Intro
Discover US Army JROTC ranks, including cadet ranks, officer ranks, and insignia. Learn about Junior ROTC rank structure, promotions, and leadership roles.
The United States Army Junior Reserve Officers' Training Corps (JROTC) is a program designed to teach high school students leadership skills, citizenship, and the importance of community service. The JROTC program is led by retired Army officers and non-commissioned officers who serve as instructors. As students progress through the program, they are eligible to receive promotions in rank, which reflect their growing leadership skills and responsibilities. Understanding the rank structure of the US Army JROTC is essential for both students and parents who are interested in the program.
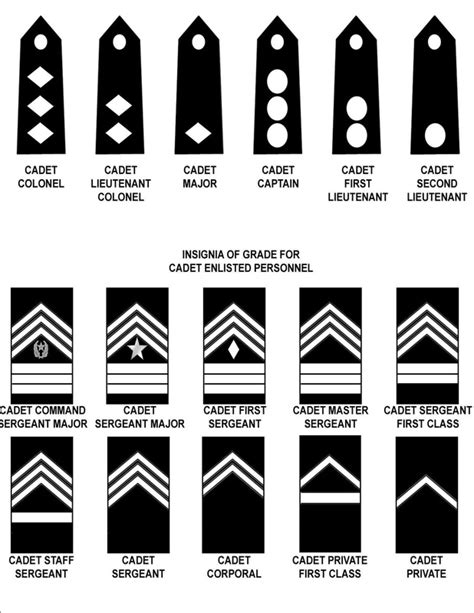
The rank structure of the US Army JROTC is modeled after the rank structure of the US Army, with some modifications to reflect the cadet status of the students. The ranks are divided into three main categories: cadet private through cadet sergeant, cadet staff sergeant through cadet sergeant major, and cadet second lieutenant through cadet colonel. Each rank has its own set of responsibilities and requirements, and students must meet specific criteria to be eligible for promotion.
As students enter the JROTC program, they typically start at the rank of cadet private and work their way up through the ranks as they complete each year of the program. The ranks of cadet private through cadet sergeant are considered to be the lower ranks, and students in these ranks are still learning the basics of leadership and the JROTC program. As students progress to the higher ranks, they take on more responsibilities and are expected to demonstrate greater leadership skills.
Introduction to US Army JROTC Ranks
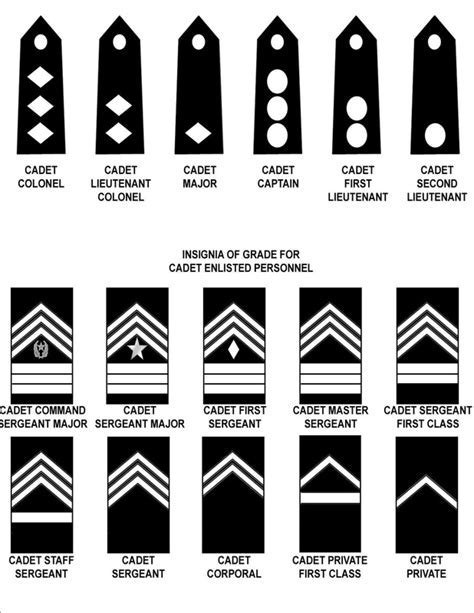
The JROTC program is designed to be a four-year program, with each year building on the previous one. The first year, known as the Leadership Education and Training (LET) 1 year, focuses on introducing students to the basics of leadership and the JROTC program. The second year, LET 2, builds on the skills learned in the first year and introduces students to more advanced leadership concepts. The third year, LET 3, focuses on developing students' leadership skills and preparing them for leadership positions within the JROTC program. The fourth year, LET 4, is the final year of the program, and students in this year are expected to demonstrate advanced leadership skills and take on significant responsibilities within the program.
Lower Ranks of US Army JROTC
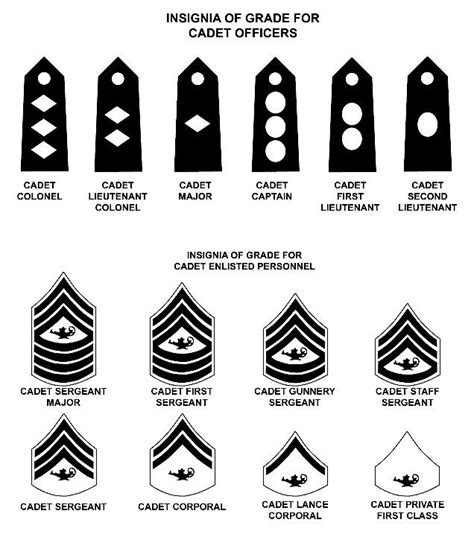
The lower ranks of the US Army JROTC, from cadet private through cadet sergeant, are the foundation of the program. These ranks are where students learn the basics of leadership and the JROTC program. The ranks are as follows:
- Cadet Private (PVT): This is the entry-level rank for all JROTC cadets.
- Cadet Private First Class (PFC): To be eligible for promotion to PFC, cadets must have completed the first semester of the LET 1 year and have demonstrated a basic understanding of leadership concepts.
- Cadet Specialist/Corporal (CPL): To be eligible for promotion to CPL, cadets must have completed the LET 1 year and have demonstrated a good understanding of leadership concepts.
- Cadet Sergeant (SGT): To be eligible for promotion to SGT, cadets must have completed the LET 2 year and have demonstrated a strong understanding of leadership concepts.
Higher Ranks of US Army JROTC
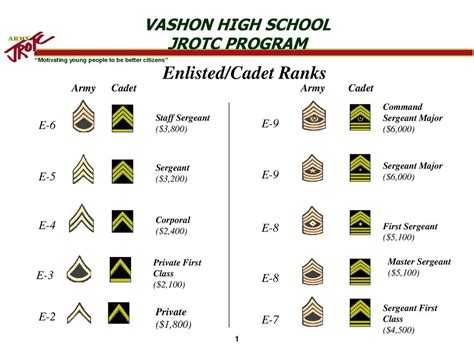
The higher ranks of the US Army JROTC, from cadet staff sergeant through cadet colonel, are the leadership ranks of the program. These ranks are where students take on significant responsibilities and demonstrate advanced leadership skills. The ranks are as follows:
- Cadet Staff Sergeant (SSG): To be eligible for promotion to SSG, cadets must have completed the LET 2 year and have demonstrated strong leadership skills.
- Cadet Sergeant First Class (SFC): To be eligible for promotion to SFC, cadets must have completed the LET 3 year and have demonstrated advanced leadership skills.
- Cadet Master Sergeant (MSG): To be eligible for promotion to MSG, cadets must have completed the LET 3 year and have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills.
- Cadet First Sergeant (1SG): To be eligible for promotion to 1SG, cadets must have completed the LET 3 year and have demonstrated outstanding leadership skills.
- Cadet Sergeant Major (SGM): To be eligible for promotion to SGM, cadets must have completed the LET 4 year and have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills.
Officer Ranks of US Army JROTC
The officer ranks of the US Army JROTC, from cadet second lieutenant through cadet colonel, are the highest ranks in the program. These ranks are where students demonstrate exceptional leadership skills and take on significant responsibilities within the program. The ranks are as follows:
- Cadet Second Lieutenant (2LT): To be eligible for promotion to 2LT, cadets must have completed the LET 3 year and have demonstrated strong leadership skills.
- Cadet First Lieutenant (1LT): To be eligible for promotion to 1LT, cadets must have completed the LET 4 year and have demonstrated advanced leadership skills.
- Cadet Captain (CPT): To be eligible for promotion to CPT, cadets must have completed the LET 4 year and have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills.
- Cadet Major (MAJ): To be eligible for promotion to MAJ, cadets must have completed the LET 4 year and have demonstrated outstanding leadership skills.
- Cadet Lieutenant Colonel (LTC): To be eligible for promotion to LTC, cadets must have completed the LET 4 year and have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills.
- Cadet Colonel (COL): To be eligible for promotion to COL, cadets must have completed the LET 4 year and have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills.
Benefits of US Army JROTC Ranks
The US Army JROTC rank structure provides several benefits to students, including: * Leadership skills: The JROTC program teaches students leadership skills, which are essential for success in any career. * Discipline: The JROTC program teaches students discipline, which is essential for achieving goals and overcoming obstacles. * Citizenship: The JROTC program teaches students the importance of citizenship and community service. * College scholarships: Students who participate in the JROTC program may be eligible for college scholarships.Gallery of US Army JROTC Ranks
US Army JROTC Ranks Image Gallery










Frequently Asked Questions
What is the US Army JROTC program?
+The US Army JROTC program is a program designed to teach high school students leadership skills, citizenship, and the importance of community service.
What are the benefits of participating in the US Army JROTC program?
+The benefits of participating in the US Army JROTC program include leadership skills, discipline, citizenship, and college scholarships.
How do students get promoted in the US Army JROTC program?
+Students get promoted in the US Army JROTC program by meeting specific criteria, such as completing each year of the program and demonstrating leadership skills.
What is the highest rank in the US Army JROTC program?
+The highest rank in the US Army JROTC program is cadet colonel.
Can students who participate in the US Army JROTC program join the military?
+Yes, students who participate in the US Army JROTC program can join the military, and they may be eligible for advanced rank and other benefits.
In conclusion, the US Army JROTC rank structure is an essential part of the JROTC program, providing students with a sense of accomplishment and motivation to continue developing their leadership skills. By understanding the rank structure and the benefits of participating in the JROTC program, students and parents can make informed decisions about whether the program is right for them. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the US Army JROTC program in the comments below. If you have any questions or would like to learn more about the program, please don't hesitate to reach out.
