Intro
Discover the Backbone Cost Explained, understanding network infrastructure expenses, including internet transit, colocation, and bandwidth costs, to optimize your IT budget and improve connectivity.
The concept of backbone cost is a crucial aspect of network infrastructure, particularly in the context of telecommunications and internet service provision. Understanding the backbone cost is essential for internet service providers (ISPs), network operators, and even individual consumers who rely on stable and efficient internet connectivity. In this article, we will delve into the details of backbone cost, its components, and its significance in the modern digital landscape.
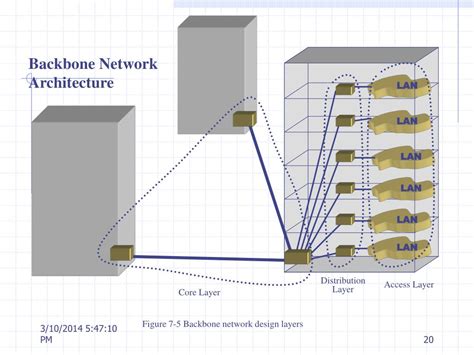
The backbone of the internet refers to the high-speed, high-capacity networks that form the core of the global internet infrastructure. These networks are typically operated by major telecommunications companies and are responsible for carrying vast amounts of data across long distances. The backbone cost encompasses the expenses associated with building, maintaining, and upgrading these critical networks. It includes a wide range of components, from the cost of laying down fiber optic cables to the expenses related to network equipment, personnel, and energy consumption.
As the demand for internet services continues to grow, driven by the increasing adoption of online technologies, social media, and cloud computing, the importance of understanding backbone cost has never been more pressing. For ISPs and network operators, managing backbone costs effectively is crucial for maintaining profitability and competitiveness in a rapidly evolving market. Similarly, for consumers, a stable and efficient backbone network translates into faster, more reliable internet services, which are essential for both personal and professional activities.
Introduction to Backbone Cost
The backbone cost is a multifaceted concept that involves various expenses, including capital expenditures (CapEx) and operational expenditures (OpEx). CapEx includes the costs associated with the initial setup and expansion of the network infrastructure, such as purchasing equipment, laying fiber optic cables, and constructing data centers. On the other hand, OpEx covers the ongoing expenses required to maintain and operate the network, including energy costs, personnel salaries, and maintenance fees.
Understanding the breakdown of backbone costs is essential for network operators to optimize their resources and ensure the long-term sustainability of their operations. By analyzing the various components of backbone cost, operators can identify areas where efficiencies can be improved, thereby reducing costs without compromising the quality of service.
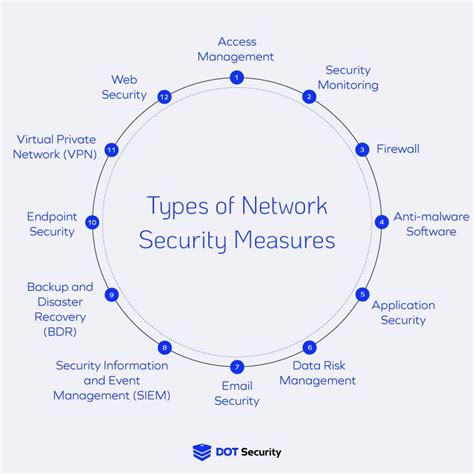
Components of Backbone Cost

The components of backbone cost can be broadly categorized into several key areas:
- Network Equipment: This includes the costs associated with purchasing and upgrading network devices such as routers, switches, and servers.
- Fiber Optic Cables: Laying down fiber optic cables is a significant expense, especially for networks that span across long distances.
- Data Centers: The construction and maintenance of data centers, which house critical network infrastructure, contribute to the overall backbone cost.
- Energy Consumption: Operating network equipment and data centers requires significant amounts of energy, contributing to operational expenses.
- Personnel and Training: Employing skilled personnel to manage and maintain the network, as well as providing ongoing training, is essential but costly.
- Maintenance and Upgrades: Regular maintenance and upgrades are necessary to ensure the network remains efficient and secure, adding to the OpEx.
Each of these components plays a critical role in the overall functionality and efficiency of the backbone network. By carefully managing these expenses, network operators can ensure a high-quality service while keeping costs under control.
Significance of Backbone Cost

The significance of backbone cost extends beyond the financial aspects of network operation. It has a direct impact on the quality of internet services provided to consumers. A well-managed backbone network, with optimized costs, can offer faster data transfer rates, lower latency, and higher reliability. This, in turn, supports the growth of digital technologies, including cloud computing, online gaming, and video streaming, which are increasingly integral to modern life.
Moreover, the backbone cost influences the pricing strategies of ISPs and network operators. By controlling costs, operators can offer competitive pricing to their customers, making internet services more accessible to a broader audience. This accessibility is crucial for bridging the digital divide, especially in underserved communities where internet penetration is low.
Managing Backbone Cost

Managing backbone cost requires a strategic approach that balances the need for high-quality, reliable internet services with the imperative to control expenses. Several strategies can be employed to achieve this balance:
- Network Optimization: Regularly assessing and optimizing network configuration to ensure it operates at peak efficiency.
- Technological Upgrades: Adopting newer technologies that offer better performance at lower costs, such as software-defined networking (SDN) and network functions virtualization (NFV).
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-saving measures in data centers and network operations to reduce power consumption.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Forming alliances with other network operators to share resources and reduce costs.
By adopting these strategies, network operators can effectively manage their backbone costs, ensuring the sustainability of their operations while providing high-quality internet services to their customers.
Future of Backbone Cost
The future of backbone cost is closely tied to the evolving demands of the digital landscape. As technologies like 5G, edge computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) become more prevalent, the need for faster, more reliable, and secure internet connections will increase. This will necessitate further investments in backbone infrastructure, potentially leading to higher costs.
However, advancements in technology also offer opportunities for cost reduction. Innovations in network architecture, such as the adoption of open networking standards and the use of artificial intelligence (AI) for network management, could lead to more efficient and cost-effective backbone networks.
Gallery of Backbone Cost
Backbone Cost Image Gallery





What is backbone cost in the context of network infrastructure?
+Backbone cost refers to the expenses associated with building, maintaining, and upgrading the high-speed, high-capacity networks that form the core of the global internet infrastructure.
What are the main components of backbone cost?
+The main components include network equipment, fiber optic cables, data centers, energy consumption, personnel and training, and maintenance and upgrades.
Why is managing backbone cost important for network operators?
+Managing backbone cost is crucial for network operators to maintain profitability, offer competitive pricing, and ensure the quality and reliability of internet services.
In conclusion, the backbone cost is a critical aspect of the internet infrastructure, influencing both the quality of service and the financial sustainability of network operations. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, understanding and managing backbone costs will remain essential for ISPs, network operators, and consumers alike. By embracing technological innovations and adopting strategic cost management practices, it is possible to create a more efficient, reliable, and accessible internet for everyone. We invite our readers to share their thoughts on the importance of backbone cost and how it affects their internet experience. Your insights and feedback are invaluable in helping us better understand the complexities of the digital world and its underlying infrastructure.
