Intro
Discover how turbine power jets work with 5 key methods, exploring jet engine mechanics, turbine technology, and aerodynamics principles.
The importance of turbine power jets cannot be overstated, as they have revolutionized the way we travel by air. From commercial airliners to military aircraft, turbine power jets have become the backbone of modern aviation. But have you ever wondered how these magnificent machines work? In this article, we will delve into the world of turbine power jets and explore the five ways they work to provide thrust and power to aircraft.
Turbine power jets are a type of engine that uses a turbine to generate power, which is then used to produce thrust. This is in contrast to traditional piston engines, which use a combination of pistons, cylinders, and crankshafts to generate power. The use of turbines in aircraft engines has several advantages, including increased efficiency, reliability, and power-to-weight ratio. As a result, turbine power jets have become the preferred choice for many aircraft manufacturers and operators.
The development of turbine power jets has a rich history, dating back to the early 20th century. The first turbine-powered aircraft was the British Gloster E.28/39, which made its maiden flight in 1941. Since then, turbine power jets have undergone significant improvements, with advances in materials, design, and technology. Today, turbine power jets are used in a wide range of applications, from commercial aviation to military and space exploration.
Introduction to Turbine Power Jets

Turbine power jets work by using a combination of air, fuel, and ignition to generate power. The process begins with the ingestion of air, which is then compressed and mixed with fuel. The resulting mixture is then ignited, producing a high-temperature and high-pressure gas. This gas is then expanded through a turbine, which extracts energy from the gas and uses it to drive a compressor. The compressor is used to compress the air, which is then mixed with fuel and ignited, creating a continuous cycle.
Components of a Turbine Power Jet
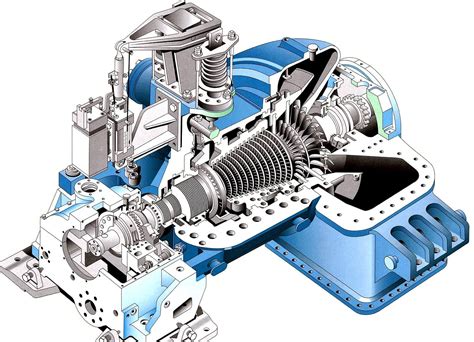
A turbine power jet consists of several components, including the compressor, turbine, combustion chamber, and nozzle. The compressor is responsible for compressing the air, which is then mixed with fuel in the combustion chamber. The combustion chamber is where the fuel is ignited, producing a high-temperature and high-pressure gas. The turbine is used to extract energy from the gas, which is then used to drive the compressor. The nozzle is used to accelerate the gas, producing a high-velocity exhaust that generates thrust.
Compressor
The compressor is a critical component of a turbine power jet, as it is responsible for compressing the air. The compressor uses a series of blades and vanes to compress the air, which is then mixed with fuel in the combustion chamber. The compressor is typically driven by the turbine, which extracts energy from the gas and uses it to drive the compressor.Turbine
The turbine is another critical component of a turbine power jet, as it is responsible for extracting energy from the gas. The turbine uses a series of blades and vanes to extract energy from the gas, which is then used to drive the compressor. The turbine is typically driven by the expansion of the gas, which is produced by the combustion of fuel in the combustion chamber.Working Mechanism of Turbine Power Jets
The working mechanism of turbine power jets is based on the principle of thermodynamics. The process begins with the ingestion of air, which is then compressed and mixed with fuel. The resulting mixture is then ignited, producing a high-temperature and high-pressure gas. This gas is then expanded through a turbine, which extracts energy from the gas and uses it to drive a compressor. The compressor is used to compress the air, which is then mixed with fuel and ignited, creating a continuous cycle.
Thermodynamic Cycle
The thermodynamic cycle of a turbine power jet is based on the Brayton cycle, which is a type of gas turbine cycle. The cycle consists of four stages: compression, combustion, expansion, and exhaust. The compression stage is where the air is compressed, which is then mixed with fuel in the combustion stage. The combustion stage is where the fuel is ignited, producing a high-temperature and high-pressure gas. The expansion stage is where the gas is expanded through a turbine, which extracts energy from the gas and uses it to drive a compressor. The exhaust stage is where the gas is exhausted, producing a high-velocity exhaust that generates thrust.Types of Turbine Power Jets
There are several types of turbine power jets, including turbojet, turboprop, and turbofan. Turbojet engines are the simplest type of turbine power jet, as they use a single turbine to extract energy from the gas. Turboprop engines are more complex, as they use a turbine to drive a propeller. Turbofan engines are the most complex, as they use a turbine to drive a fan, which generates additional thrust.
Turbojet Engines
Turbojet engines are the simplest type of turbine power jet, as they use a single turbine to extract energy from the gas. The gas is expanded through the turbine, which extracts energy from the gas and uses it to drive the compressor. The compressor is used to compress the air, which is then mixed with fuel and ignited, creating a continuous cycle.Turboprop Engines
Turboprop engines are more complex, as they use a turbine to drive a propeller. The turbine extracts energy from the gas, which is then used to drive the propeller. The propeller generates additional thrust, which is used to propel the aircraft.Turbofan Engines
Turbofan engines are the most complex, as they use a turbine to drive a fan. The fan generates additional thrust, which is used to propel the aircraft. The fan is typically driven by the turbine, which extracts energy from the gas and uses it to drive the fan.Advantages of Turbine Power Jets
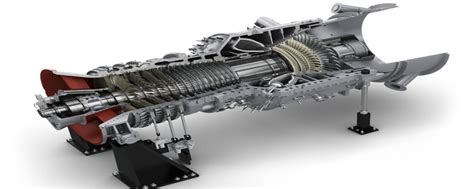
Turbine power jets have several advantages, including increased efficiency, reliability, and power-to-weight ratio. The use of turbines in aircraft engines has several benefits, including reduced fuel consumption, increased range, and improved performance. Additionally, turbine power jets are more reliable and require less maintenance than traditional piston engines.
Increased Efficiency
Turbine power jets are more efficient than traditional piston engines, as they use a turbine to extract energy from the gas. The turbine extracts energy from the gas, which is then used to drive the compressor. The compressor is used to compress the air, which is then mixed with fuel and ignited, creating a continuous cycle.Reliability
Turbine power jets are more reliable than traditional piston engines, as they have fewer moving parts. The turbine is the only moving part in a turbine power jet, which reduces the risk of mechanical failure. Additionally, turbine power jets are less prone to overheating, which reduces the risk of engine failure.Power-to-Weight Ratio
Turbine power jets have a higher power-to-weight ratio than traditional piston engines, which means they produce more power per unit of weight. The use of turbines in aircraft engines has several benefits, including increased performance, range, and efficiency.Turbine Power Jets Image Gallery










What is the main advantage of turbine power jets?
+The main advantage of turbine power jets is their increased efficiency, reliability, and power-to-weight ratio compared to traditional piston engines.
How do turbine power jets work?
+Turbine power jets work by using a combination of air, fuel, and ignition to generate power. The process begins with the ingestion of air, which is then compressed and mixed with fuel. The resulting mixture is then ignited, producing a high-temperature and high-pressure gas. This gas is then expanded through a turbine, which extracts energy from the gas and uses it to drive a compressor.
What are the different types of turbine power jets?
+There are several types of turbine power jets, including turbojet, turboprop, and turbofan. Each type has its own unique characteristics and advantages, and is used in different applications.
In conclusion, turbine power jets are a critical component of modern aviation, providing the power and thrust needed to propel aircraft through the skies. By understanding the five ways turbine power jets work, including the use of compressors, turbines, combustion chambers, and nozzles, we can appreciate the complexity and sophistication of these machines. Whether you are an aviation enthusiast or simply someone who appreciates the wonders of modern technology, turbine power jets are sure to fascinate and inspire. So next time you board a plane or watch a jet take off, remember the incredible engineering and technology that goes into making these machines fly. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of turbine power jets and their importance in modern aviation. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more, please don't hesitate to comment or share this article with others.
