Intro
Discover the latest Marine Corps retention rates, factors influencing re-enlistment, and recruitment strategies, including career advancement and military benefits, to understand the dynamics of Marine Corps personnel management and career retention.
The United States Marine Corps is one of the most elite fighting forces in the world, known for its rigorous training, esprit de corps, and unwavering commitment to defending the nation. However, like all branches of the military, the Marine Corps faces challenges in retaining its talented and dedicated personnel. Retention rates are a critical metric for the Marine Corps, as they directly impact the branch's ability to maintain its combat readiness, fulfill its mission, and ensure the well-being of its Marines.
The importance of retention rates cannot be overstated. High retention rates indicate that Marines are satisfied with their service, feel valued and supported, and are committed to continuing their careers in the Corps. On the other hand, low retention rates can signal underlying issues, such as inadequate compensation, poor working conditions, or limited opportunities for advancement. As the Marine Corps continues to evolve and adapt to emerging threats and technological advancements, it is essential to understand the factors that influence retention rates and develop effective strategies to retain its most talented and dedicated personnel.
The Marine Corps has implemented various initiatives to improve retention rates, including enhanced compensation and benefits packages, expanded education and training opportunities, and improved quality of life programs. However, despite these efforts, retention rates remain a concern, particularly among certain demographics and occupational specialties. To better understand the complexities of retention rates in the Marine Corps, it is essential to examine the historical context, current trends, and future challenges facing the branch.
Historical Context of Marine Corps Retention Rates
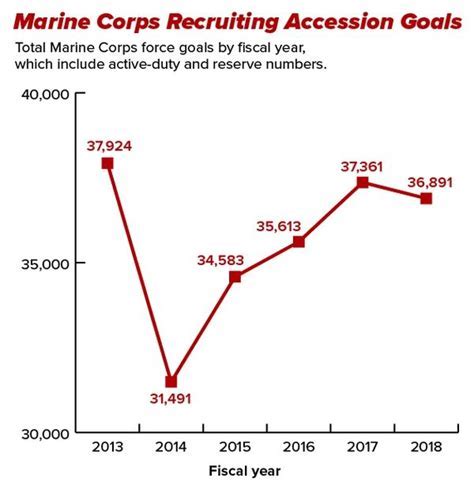
In the post-Vietnam era, the Marine Corps implemented various reforms, including the introduction of the All-Volunteer Force (AVF), which aimed to improve retention rates by providing better compensation, benefits, and training opportunities. The AVF has been largely successful, with retention rates increasing significantly during the 1980s and 1990s. However, the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq presented new challenges, as the Marine Corps faced increased operational tempo, decreased dwell time, and rising casualties, all of which contributed to decreased retention rates.
Current Trends in Marine Corps Retention Rates

However, the Marine Corps has also experienced increased retention rates among certain demographics, such as female Marines and those in technical specialties, such as cyber and intelligence. These trends suggest that the Marine Corps is adapting to changing societal and technological trends, with a growing recognition of the importance of diversity, inclusion, and technical expertise in the 21st-century battlefield.
Factors Influencing Marine Corps Retention Rates
Several factors influence Marine Corps retention rates, including: * Compensation and benefits: Competitive pay, bonuses, and benefits are essential for attracting and retaining top talent. * Education and training opportunities: Access to education and training programs, such as the Marine Corps' Tuition Assistance Program, can enhance career prospects and increase job satisfaction. * Quality of life: Adequate housing, healthcare, and family support services are critical for maintaining morale and reducing stress. * Leadership and mentorship: Effective leadership and mentorship can foster a sense of belonging, purpose, and career advancement opportunities. * Operational tempo and deployment cycles: Frequent deployments and high operational tempo can lead to burnout, decreased morale, and increased turnover.Strategies to Improve Marine Corps Retention Rates

Best Practices for Retention
Best practices for retention in the Marine Corps include: * Regular feedback and communication: Regular feedback and communication between leaders and Marines can help identify and address concerns, improve job satisfaction, and increase retention. * Career development and advancement opportunities: Providing opportunities for career development and advancement can enhance job satisfaction, increase motivation, and reduce turnover. * Recognition and reward: Recognizing and rewarding outstanding performance and contributions can foster a sense of appreciation, increase morale, and encourage retention. * Support for families: Providing support for families, including spouse employment assistance, childcare, and education resources, can reduce stress, improve quality of life, and increase retention.Challenges and Future Directions

Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, retention rates are a critical metric for the Marine Corps, reflecting the branch's ability to attract, retain, and develop top talent. To improve retention rates, the Marine Corps must continue to adapt to changing demographics and expectations, leverage technological advancements, and prepare for Great Power Competition. Recommendations for improving retention rates include: * Enhancing compensation and benefits packages * Expanding education and training opportunities * Improving quality of life programs * Developing effective leadership and mentorship initiatives * Managing operational tempo and deployment cyclesMarine Corps Retention Image Gallery










What are the primary factors influencing Marine Corps retention rates?
+The primary factors influencing Marine Corps retention rates include compensation and benefits, education and training opportunities, quality of life, leadership and mentorship, and operational tempo and deployment cycles.
What strategies has the Marine Corps implemented to improve retention rates?
+The Marine Corps has implemented various strategies to improve retention rates, including enhanced compensation and benefits packages, expanded education and training opportunities, improved quality of life programs, and leadership development and mentorship initiatives.
What are the best practices for retention in the Marine Corps?
+Best practices for retention in the Marine Corps include regular feedback and communication, career development and advancement opportunities, recognition and reward, and support for families.
What are the challenges and future directions for Marine Corps retention?
+The challenges and future directions for Marine Corps retention include changing demographics and expectations, technological advancements, and Great Power Competition.
How can the Marine Corps improve its retention rates?
+The Marine Corps can improve its retention rates by enhancing compensation and benefits packages, expanding education and training opportunities, improving quality of life programs, developing effective leadership and mentorship initiatives, and managing operational tempo and deployment cycles.
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the complex issue of Marine Corps retention rates. If you have any further questions or comments, please do not hesitate to reach out. Share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about the Marine Corps and its efforts to retain top talent. Together, we can support the men and women who serve our nation and ensure the continued strength and readiness of the Marine Corps.
