Intro
Join the military with a GED, exploring enlistment options, GED requirements, and military career paths for non-traditional students, including benefits and challenges of serving with a General Educational Development certificate.
Joining the military can be a life-changing decision, offering a unique opportunity for personal growth, career development, and service to one's country. For individuals who have obtained a General Educational Development (GED) certificate, the prospect of joining the military can be both exciting and intimidating. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of joining the military with a GED, exploring the benefits, requirements, and steps involved in this process.
The military is an attractive career option for many individuals, regardless of their educational background. With a GED, you can still pursue a military career, although there may be certain limitations and requirements to be aware of. The military recognizes the GED as an equivalent to a high school diploma, but the acceptance criteria may vary between branches. It's essential to understand these differences and plan accordingly.
The benefits of joining the military are numerous, ranging from education and training opportunities to career advancement and personal development. Military service can provide a sense of purpose, discipline, and camaraderie, as well as access to comprehensive healthcare, housing, and food benefits. Additionally, the military offers a range of educational assistance programs, including the GI Bill, which can help you pursue higher education or vocational training.
Understanding the Military's Education Requirements

To join the military, you typically need to meet specific education requirements, which may include a high school diploma or equivalent. The GED is recognized as an equivalent to a high school diploma, but the military may have additional requirements or restrictions for GED holders. For example, some branches may require GED holders to score higher on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test or to complete additional education or training.
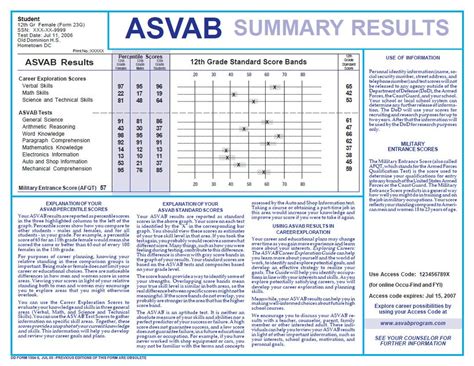
The ASVAB test is a multiple-choice exam that measures your aptitude in various subjects, including mathematics, reading, and science. The test is used to determine your eligibility for different military careers and to identify areas where you may need additional training. As a GED holder, you may need to score higher on the ASVAB test to compensate for your non-traditional educational background.
Military Branches and Their GED Policies

Each military branch has its own policies and requirements for GED holders. Here's a brief overview of the GED policies for each branch:
- Army: The Army accepts GED holders, but they must score a minimum of 50 on the ASVAB test and meet other eligibility requirements.
- Navy: The Navy also accepts GED holders, but they must score a minimum of 50 on the ASVAB test and complete a vocational or technical training program.
- Air Force: The Air Force is more restrictive, requiring GED holders to score a minimum of 65 on the ASVAB test and complete a vocational or technical training program.
- Marine Corps: The Marine Corps accepts GED holders, but they must score a minimum of 50 on the ASVAB test and meet other eligibility requirements.
- Coast Guard: The Coast Guard is the most restrictive, requiring GED holders to score a minimum of 40 on the ASVAB test and complete a vocational or technical training program.
Steps to Join the Military with a GED

If you're interested in joining the military with a GED, here are the steps to follow:
- Meet the basic eligibility requirements: You must be a U.S. citizen, be between the ages of 17 and 35, and meet the physical and medical requirements.
- Choose a military branch: Research the different branches and their GED policies to determine which one is the best fit for you.
- Take the ASVAB test: The ASVAB test is used to determine your eligibility for different military careers. You can prepare for the test by studying and practicing with sample questions.
- Complete the enlistment process: Once you've met the eligibility requirements and taken the ASVAB test, you can complete the enlistment process, which includes filling out paperwork, undergoing a physical exam, and taking the oath of enlistment.
- Attend basic training: After enlisting, you'll attend basic training, which is a rigorous program that teaches you the skills and discipline you need to succeed in the military.
Benefits of Joining the Military with a GED

Joining the military with a GED can have numerous benefits, including:
- Education and training opportunities: The military offers a range of educational assistance programs, including the GI Bill, which can help you pursue higher education or vocational training.
- Career advancement: The military provides opportunities for career advancement and promotion, which can lead to higher pay and greater responsibility.
- Personal development: Military service can help you develop important skills, such as discipline, leadership, and teamwork.
- Comprehensive benefits: The military offers comprehensive benefits, including healthcare, housing, and food benefits.
Challenges of Joining the Military with a GED

While joining the military with a GED can be a rewarding experience, there are also challenges to consider:
- Limited career options: Some military careers may be closed to GED holders, or they may require additional education or training.
- Higher ASVAB scores: GED holders may need to score higher on the ASVAB test to compensate for their non-traditional educational background.
- Stigma: Some people may view a GED as inferior to a high school diploma, which can lead to stigma or bias.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, joining the military with a GED can be a challenging but rewarding experience. While there may be limitations and requirements to be aware of, the benefits of military service can far outweigh the challenges. If you're interested in joining the military with a GED, it's essential to research the different branches and their GED policies, prepare for the ASVAB test, and complete the enlistment process.
To learn more about joining the military with a GED, you can visit the website of the military branch you're interested in or speak with a recruiter. Additionally, you can prepare for the ASVAB test by studying and practicing with sample questions.
Military and GED Image Gallery









What are the basic eligibility requirements to join the military with a GED?
+To join the military with a GED, you must be a U.S. citizen, be between the ages of 17 and 35, and meet the physical and medical requirements. You must also score a minimum of 50 on the ASVAB test and meet other eligibility requirements.
Which military branches accept GED holders?
+All military branches accept GED holders, but each branch has its own policies and requirements. The Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard all accept GED holders, but they may require higher ASVAB scores or additional education or training.
What are the benefits of joining the military with a GED?
+The benefits of joining the military with a GED include education and training opportunities, career advancement, personal development, and comprehensive benefits. The military offers a range of educational assistance programs, including the GI Bill, which can help you pursue higher education or vocational training.
How can I prepare for the ASVAB test?
+You can prepare for the ASVAB test by studying and practicing with sample questions. You can find study materials and practice tests online or through a recruiter. It's essential to prepare for the test to ensure you score well and meet the eligibility requirements for your desired military career.
What are the challenges of joining the military with a GED?
+The challenges of joining the military with a GED include limited career options, higher ASVAB scores, and stigma. Some military careers may be closed to GED holders, or they may require additional education or training. Additionally, some people may view a GED as inferior to a high school diploma, which can lead to stigma or bias.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of joining the military with a GED. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in joining the military with a GED. Remember, military service can be a rewarding and challenging experience, and we're here to support you every step of the way.
