Intro
Discover the 5 Military Ranks, including enlisted, officer, and warrant ranks, understanding rank structures, insignia, and responsibilities in military hierarchy and careers.
The hierarchy of military ranks is a fundamental aspect of any armed forces, providing a clear chain of command and structure for personnel to follow. Understanding these ranks is essential for both military personnel and civilians, as it reflects the level of responsibility, expertise, and authority an individual holds within the military. In this article, we will delve into the world of military ranks, focusing on five key ranks that form the backbone of most military organizations.
The importance of military ranks cannot be overstated. They serve as a visual representation of a soldier's experience, training, and capabilities, making it easier for commanders to assign tasks and make informed decisions. Moreover, military ranks play a crucial role in maintaining discipline and order within the military, as they provide a clear understanding of the hierarchy and the expectations that come with each position. Whether you are a seasoned veteran or a new recruit, understanding military ranks is vital for success in the armed forces.
As we explore the five military ranks, it is essential to note that the specific ranks and their corresponding responsibilities may vary between countries and branches of the military. However, the core principles and functions of these ranks remain relatively consistent across different military organizations. By examining these ranks in detail, we can gain a deeper understanding of the military's inner workings and the individuals who serve within it.
Introduction to Military Ranks

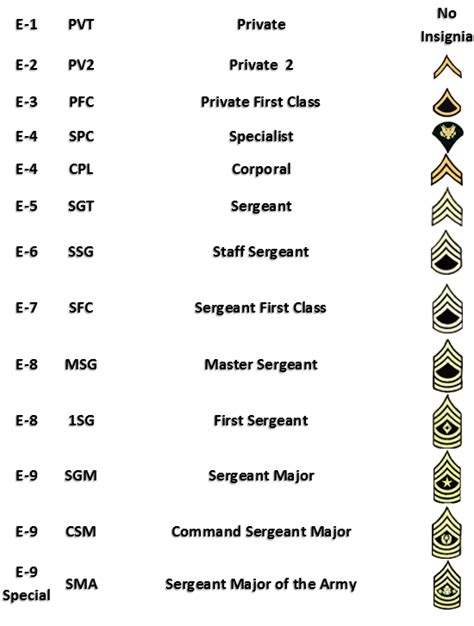
Military ranks are typically divided into several categories, including enlisted personnel, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), and commissioned officers. Each category has its unique set of ranks, with varying levels of authority and responsibility. The five military ranks we will be discussing are: Private, Sergeant, Lieutenant, Captain, and Colonel. These ranks represent a mix of junior and senior positions, providing a comprehensive overview of the military's rank structure.
Private: The Entry-Level Rank

The Private rank is the most junior position in the military, typically held by new recruits or soldiers in the early stages of their training. Privates are responsible for following orders and completing tasks assigned to them by their superiors. They may also be required to participate in basic training, where they learn essential skills such as first aid, combat techniques, and military protocols. As Privates gain experience and complete their training, they may be eligible for promotion to higher ranks.
Responsibilities of a Private
- Follow orders from superiors
- Complete assigned tasks and training exercises
- Participate in basic training and skills development
- Maintain equipment and uniforms
- Contribute to team efforts and unit cohesion
Sergeant: The Non-Commissioned Officer

The Sergeant rank is a non-commissioned officer (NCO) position, typically held by experienced soldiers who have demonstrated leadership potential and a strong understanding of military protocols. Sergeants are responsible for leading teams of soldiers, providing guidance and mentorship, and ensuring that tasks are completed efficiently and effectively. They may also be involved in training and development programs, helping to shape the next generation of military leaders.
Responsibilities of a Sergeant
- Lead teams of soldiers and provide guidance
- Mentor junior personnel and provide feedback
- Coordinate training exercises and development programs
- Ensure compliance with military protocols and regulations
- Represent the unit in formal and informal settings
Lieutenant: The Junior Officer

The Lieutenant rank is a junior officer position, typically held by individuals who have completed officer training and have been commissioned into the military. Lieutenants are responsible for leading platoons or smaller units, making tactical decisions, and coordinating with other officers to achieve strategic objectives. They may also be involved in planning and executing missions, as well as evaluating the performance of their unit.
Responsibilities of a Lieutenant
- Lead platoons or smaller units
- Make tactical decisions and coordinate with other officers
- Plan and execute missions
- Evaluate unit performance and provide feedback
- Develop and implement training programs
Captain: The Senior Officer

The Captain rank is a senior officer position, typically held by experienced officers who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and strategic thinking. Captains are responsible for commanding companies or battalions, developing and implementing operational plans, and coordinating with other units to achieve strategic objectives. They may also be involved in mentoring junior officers and providing guidance on career development.
Responsibilities of a Captain
- Command companies or battalions
- Develop and implement operational plans
- Coordinate with other units and stakeholders
- Mentor junior officers and provide guidance
- Evaluate unit performance and provide feedback
Colonel: The Senior Leader

The Colonel rank is a senior leadership position, typically held by experienced officers who have demonstrated exceptional strategic thinking and leadership abilities. Colonels are responsible for commanding brigades or larger units, developing and implementing strategic plans, and coordinating with other senior leaders to achieve national or international objectives. They may also be involved in shaping military policy and providing guidance on operational matters.
Responsibilities of a Colonel
- Command brigades or larger units
- Develop and implement strategic plans
- Coordinate with other senior leaders and stakeholders
- Shape military policy and provide guidance
- Evaluate unit performance and provide feedback
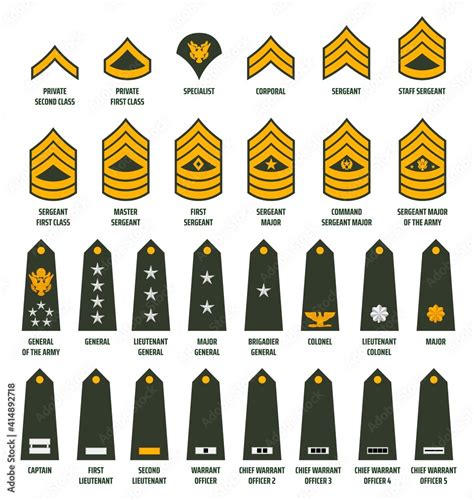
Military Ranks Image Gallery









What is the highest military rank?
+The highest military rank is typically the General or Admiral rank, depending on the branch of the military.
How do military ranks work?
+Military ranks work by providing a clear hierarchy and chain of command, with each rank having its own set of responsibilities and authority.
What is the difference between a Private and a Sergeant?
+A Private is a junior enlisted rank, while a Sergeant is a non-commissioned officer (NCO) rank, with more responsibility and authority.
How do I get promoted in the military?
+Promotions in the military typically require a combination of time in service, performance evaluations, and completion of training and education programs.
What is the role of a Colonel in the military?
+A Colonel is a senior officer rank, responsible for commanding brigades or larger units, developing and implementing strategic plans, and coordinating with other senior leaders.
As we conclude our exploration of the five military ranks, it is clear that each position plays a vital role in the functioning of the military. From the junior Private to the senior Colonel, each rank requires a unique set of skills, knowledge, and leadership abilities. By understanding these ranks and their responsibilities, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the men and women who serve in the armed forces, and the sacrifices they make to protect our nations and communities. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about military ranks, and to explore the many resources available for those interested in pursuing a career in the military.
