Intro
Discover B Age Information, exploring birth age details, age calculation methods, and related birthday facts, to uncover insights into life stages and development milestones.
The importance of age information cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in various aspects of life, including healthcare, education, and social security. Understanding age-related data is essential for policymakers, researchers, and individuals alike, as it helps inform decisions about resource allocation, program development, and personal planning. In this article, we will delve into the significance of age information, its applications, and the benefits of having accurate and reliable age-related data.
Age information is vital in the healthcare sector, where it is used to assess health risks, diagnose age-related diseases, and develop targeted treatment plans. For instance, certain health conditions, such as dementia and osteoporosis, are more prevalent among older adults, and age-specific data can help healthcare providers identify high-risk individuals and provide early interventions. Moreover, age information is used to determine eligibility for age-related benefits, such as Medicare and Social Security, which are critical for ensuring the well-being and financial security of older adults.
The significance of age information extends beyond healthcare, as it is also used in education and social services. Age-related data can help educators develop age-appropriate curricula, identify learning gaps, and provide targeted support to students. Additionally, age information is used to determine eligibility for age-related programs, such as youth employment initiatives, vocational training, and senior citizen services. By having accurate age-related data, policymakers and service providers can ensure that resources are allocated effectively and that programs are tailored to meet the unique needs of different age groups.
Introduction to Age Information

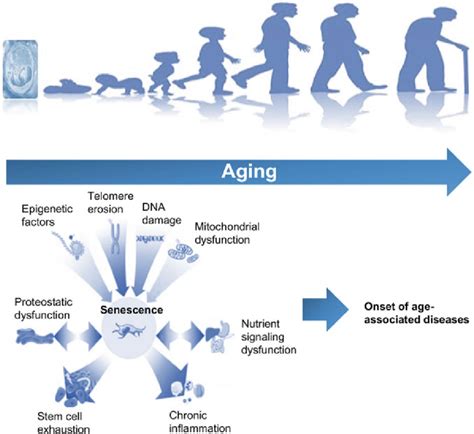
Age information is typically collected through surveys, censuses, and administrative records, which provide a wealth of data on age-related demographics, health outcomes, and socioeconomic characteristics. This data can be used to analyze age-related trends, identify disparities, and inform policy decisions. For example, age-specific data on mortality rates, life expectancy, and health outcomes can help researchers understand the impact of aging on population health and develop targeted interventions to promote healthy aging.
Types of Age Information
There are several types of age information, including chronological age, biological age, and psychological age. Chronological age refers to an individual's age in years, months, and days, while biological age refers to an individual's physical and physiological age, which can be influenced by factors such as lifestyle, genetics, and environmental exposures. Psychological age, on the other hand, refers to an individual's perceived age, which can be influenced by factors such as self-esteem, cognitive function, and social engagement.Applications of Age Information

Age information has numerous applications in various fields, including healthcare, education, and social services. In healthcare, age-specific data is used to develop targeted treatment plans, assess health risks, and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions. In education, age-related data is used to develop age-appropriate curricula, identify learning gaps, and provide targeted support to students. In social services, age information is used to determine eligibility for age-related programs, such as youth employment initiatives, vocational training, and senior citizen services.
Benefits of Accurate Age Information
Accurate age information is essential for ensuring that resources are allocated effectively and that programs are tailored to meet the unique needs of different age groups. By having reliable age-related data, policymakers and service providers can identify disparities, analyze trends, and develop targeted interventions to promote healthy aging, improve health outcomes, and enhance quality of life. Additionally, accurate age information can help individuals make informed decisions about their health, education, and financial planning, which can have a significant impact on their overall well-being and life satisfaction.Methods for Collecting Age Information
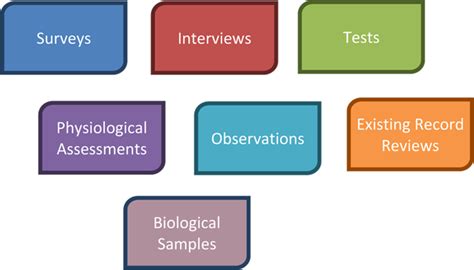
Age information can be collected through various methods, including surveys, censuses, and administrative records. Surveys are a common method for collecting age-related data, as they provide a wealth of information on demographics, health outcomes, and socioeconomic characteristics. Censuses, on the other hand, provide a comprehensive picture of a population's age structure, which can be used to analyze trends and identify disparities. Administrative records, such as birth and death certificates, also provide valuable age-related data, which can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions and track population health trends.
Challenges in Collecting Age Information
Collecting age information can be challenging, particularly in settings where birth registration is incomplete or inaccurate. In some countries, age-related data may be limited due to lack of infrastructure, resources, or technical capacity. Additionally, age information may be subject to errors or biases, which can affect the accuracy and reliability of the data. To overcome these challenges, it is essential to invest in data collection infrastructure, develop standardized methods for collecting age-related data, and provide training and technical assistance to data collectors and analysts.Analysis of Age Information
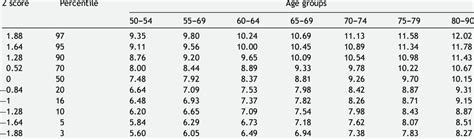
Analyzing age information requires specialized skills and techniques, as it involves working with complex data sets and applying statistical methods to identify trends and patterns. Age-related data can be analyzed using various statistical software packages, such as SAS, SPSS, and R, which provide a range of tools for data manipulation, visualization, and modeling. Additionally, age information can be analyzed using data visualization techniques, such as charts, graphs, and maps, which can help communicate complex data insights to non-technical audiences.
Interpretation of Age Information
Interpreting age information requires a deep understanding of the data, as well as the context in which it was collected. Age-related data can be influenced by various factors, such as cultural and socioeconomic characteristics, which can affect the accuracy and reliability of the data. To interpret age information accurately, it is essential to consider these factors and to use statistical methods to adjust for biases and errors. Additionally, age information should be interpreted in the context of other demographic and socioeconomic characteristics, such as sex, ethnicity, and education level, which can provide a more comprehensive picture of population health and well-being.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, age information is a critical component of demographic and socioeconomic data, which provides insights into population health, well-being, and quality of life. Collecting, analyzing, and interpreting age information requires specialized skills and techniques, as well as a deep understanding of the data and its limitations. Future directions for age information research include developing new methods for collecting and analyzing age-related data, improving data quality and accuracy, and applying age information to inform policy decisions and program development.
Final Thoughts
Age information is a valuable resource that can be used to promote healthy aging, improve health outcomes, and enhance quality of life. By investing in age-related data collection, analysis, and interpretation, we can gain a deeper understanding of population health and well-being, and develop targeted interventions to address the unique needs of different age groups. As the global population continues to age, it is essential that we prioritize age information research and application, to ensure that we are equipped to meet the challenges and opportunities of an aging population.Age Information Image Gallery





What is the importance of age information?
+Age information is crucial for understanding population health, well-being, and quality of life. It provides insights into age-related diseases, health outcomes, and socioeconomic characteristics, which can inform policy decisions and program development.
How is age information collected?
+Age information can be collected through surveys, censuses, and administrative records. Surveys provide a wealth of information on demographics, health outcomes, and socioeconomic characteristics, while censuses provide a comprehensive picture of a population's age structure.
What are the challenges in collecting age information?
+Collecting age information can be challenging, particularly in settings where birth registration is incomplete or inaccurate. Additionally, age information may be subject to errors or biases, which can affect the accuracy and reliability of the data.
How is age information analyzed and interpreted?
+Age information can be analyzed using statistical software packages and data visualization techniques. Interpreting age information requires a deep understanding of the data, as well as the context in which it was collected. Age-related data can be influenced by various factors, such as cultural and socioeconomic characteristics, which can affect the accuracy and reliability of the data.
What are the future directions for age information research?
+Future directions for age information research include developing new methods for collecting and analyzing age-related data, improving data quality and accuracy, and applying age information to inform policy decisions and program development. Additionally, there is a need to prioritize age information research and application, to ensure that we are equipped to meet the challenges and opportunities of an aging population.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the importance of age information and its applications in various fields. If you have any further questions or would like to share your thoughts on this topic, please do not hesitate to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative and useful, please share it with your friends and colleagues, and consider subscribing to our newsletter for more updates on age-related research and policy.
