Intro
Discover Army soldier income details, including salary, benefits, and allowances, to understand military compensation packages and career financial rewards.
The life of an army soldier is one of sacrifice, discipline, and service to their country. These brave men and women put their lives on the line every day to protect their nation and its people. But have you ever wondered how much an army soldier earns? The answer may surprise you. In this article, we will delve into the details of an army soldier's income, including their basic pay, allowances, and benefits.
The income of an army soldier varies based on their rank, time in service, and location. In the United States, for example, the basic pay for an army soldier can range from around $1,600 per month for a private (E-1) to over $12,000 per month for a general (O-10). However, this is not the only source of income for army soldiers. They also receive a range of allowances and benefits that can significantly boost their take-home pay.
Basic Pay for Army Soldiers
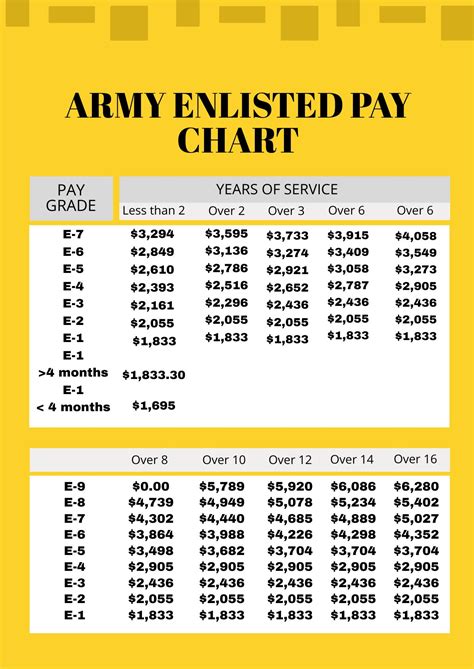
Allowances and Benefits for Army Soldiers

How Army Soldiers Can Increase Their Income
There are several ways that army soldiers can increase their income, including: * Promotions: Army soldiers who are promoted to higher ranks can earn higher basic pay and allowances. * Special duty pay: Army soldiers who perform special duties, such as flight duty or hazardous duty, may be eligible for special duty pay. * Education benefits: Army soldiers who take advantage of education benefits, such as the GI Bill, can earn higher pay and benefits in their civilian careers. * Special skills: Army soldiers who acquire special skills, such as language skills or technical skills, may be eligible for higher pay and benefits. * Deployment: Army soldiers who deploy to combat zones or other hazardous areas may be eligible for hazardous duty pay and other benefits.Army Soldier Income by Rank and Time in Service

Army Soldier Income vs. Civilian Income
The income of an army soldier is generally lower than that of a civilian with similar education and experience. However, army soldiers receive a range of benefits and allowances that can significantly boost their take-home pay. Additionally, army soldiers have the opportunity to acquire valuable skills and experience that can increase their earning potential in their civilian careers.Gallery of Army Soldier Income
Army Soldier Income Gallery
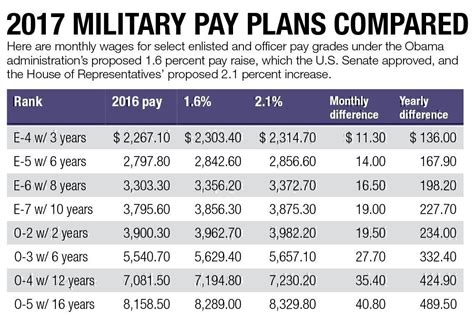


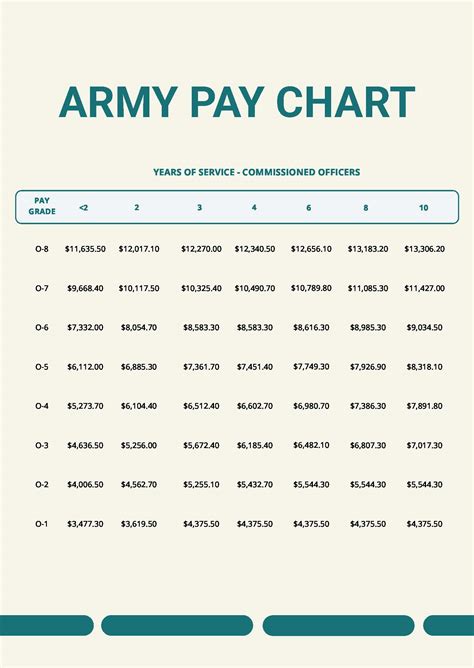
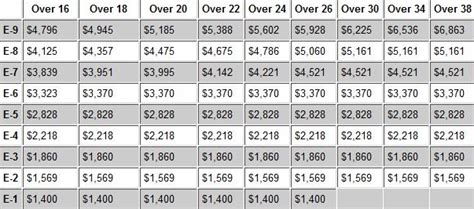




What is the basic pay for an army soldier?
+The basic pay for an army soldier varies based on their rank and time in service. The pay scale is divided into two main categories: enlisted personnel and officers.
What allowances and benefits do army soldiers receive?
+Army soldiers receive a range of allowances and benefits, including Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH), Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS), Cost of Living Allowance (COLA), special duty pay, education benefits, and health insurance.
How can army soldiers increase their income?
+Army soldiers can increase their income by promoting to higher ranks, performing special duties, acquiring special skills, deploying to combat zones or other hazardous areas, and taking advantage of education benefits.
What is the difference between army soldier income and civilian income?
+The income of an army soldier is generally lower than that of a civilian with similar education and experience. However, army soldiers receive a range of benefits and allowances that can significantly boost their take-home pay.
Do army soldiers pay taxes on their income?
+Yes, army soldiers pay taxes on their income, but they may be eligible for tax exemptions or deductions based on their location and duties.
In conclusion, the income of an army soldier is a complex and multifaceted topic that depends on a range of factors, including rank, time in service, location, and duties. While the basic pay for army soldiers may be lower than that of civilians, the range of allowances and benefits they receive can significantly boost their take-home pay. If you're considering a career in the army, it's essential to understand the different components of army soldier income and how they can impact your financial situation. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of army soldier income and has helped you make an informed decision about your career. If you have any further questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. Share this article with your friends and family to help them understand the importance of army soldier income.
