-3)
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (W-4)
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5)
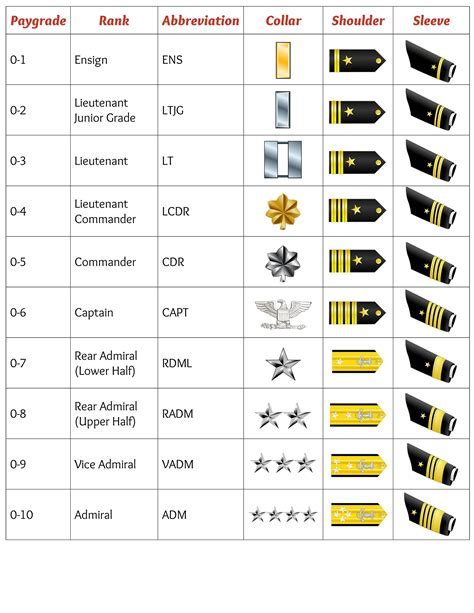
Commissioned Officer Ranks

Commissioned officer ranks are the highest level of ranks in both the Navy and the Army, reflecting a high level of command authority and responsibility. Commissioned officers are responsible for leading and commanding junior personnel, and for carrying out a wide range of missions and tasks.
Some of the key commissioned officer ranks in the Navy include:
- Ensign (O-1)
- Lieutenant Junior Grade (O-2)
- Lieutenant (O-3)
- Lieutenant Commander (O-4)
- Commander (O-5)
Some of the key commissioned officer ranks in the Army include:
- Second Lieutenant (O-1)
- First Lieutenant (O-2)
- Captain (O-3)
- Major (O-4)
- Lieutenant Colonel (O-5)
Gallery of Naval and Army Ranks
Naval and Army Ranks Image Gallery




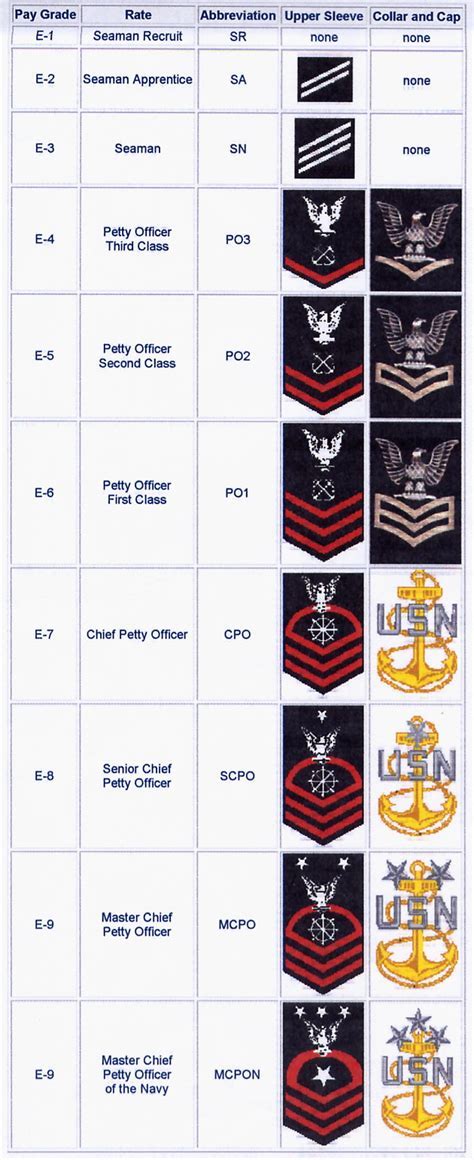


What is the difference between naval and army ranks?
+The main difference between naval and army ranks is the emphasis on maritime operations in the Navy, versus the emphasis on land-based operations in the Army. This difference is reflected in the rank structures and the specialized skills and knowledge required for each branch.
How do naval and army ranks compare in terms of responsibility and authority?
+Both naval and army ranks have a clear hierarchy, with higher ranks reflecting greater levels of responsibility and authority. However, the specific responsibilities and authorities associated with each rank can vary between the two branches, reflecting the unique needs and traditions of each service.
What are the key similarities and differences between naval and army enlisted ranks?
+The key similarities between naval and army enlisted ranks include a clear hierarchy and a system of promotion based on merit and performance. The key differences include the specialized skills and knowledge required for each branch, with the Navy emphasizing maritime operations and the Army emphasizing land-based operations.
How do naval and army warrant officer ranks compare in terms of responsibility and authority?
+Both naval and army warrant officer ranks are technical experts who have advanced knowledge and skills in a specific area. They are responsible for providing guidance and expertise to junior personnel, and for carrying out specialized tasks and duties. The key differences between the two branches include the specific areas of expertise and the level of responsibility and authority associated with each rank.
What are the key similarities and differences between naval and army commissioned officer ranks?
+The key similarities between naval and army commissioned officer ranks include a high level of command authority and responsibility, and a system of promotion based on merit and performance. The key differences include the specialized skills and knowledge required for each branch, with the Navy emphasizing maritime operations and the Army emphasizing land-based operations.
As we conclude our exploration of naval ranks vs army ranks, it's essential to remember that both branches have their own unique cultures and traditions. By understanding these differences, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and nuances of military life. Whether you're a seasoned veteran or just starting out, knowing the ins and outs of naval and army ranks can help you navigate the challenges and opportunities of military service. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with us, and to continue the conversation about the importance of military ranks and the differences between the Navy and the Army.
