Intro
Discover Army Infantry Units, including light infantry, airborne, and mechanized units, exploring their roles, tactics, and equipment in modern warfare and combat operations.
The backbone of any military force, army infantry units are the ground troops that engage in combat, securing and holding territory, and conducting a wide range of operations. These units are the most visible and often the most critical component of a military's overall structure. The importance of infantry units cannot be overstated, as they are the ones who directly interact with the enemy, gather intelligence, and execute the tactical plans devised by their commanders.
Infantry units have been the cornerstone of military forces throughout history, from ancient times to the present day. Their role has evolved over the centuries, adapting to changes in technology, tactics, and the nature of warfare itself. Despite these changes, the fundamental mission of infantry units remains the same: to close with and defeat the enemy, using a combination of firepower, maneuver, and shock action. The bravery, sacrifice, and camaraderie of infantry soldiers have become legendary, inspiring countless stories, songs, and works of art.
The composition and organization of infantry units vary depending on the country, the type of terrain, and the specific mission. Generally, infantry units are divided into smaller sub-units, such as squads, platoons, companies, and battalions. Each of these sub-units has its own unique role and responsibilities, working together to achieve the overall objectives of the larger unit. Infantry soldiers are trained to be versatile and adaptable, able to operate in a wide range of environments, from urban jungles to deserts, and from mountains to forests.
Types of Infantry Units
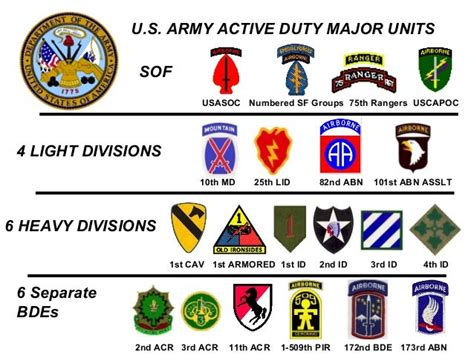
There are several types of infantry units, each with its own specialized role and capabilities. These include light infantry, mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, and special forces. Light infantry units are designed to be highly mobile and flexible, often operating in remote or hard-to-reach areas. Mechanized infantry units, on the other hand, are equipped with armored vehicles, such as tanks and infantry fighting vehicles, which provide them with increased firepower and protection. Airborne infantry units are trained to conduct parachute assaults, inserting themselves behind enemy lines to secure key objectives. Special forces units, such as ranger and special operations units, are elite troops that conduct unconventional warfare, counterterrorism, and direct action missions.
Light Infantry Units
Light infantry units are the most common type of infantry unit, and are often the first to be deployed in a combat zone. These units are designed to be highly mobile and flexible, able to operate in a wide range of environments and terrain. Light infantry soldiers are trained to be self-sufficient, able to survive and fight for extended periods without external support. They are equipped with lightweight weapons and equipment, such as rifles, machine guns, and mortars, which allow them to move quickly and easily.Mechanized Infantry Units
Mechanized infantry units are equipped with armored vehicles, such as tanks and infantry fighting vehicles, which provide them with increased firepower and protection. These units are designed to operate in conjunction with armor units, providing close support and security for the tanks and other armored vehicles. Mechanized infantry soldiers are trained to work closely with the armor crews, using their vehicles to transport them to the battlefield and provide covering fire during assaults.Infantry Unit Operations

Infantry units conduct a wide range of operations, from offensive and defensive battles to patrols and raids. These operations are designed to achieve specific tactical objectives, such as securing key terrain, gathering intelligence, or disrupting enemy supply lines. Infantry soldiers are trained to be highly adaptable, able to adjust their tactics and techniques to suit the changing circumstances of the battlefield.
Some common infantry unit operations include:
- Patrols: These are reconnaissance missions designed to gather information about the enemy and the terrain.
- Raids: These are surprise attacks on enemy positions, designed to disrupt their operations and destroy key assets.
- Ambushes: These are surprise attacks on enemy units, designed to inflict maximum casualties and disrupt their movement.
- Assaults: These are direct attacks on enemy positions, designed to capture key terrain and defeat the enemy.
Patrolling
Patrolling is a critical component of infantry unit operations, as it allows soldiers to gather information about the enemy and the terrain. Patrols can be conducted on foot or in vehicles, and can range in size from a few soldiers to an entire platoon. The objectives of a patrol can vary, but common tasks include: * Gathering intelligence about the enemy * Conducting reconnaissance of key terrain * Securing key routes and infrastructure * Providing security for other unitsRaids and Ambushes
Raids and ambushes are types of surprise attacks that infantry units use to disrupt enemy operations and inflict casualties. These operations are designed to be quick and decisive, using speed and surprise to achieve their objectives. Raids and ambushes can be conducted against a wide range of targets, including enemy positions, supply lines, and communication networks.Infantry Unit Tactics

Infantry unit tactics are the techniques and procedures used by soldiers to achieve their objectives on the battlefield. These tactics are designed to be flexible and adaptable, allowing soldiers to adjust their approach to suit the changing circumstances of the battle. Some common infantry unit tactics include:
- Fire and maneuver: This involves using firepower to suppress the enemy, while maneuvering to outflank and defeat them.
- Cover and concealment: This involves using terrain and other features to protect oneself from enemy fire, while still being able to observe and engage the enemy.
- Suppression: This involves using firepower to suppress the enemy, making it difficult for them to return fire or maneuver.
Fire and Maneuver
Fire and maneuver is a fundamental infantry tactic that involves using firepower to suppress the enemy, while maneuvering to outflank and defeat them. This tactic is designed to be flexible and adaptable, allowing soldiers to adjust their approach to suit the changing circumstances of the battle. Fire and maneuver involves several key components, including: * Suppressing the enemy with firepower * Maneuvering to outflank and defeat the enemy * Using cover and concealment to protect oneself * Coordinating with other units to achieve a common objectiveCover and Concealment
Cover and concealment are critical components of infantry tactics, as they allow soldiers to protect themselves from enemy fire while still being able to observe and engage the enemy. Cover refers to features that provide protection from enemy fire, such as buildings, walls, and trenches. Concealment refers to features that hide soldiers from enemy observation, such as vegetation, fog, and smoke.Infantry Unit Equipment

Infantry units use a wide range of equipment to conduct their operations, from small arms and machine guns to mortars and anti-tank missiles. This equipment is designed to be portable and versatile, allowing soldiers to adapt to changing circumstances on the battlefield. Some common types of infantry unit equipment include:
- Small arms: These include rifles, pistols, and machine guns, which are used to engage enemy personnel at close range.
- Mortars: These are indirect fire weapons that are used to attack enemy positions and fortifications.
- Anti-tank missiles: These are guided missiles that are used to attack and destroy enemy tanks and armored vehicles.
- Body armor: This includes helmets, vests, and other protective gear that is used to protect soldiers from enemy fire.
Small Arms
Small arms are the primary weapons used by infantry soldiers, and include rifles, pistols, and machine guns. These weapons are designed to be portable and versatile, allowing soldiers to engage enemy personnel at close range. Small arms are typically used in conjunction with other types of equipment, such as mortars and anti-tank missiles, to achieve a common objective.Mortars
Mortars are indirect fire weapons that are used to attack enemy positions and fortifications. These weapons are designed to be portable and versatile, allowing soldiers to adapt to changing circumstances on the battlefield. Mortars are typically used in conjunction with other types of equipment, such as small arms and anti-tank missiles, to achieve a common objective.Gallery of Infantry Units
Infantry Units Image Gallery







Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of infantry units in modern warfare?
+Infantry units play a critical role in modern warfare, as they are responsible for securing and holding territory, conducting patrols and raids, and engaging enemy forces in close combat.
What types of infantry units are there?
+There are several types of infantry units, including light infantry, mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, and special forces.
What equipment do infantry units use?
+Infantry units use a wide range of equipment, including small arms, mortars, anti-tank missiles, and body armor.
How are infantry units organized?
+Infantry units are typically organized into smaller sub-units, such as squads, platoons, companies, and battalions.
What is the history of infantry units?
+Infantry units have a long and storied history, dating back to ancient times. Over the centuries, infantry units have evolved to adapt to changing technologies and tactics.
In conclusion, army infantry units are the backbone of any military force, playing a critical role in securing and holding territory, conducting patrols and raids, and engaging enemy forces in close combat. These units are highly adaptable and versatile, able to operate in a wide range of environments and terrain. By understanding the role, organization, and equipment of infantry units, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the bravery and sacrifice of the soldiers who serve in these units. Whether you are a military historian, a strategist, or simply someone interested in learning more about the military, the topic of infantry units is sure to be fascinating and informative. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about infantry units in the comments below, and to explore the many resources available online to learn more about this critical component of modern warfare.
