Intro
Discover the last age to join the military, including enlistment requirements, age limits, and eligibility criteria for various branches, such as Army, Navy, and Air Force, to determine if you can still serve.
The decision to join the military is a significant one, and it's essential to consider various factors, including age, before making this commitment. The maximum age limit to join the military varies depending on the country and the specific branch of the military. In the United States, for example, the maximum age limit to join the military is typically between 28 and 35 years old, depending on the branch and the individual's qualifications.
For those who are considering joining the military, it's crucial to understand the age requirements and the benefits of joining at different stages of life. Joining the military at a younger age can provide a sense of direction and purpose, as well as access to education and training opportunities. On the other hand, joining at an older age can bring a level of maturity and life experience that can be beneficial in a military career.
The military offers a range of benefits, including competitive pay, comprehensive healthcare, and education assistance. Additionally, military service can provide a sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps that is hard to find in civilian life. However, military service also requires a significant commitment, including the possibility of deployment and time away from family and friends.
Maximum Age Limit to Join the Military
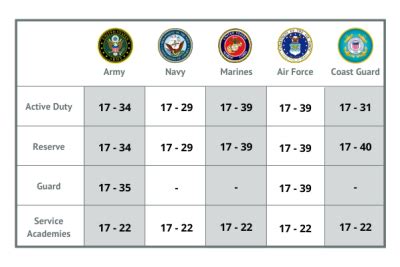
The maximum age limit to join the military varies depending on the branch and the individual's qualifications. In the United States, the maximum age limits are as follows:
- Army: 35 years old
- Navy: 34 years old
- Air Force: 39 years old
- Marine Corps: 28 years old
- Coast Guard: 27 years old
It's worth noting that these age limits can vary depending on the individual's qualifications and the needs of the military. For example, individuals with specialized skills or experience may be eligible to join the military at an older age.
Benefits of Joining the Military at a Younger Age
Joining the military at a younger age can provide a range of benefits, including: * Access to education and training opportunities * A sense of direction and purpose * Competitive pay and benefits * The opportunity to see the world and experience different cultures * A sense of camaraderie and esprit de corpsBenefits of Joining the Military at an Older Age

Joining the military at an older age can also provide a range of benefits, including:
- A level of maturity and life experience that can be beneficial in a military career
- The opportunity to bring specialized skills and experience to the military
- A sense of purpose and fulfillment
- The opportunity to serve as a role model and mentor to younger service members
- Access to education and training opportunities
Steps to Join the Military
The process of joining the military typically involves the following steps: 1. Meet the basic qualifications: This includes being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35 (depending on the branch), and meeting the physical and medical requirements. 2. Take the ASVAB test: The ASVAB test is used to determine an individual's qualifications for different military careers. 3. Choose a career path: The military offers a range of career paths, from combat roles to support roles. 4. Enlist or receive a commission: Individuals can enlist in the military or receive a commission as an officer. 5. Complete basic training: All new service members are required to complete basic training, which provides an introduction to military life and prepares individuals for their role in the military.Military Careers

The military offers a range of career paths, from combat roles to support roles. Some examples of military careers include:
- Infantry: The infantry is the backbone of the military, and is responsible for engaging the enemy on the ground.
- Aviation: The aviation career path includes roles such as pilots, mechanics, and air traffic controllers.
- Healthcare: The military offers a range of healthcare careers, from doctors and nurses to medical administrators.
- Intelligence: The intelligence career path includes roles such as analysts, linguists, and cryptologists.
- Cybersecurity: The cybersecurity career path includes roles such as network administrators, cybersecurity specialists, and cryptologists.
Military Ranks
The military uses a system of ranks to denote an individual's level of experience and responsibility. The ranks are as follows: * Enlisted ranks: These include ranks such as private, corporal, and sergeant. * Warrant officer ranks: These include ranks such as warrant officer 1 and chief warrant officer 4. * Officer ranks: These include ranks such as second lieutenant, captain, and colonel.Military Education and Training

The military offers a range of education and training opportunities, from basic training to advanced degree programs. Some examples of military education and training programs include:
- Basic training: This provides an introduction to military life and prepares individuals for their role in the military.
- Advanced individual training: This provides specialized training in a specific career path.
- Officer candidate school: This provides training for individuals who want to become officers.
- Degree programs: The military offers a range of degree programs, from associate's degrees to doctoral degrees.
Military Pay and Benefits
The military offers a range of pay and benefits, including: * Competitive pay: The military offers competitive pay, based on an individual's rank and experience. * Comprehensive healthcare: The military offers comprehensive healthcare, including medical, dental, and vision coverage. * Education assistance: The military offers education assistance, including the GI Bill and tuition assistance. * Housing allowance: The military offers a housing allowance, to help service members pay for housing.Military Life

Military life can be challenging, but it also offers a range of benefits and opportunities. Some examples of military life include:
- Deployment: Service members may be deployed to different parts of the world, to support military operations or humanitarian missions.
- Training exercises: The military conducts regular training exercises, to prepare service members for different scenarios.
- Community service: The military offers a range of community service opportunities, from volunteer work to disaster relief.
- Esprit de corps: The military offers a sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps, that is hard to find in civilian life.
Military History
The military has a rich and varied history, from the Revolutionary War to the present day. Some examples of military history include: * The Revolutionary War: This was the first major conflict fought by the United States, and marked the beginning of the country's military history. * The Civil War: This was a brutal and devastating conflict, that marked a turning point in the country's history. * World War I: This was a global conflict, that marked the United States' emergence as a major military power. * World War II: This was a global conflict, that marked the United States' emergence as a superpower. * The Cold War: This was a period of tension and competition, between the United States and the Soviet Union.Military Technology

The military uses a range of technologies, from weapons systems to communication networks. Some examples of military technology include:
- Drones: These are unmanned aerial vehicles, used for reconnaissance and combat missions.
- Cybersecurity: This is the practice of protecting computer systems and networks, from cyber threats.
- Artificial intelligence: This is the use of computer systems, to perform tasks that would normally require human intelligence.
- Robotics: This is the use of robots, to perform tasks that would normally require human labor.
Military Strategy
The military uses a range of strategies, from conventional warfare to asymmetric warfare. Some examples of military strategy include: * Conventional warfare: This is the use of traditional military tactics, such as infantry and armor. * Asymmetric warfare: This is the use of unconventional tactics, such as guerrilla warfare and terrorism. * Counterinsurgency: This is the use of military tactics, to counter an insurgency or rebellion. * Deterrence: This is the use of military power, to deter an enemy from attacking.Last Age to Join Military Image Gallery










What is the maximum age limit to join the military?
+The maximum age limit to join the military varies depending on the branch and the individual's qualifications. In the United States, the maximum age limits are as follows: Army: 35 years old, Navy: 34 years old, Air Force: 39 years old, Marine Corps: 28 years old, Coast Guard: 27 years old.
What are the benefits of joining the military at a younger age?
+Joining the military at a younger age can provide a range of benefits, including access to education and training opportunities, a sense of direction and purpose, competitive pay and benefits, and the opportunity to see the world and experience different cultures.
What are the steps to join the military?
+The steps to join the military include meeting the basic qualifications, taking the ASVAB test, choosing a career path, enlisting or receiving a commission, and completing basic training.
What are the different types of military careers?
+The military offers a range of career paths, from combat roles to support roles. Some examples of military careers include infantry, aviation, healthcare, intelligence, and cybersecurity.
What are the benefits of joining the military at an older age?
+Joining the military at an older age can provide a range of benefits, including a level of maturity and life experience that can be beneficial in a military career, the opportunity to bring specialized skills and experience to the military, and access to education and training opportunities.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the last age to join the military. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about military careers, please don't hesitate to comment or share this article with others. Additionally, if you're considering joining the military, we encourage you to research and explore the different branches and career paths to find the best fit for you. Remember, joining the military is a significant commitment, but it can also provide a range of benefits and opportunities that can last a lifetime.
