Intro
Discover 5 ways to join the military, including enlistment, officer programs, and special forces. Explore military careers, service branches, and recruitment processes to start your journey.
The decision to join the military is a significant one, offering a unique blend of challenge, adventure, and service to one's country. For many, it represents a path to personal growth, education, and career development, set against the backdrop of contributing to national defense and global peacekeeping efforts. The military provides a structured environment that fosters discipline, camaraderie, and leadership skills, making it an attractive option for those seeking more than just a conventional career. Whether motivated by patriotism, the desire for advanced training, or the pursuit of educational benefits, individuals considering military service have several paths to explore.
Joining the military can be a life-changing decision, offering a wide range of benefits including education assistance, career training, and the opportunity to serve in various roles across different branches of the military. Each branch, including the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard, offers unique experiences and opportunities for advancement. The process of joining involves several steps, from initial recruitment to basic training, and requires a commitment to service that can last from a few years to an entire career.
For those interested in military service, understanding the various ways to join is crucial. This includes enlisting directly, attending a military academy, joining the Reserve or National Guard, participating in ROTC programs, or even pursuing a career as an officer through Officer Candidate School (OCS). Each method has its own set of requirements, benefits, and commitments, allowing individuals to choose the path that best aligns with their goals, skills, and preferences.
Understanding the Military Branches
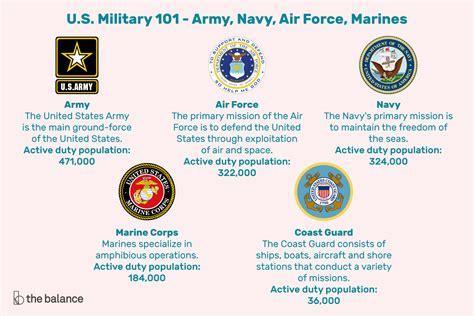
The United States military is composed of five branches: the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard. Each branch has its own specific role and responsibilities, from land-based operations (Army) and sea-based operations (Navy) to air and space operations (Air Force), amphibious and expeditionary operations (Marine Corps), and maritime law enforcement and search and rescue (Coast Guard). Understanding the missions and cultures of these branches can help prospective recruits decide which one aligns best with their interests and skills.
Army: The Largest Branch
The Army is the largest branch of the military and is responsible for land-based military operations. It offers a wide range of Military Occupational Specialties (MOS), from infantry and armor to engineering and medical specialties. The Army provides extensive training and education opportunities, both during and after service, making it a popular choice for those seeking career advancement and personal development.Paths to Joining the Military

There are several paths to joining the military, each with its own requirements and benefits. These include enlisting, attending a military academy, joining the Reserve or National Guard, participating in ROTC programs, and attending Officer Candidate School (OCS).
Enlisting in the Military
Enlisting is the most common way to join the military. It involves signing an enlistment contract, which specifies the length of service and the Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) or job. The enlistment process includes taking the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test, passing a physical fitness test, and completing basic training.Military Academies

Attending a military academy is another route to joining the military. The United States Military Academy (West Point), the United States Naval Academy, the United States Air Force Academy, the United States Coast Guard Academy, and the United States Merchant Marine Academy offer four-year degrees and a commission as an officer upon graduation. Admission to these academies is highly competitive and requires a nomination from a member of Congress, the Vice President, or the President.
ROTC Programs
The Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC) provides another path to becoming an officer. ROTC programs are offered at many colleges and universities and allow students to pursue a degree while also receiving military training. Upon graduation, ROTC cadets are commissioned as officers. ROTC scholarships are available and can cover the full cost of tuition, making it an attractive option for students.Reserve and National Guard

Joining the Reserve or National Guard allows individuals to serve part-time and pursue civilian careers. Members typically serve one weekend a month and two weeks a year, with the option to be called to active duty in times of need. The Reserve and National Guard offer many of the same benefits as active duty service, including education assistance and career training, but with the flexibility to maintain a civilian life.
Officer Candidate School (OCS)
Officer Candidate School (OCS) is a training program for individuals who wish to become officers but do not have a degree from a military academy or an ROTC program. OCS is a challenging course that teaches leadership and military skills, culminating in a commission as an officer. It is an option for those who have a bachelor's degree and are looking for a career change or advancement.Benefits of Military Service
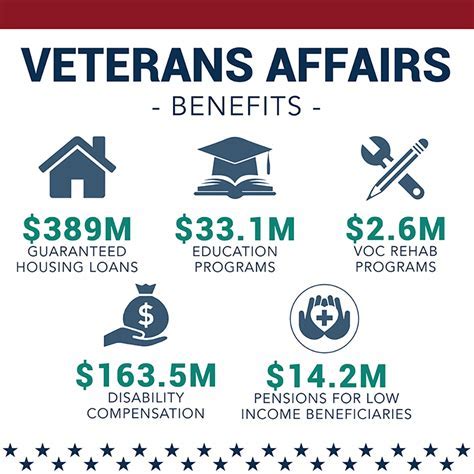
Military service offers a wide range of benefits, including education assistance through the GI Bill, which can cover the full cost of tuition, housing, and other expenses. The military also provides comprehensive healthcare, housing allowances, and food stipends. Additionally, service members have access to on-base facilities such as gyms, libraries, and shopping centers, enhancing their quality of life.
Career Opportunities and Advancement
The military offers numerous career paths and opportunities for advancement. With over 150 MOS, individuals can find roles that match their skills and interests, from technical fields like cybersecurity and engineering to medical and administrative positions. The military also provides extensive training and education programs, allowing service members to acquire new skills and certifications, which are valuable both in and out of the military.Challenges and Considerations
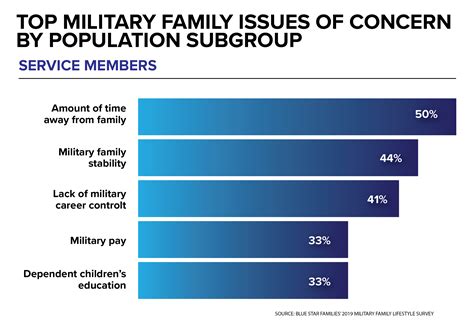
While military service offers many benefits, it also comes with significant challenges and considerations. Service members may be deployed to combat zones or other locations around the world, spending extended periods away from family and friends. The military lifestyle requires adaptability, resilience, and a commitment to service that can be demanding. Additionally, the transition back to civilian life after service can be challenging, requiring support and resources to navigate successfully.
Support for Veterans
To support the transition back to civilian life, the military and various organizations offer a range of resources for veterans. These include assistance with finding employment, accessing healthcare and education benefits, and coping with the psychological and physical challenges of military service. Support groups and counseling services are also available to help veterans and their families adjust to life after service.Gallery of Military Service
Military Service Image Gallery










Frequently Asked Questions
What are the basic requirements to join the military?
+To join the military, one must be a U.S. citizen, be between the ages of 17 and 35 (with some exceptions), have a high school diploma, and meet certain physical and moral standards.
How long does basic training last?
+Basic training, also known as boot camp, typically lasts between 7 to 12 weeks, depending on the branch of the military.
What education benefits does the military offer?
+The military offers the GI Bill, which can cover the full cost of tuition, housing, and other expenses for higher education, as well as other education assistance programs.
Can I choose my job in the military?
+Yes, to some extent. The military uses the ASVAB test to determine aptitude for various jobs. While there is some flexibility, job assignments are based on the needs of the military and the individual's skills and test scores.
How do I apply to a military academy?
+Application to a military academy requires a nomination from a member of Congress, the Vice President, or the President, along with meeting strict academic, physical, and medical standards.
In conclusion, joining the military is a profound decision that can lead to personal growth, career advancement, and a sense of service and fulfillment. With various paths to join, including enlisting, attending a military academy, joining the Reserve or National Guard, participating in ROTC programs, and attending Officer Candidate School, individuals have the opportunity to choose the route that best fits their goals and aspirations. As one considers this significant commitment, understanding the benefits, challenges, and requirements of military service is essential. By exploring these aspects and reaching out to military recruiters and veterans, prospective service members can make an informed decision about their future and the role they wish to play in defending and serving their country. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about military service, and to explore the many resources available for those considering this noble path.
