Intro
Mach 7 speed converts to approximately 5,328 miles per hour, exploring supersonic and hypersonic velocities, sonic booms, and high-speed flight regimes.
The speed of Mach 7 is an incredibly high velocity that is typically associated with advanced military aircraft and spacecraft. To put this speed into perspective, it's essential to understand what Mach 7 represents and how it translates to miles per hour. Mach 7 is equivalent to seven times the speed of sound, which is approximately 768 miles per hour at sea level in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit.
The calculation to convert Mach 7 to miles per hour involves multiplying the speed of sound by 7. Given that the speed of sound is about 768 miles per hour, Mach 7 would be 7 * 768 = 5376 miles per hour. This speed is remarkably fast, and only a few vehicles have been able to achieve such velocities. For instance, some experimental aircraft and spacecraft have reached speeds of over 4,000 miles per hour, but achieving Mach 7 is a significant technological challenge.
Understanding the implications of such high speeds is crucial for the development of advanced aerospace technologies. The ability to travel at speeds of Mach 7 or higher could revolutionize transportation, enabling rapid travel across the globe and potentially even facilitating space exploration. However, achieving and sustaining such speeds poses significant engineering challenges, including managing the intense heat generated by friction with the atmosphere and developing materials that can withstand the stresses of high-speed flight.
Introduction to Mach Speed
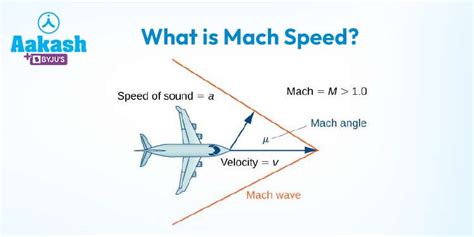
The concept of Mach speed is fundamental to aerodynamics and aerospace engineering. It is named after Ernst Mach, an Austrian physicist who made significant contributions to the study of supersonic flight. Mach speed is a measure of an object's speed relative to the speed of sound, which varies depending on the temperature and pressure of the surrounding air. At sea level, under standard conditions, the speed of sound is approximately 768 miles per hour.
Mach 1 represents the speed of sound, Mach 2 is twice the speed of sound, and so on. Each increment in Mach number represents a significant increase in speed and poses unique engineering challenges, particularly in terms of heat management and aerodynamic stability. For example, as an object approaches Mach 1, it encounters a barrier known as the sound barrier, where the airflow around the object becomes turbulent, generating shock waves and significant resistance.
Calculating Mach 7 in Miles Per Hour
To calculate Mach 7 in miles per hour, one must first know the speed of sound in miles per hour. As mentioned, this is approximately 768 miles per hour at sea level. Multiplying this speed by 7 gives the speed of Mach 7: 768 mph * 7 = 5376 mph. This calculation provides a straightforward conversion from Mach number to miles per hour, allowing for a better understanding of the incredible velocities involved in supersonic and hypersonic flight.
The implications of achieving Mach 7 are profound. Such speeds could enable rapid global travel, potentially reducing travel times between continents to under an hour. Moreover, the technological advancements required to achieve and sustain Mach 7 could have spin-off benefits in materials science, propulsion systems, and thermal management, contributing to breakthroughs in various fields beyond aerospace.
Applications of High-Speed Flight
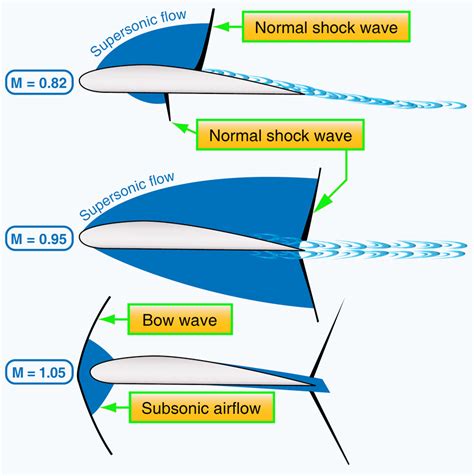
High-speed flight, particularly at velocities of Mach 7 and above, has several potential applications. In the military, such speeds could provide a significant advantage in terms of rapid deployment and response times. For civilian use, hypersonic aircraft could revolutionize air travel, making it possible to travel from one side of the globe to the other in a fraction of the time currently required.
Space exploration is another area where high-speed flight is crucial. Reaching orbit requires achieving speeds of at least Mach 25, and any significant interplanetary travel will demand even higher velocities. The development of technologies capable of sustaining high speeds through the atmosphere and into space is essential for advancing space exploration and potentially enabling human settlement of other planets.
Challenges of High-Speed Flight
The challenges associated with high-speed flight are numerous and complex. One of the primary concerns is the intense heat generated by friction with the atmosphere. As an object travels at high speeds, it encounters significant air resistance, which converts into heat. Managing this heat is crucial to prevent damage to the vehicle's structure and to maintain its stability and control.Another challenge is the development of materials that can withstand the stresses of high-speed flight. These materials must be incredibly strong, resistant to heat, and lightweight to minimize the overall weight of the vehicle. Advances in materials science, such as the development of new composites and alloys, are critical to overcoming these challenges.
Technological Advancements

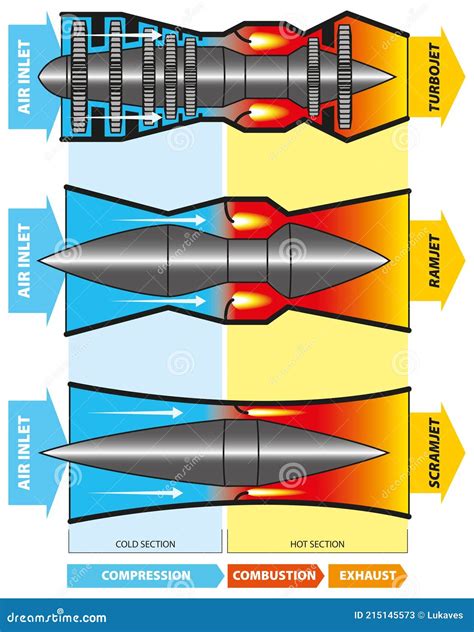
Several technological advancements are underway to address the challenges of high-speed flight. One area of focus is the development of more efficient propulsion systems, such as scramjets (supersonic combustion ramjets), which can operate at high speeds by using the atmosphere as the oxidizer. These engines have the potential to achieve hypersonic speeds but require significant technological advancements to become practical.
Another area of research is in materials science, where new materials are being developed that can withstand the extreme conditions of high-speed flight. These include advanced composites, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers, and new alloys that offer improved strength-to-weight ratios and thermal resistance.
Future Prospects
The future of high-speed flight looks promising, with several projects and initiatives aiming to achieve Mach 7 and beyond. Private companies, such as SpaceX and Blue Origin, are at the forefront of these efforts, driven by the potential for rapid global travel and space exploration. Governments are also investing in high-speed flight technologies, recognizing their strategic importance for both military and civilian applications.As technology continues to advance, the barriers to high-speed flight are gradually being overcome. While significant challenges remain, the potential benefits of achieving Mach 7 and higher speeds make the pursuit of hypersonic flight an exciting and worthwhile endeavor.
Gallery of High-Speed Flight
High-Speed Flight Image Gallery





Frequently Asked Questions
What is Mach 7 in miles per hour?
+Mach 7 is equivalent to 5376 miles per hour, calculated by multiplying the speed of sound (approximately 768 miles per hour at sea level) by 7.
What are the applications of high-speed flight?
+High-speed flight has several potential applications, including rapid global travel, space exploration, and military operations. Achieving Mach 7 could enable travel across the globe in under an hour and facilitate access to space.
What are the challenges of achieving Mach 7?
+The primary challenges include managing the intense heat generated by friction with the atmosphere and developing materials that can withstand the stresses of high-speed flight. Additionally, achieving efficient propulsion at such high speeds is a significant technological hurdle.
How is the development of high-speed flight technologies progressing?
+Several private companies and governments are investing in high-speed flight technologies, with notable advancements in materials science, propulsion systems, and aerodynamic design. While significant challenges remain, progress is being made towards achieving hypersonic flight capabilities.
What does the future hold for high-speed flight?
+The future of high-speed flight looks promising, with potential applications in rapid global travel, space exploration, and military operations. As technology continues to advance, the barriers to high-speed flight are gradually being overcome, paving the way for significant breakthroughs in the coming decades.
In conclusion, the pursuit of high-speed flight, particularly at velocities of Mach 7 and beyond, is an exciting and challenging field that holds the potential for revolutionary advancements in transportation and space exploration. As researchers and engineers continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, the future of flight looks brighter than ever. We invite you to share your thoughts on the potential applications and challenges of high-speed flight, and to explore the many resources available for those interested in learning more about this fascinating topic. Whether you're a seasoned aerospace professional or just starting to explore the wonders of flight, there's never been a more exciting time to be involved in this field.
