Intro
Discover the 7 Infantry Roles, including scout, sniper, and rifleman, and learn about combat, tactics, and military operations, in this informative guide to infantry specialties and career paths.
The infantry is the backbone of any military force, responsible for engaging the enemy on the ground and securing key objectives. Over time, the role of the infantry has evolved to include a wide range of specialized tasks and responsibilities. In this article, we will explore seven key infantry roles that are crucial to the success of modern military operations.
Infantry units are the most versatile and adaptable forces on the battlefield, capable of operating in a variety of environments and conditions. From urban warfare to jungle combat, infantry soldiers must be able to think on their feet and respond to changing circumstances. The seven infantry roles we will discuss are: riflemen, grenadiers, machine gunners, mortar men, scouts, snipers, and combat medics. Each of these roles requires unique skills and training, and together they form a cohesive and effective fighting force.
The importance of infantry roles cannot be overstated. In modern warfare, the ability to engage and defeat enemy forces on the ground is critical to achieving strategic objectives. Infantry units are often the first to enter combat, and their success or failure can have a significant impact on the outcome of a battle or campaign. By understanding the different infantry roles and how they contribute to the overall mission, military leaders can make informed decisions about how to deploy their forces and achieve their objectives.
Introduction to Infantry Roles
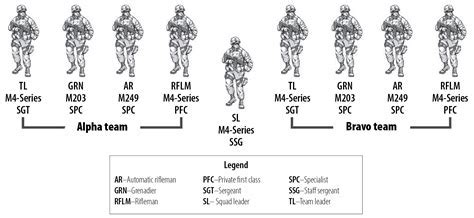
Combat Infantry Roles
Combat infantry roles are the most visible and well-known aspects of infantry operations. These roles include tasks such as engaging enemy forces, securing key objectives, and conducting reconnaissance. Combat infantry soldiers must be highly trained and equipped to operate in a variety of environments and conditions, from urban warfare to jungle combat. They must also be able to think on their feet and respond to changing circumstances, making split-second decisions that can mean the difference between life and death.Riflemen

Grenadiers
Grenadiers are specialized infantry soldiers who are trained to use explosives and other demolitions equipment. They are responsible for breaching enemy defenses, destroying key infrastructure, and conducting other high-risk missions. Grenadiers must be highly trained and equipped to operate in a variety of environments and conditions, from urban warfare to jungle combat. They must also be able to think on their feet and respond to changing circumstances, making split-second decisions that can mean the difference between life and death.Machine Gunners

Mortar Men
Mortar men are specialized infantry soldiers who are trained to operate mortars and other indirect fire systems. They are responsible for providing supporting fire, targeting enemy positions, and conducting other high-angle fire missions. Mortar men must be highly trained and equipped to operate in a variety of environments and conditions, from urban warfare to jungle combat. They must also be able to think on their feet and respond to changing circumstances, making split-second decisions that can mean the difference between life and death.Scouts

Snipers
Snipers are specialized infantry soldiers who are trained to conduct precision fire and eliminate high-value targets. They are responsible for targeting enemy commanders, destroying key infrastructure, and conducting other high-risk missions. Snipers must be highly trained and equipped to operate in a variety of environments and conditions, from urban warfare to jungle combat. They must also be able to think on their feet and respond to changing circumstances, making split-second decisions that can mean the difference between life and death.Combat Medics

Support Infantry Roles
Support infantry roles are critical to the success of combat operations, providing essential services and capabilities that enable infantry units to operate effectively. These roles include tasks such as providing medical care, maintaining equipment, and coordinating logistics. Support infantry soldiers must be highly trained and equipped to operate in a variety of environments and conditions, from urban warfare to jungle combat. They must also be able to think on their feet and respond to changing circumstances, making split-second decisions that can mean the difference between life and death.Logistics and Supply

Communication and Command
Communication and command personnel are responsible for coordinating and controlling infantry operations, including transmitting orders, receiving reports, and maintaining situational awareness. They must be highly skilled in communication protocols and procedures, as well as in tactics and techniques such as radio operation, messaging, and network management. Communication and command personnel must also be able to work effectively in teams, communicating and coordinating with other soldiers to achieve their objectives.Infantry Roles Image Gallery

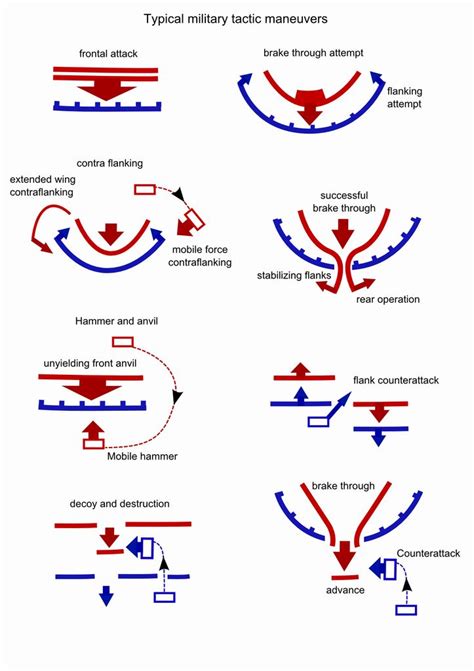






What are the different types of infantry roles?
+The different types of infantry roles include riflemen, grenadiers, machine gunners, mortar men, scouts, snipers, and combat medics.
What is the primary responsibility of a rifleman?
+The primary responsibility of a rifleman is to engage enemy forces with small arms fire and operate in a variety of environments and conditions.
What is the role of a combat medic in infantry operations?
+The role of a combat medic is to provide medical care and evacuate wounded personnel, treating injuries, stabilizing patients, and coordinating medical evacuations.
What is the importance of logistics and supply in infantry operations?
+The importance of logistics and supply in infantry operations is to manage the flow of goods and services to infantry units, including food, water, ammunition, and medical supplies.
What is the role of communication and command personnel in infantry operations?
+The role of communication and command personnel is to coordinate and control infantry operations, transmitting orders, receiving reports, and maintaining situational awareness.
In conclusion, the seven infantry roles discussed in this article are critical to the success of modern military operations. From riflemen to combat medics, each role requires unique skills and training, and together they form a cohesive and effective fighting force. By understanding the different infantry roles and how they contribute to the overall mission, military leaders can make informed decisions about how to deploy their forces and achieve their objectives. We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the world of infantry operations and the importance of these seven key roles. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about infantry roles and responsibilities.
