Intro
Discover 5 ways to join the army, including enlistment, officer programs, and special forces recruitment, to start your military career and serve your country with honor and patriotism.
The prospect of joining the army is a significant decision that can shape one's career and personal life. For those who are drawn to the idea of serving their country, being part of a disciplined and structured environment, and developing valuable skills, the army offers a challenging yet rewarding path. The process of joining the army, however, can be complex and varies significantly from one country to another. Here, we'll explore five ways to join the army, focusing on the general principles that apply across different countries, with an emphasis on the United States as a primary example.
Joining the army requires a deep understanding of the enlistment process, the various roles available, and the qualifications needed. It's a journey that demands dedication, resilience, and a strong desire to serve. Whether one is seeking a career as an officer, enlisted personnel, or looking to join through specialized programs, each path offers unique opportunities for growth and service.
For individuals considering a career in the military, it's essential to research the specific requirements and processes of their country's army. The army offers a wide range of career fields, from combat and engineering to healthcare and communications, ensuring that there are opportunities for individuals with diverse skills and interests.
Understanding the Enlistment Process
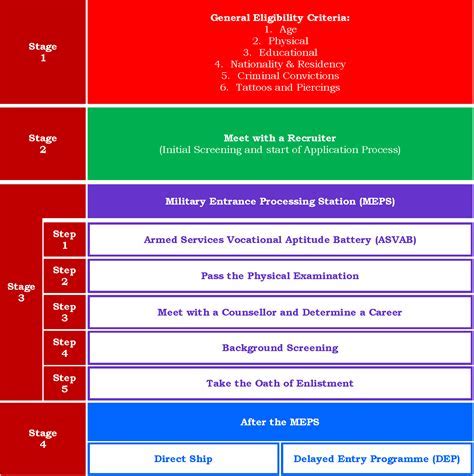
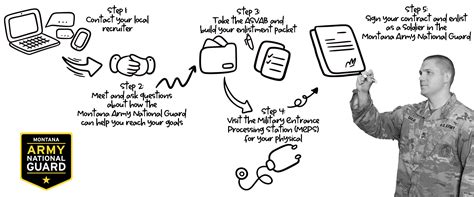
The enlistment process typically begins with meeting the basic eligibility requirements, which include age, citizenship, education, and physical fitness standards. In the United States, for example, one must be between the ages of 17 and 35 (with some exceptions for older individuals), a U.S. citizen, and have a high school diploma. The next step involves taking the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test, which helps determine one's career field or Military Occupational Specialty (MOS).
Meeting the Basic Requirements
To be eligible for enlistment, individuals must meet specific criteria. These include: - Age: Typically between 17 and 35 years old. - Citizenship: Must be a citizen of the country or meet specific residency requirements. - Education: A high school diploma or equivalent is often required. - Physical Fitness: Meeting the physical standards of the army, which includes passing a physical fitness test.Path 1: Enlisting as Active Duty
Enlisting as active duty is one of the most common ways to join the army. This path involves serving full-time in the army, typically for a period of 2-6 years, depending on the terms of enlistment. Active duty personnel can be deployed at any time and are required to move frequently as part of their service.
Benefits of Active Duty
Active duty service offers numerous benefits, including: - Comprehensive healthcare coverage. - Education assistance, such as the GI Bill. - Access to on-base facilities, including gyms, shopping, and recreational activities. - Opportunities for career advancement and professional development.Path 2: Joining the Army Reserve

The Army Reserve is a part-time service commitment. Members typically serve one weekend a month and two weeks a year, allowing them to pursue civilian careers and education while still serving their country. This path is ideal for those who wish to serve but also need to maintain civilian commitments.
Benefits of the Army Reserve
The Army Reserve offers benefits such as: - Part-time service commitment, allowing for civilian career pursuit. - Education assistance and retirement benefits. - Opportunities for advancement and professional development. - Comprehensive healthcare coverage during service periods.Path 3: Officer Candidate School (OCS)

For those interested in becoming an officer, Officer Candidate School (OCS) is a pathway. OCS is a training program that transforms civilians and enlisted service members into officers. It requires a bachelor's degree and involves intensive training to prepare candidates for leadership roles within the army.
Requirements for OCS
To be eligible for OCS, one must: - Hold a bachelor's degree from an accredited institution. - Meet physical fitness standards. - Pass the ASVAB test. - Receive a commission as an officer upon graduation from OCS.Path 4: Specialized Programs

The army offers various specialized programs for individuals with specific skills or interests. These include programs for healthcare professionals, lawyers, chaplains, and cyber security specialists, among others. These programs allow individuals to serve in their area of expertise while contributing to the army's mission.
Examples of Specialized Programs
- Medical Corps: For healthcare professionals. - Judge Advocate General's Corps (JAG): For lawyers. - Chaplain Corps: For religious leaders. - Cyber Corps: For cyber security and information technology specialists.Path 5: Army National Guard

The Army National Guard is a unique component of the army that serves both state and federal roles. Members typically serve part-time, with one weekend of training per month and a two-week annual training period. The National Guard can be called upon to support domestic emergencies and international missions.
Benefits of the Army National Guard
Serving in the Army National Guard offers benefits such as: - Part-time service commitment. - Education assistance and retirement benefits. - Opportunities for career advancement. - The ability to serve and make a difference in one's home state.Army Enlistment Image Gallery









What are the basic requirements to join the army?
+The basic requirements include meeting age, citizenship, education, and physical fitness standards. The specifics can vary by country but generally include being between certain ages, holding a high school diploma, and passing physical and medical exams.
How long does it take to join the army?
+The time it takes to join the army can vary depending on the country, the role one is applying for, and the individual's circumstances. Generally, the process from initial application to beginning basic training can take several months.
What are the different ways to join the army?
+There are several ways to join the army, including enlisting as active duty, joining the Army Reserve, attending Officer Candidate School, participating in specialized programs, and serving in the Army National Guard. Each path has its unique requirements and benefits.
For those considering joining the army, it's crucial to explore each path thoroughly, understanding the commitments, benefits, and opportunities each offers. Whether one chooses to serve full-time, part-time, or through specialized roles, the experience can be profoundly rewarding, offering personal growth, career development, and the chance to serve something greater than oneself. As you embark on this journey, remember to stay informed, ask questions, and seek guidance from military recruiters and veterans who can provide valuable insights into the process and what to expect. Your path to serving in the army begins with a single step, and with dedication and perseverance, you can achieve your goal and embark on a fulfilling career of service and distinction.
