Intro
Discover surprising Stealth Speed Facts, exploring radar-evading technology, supersonic flight, and high-speed maneuvers, unveiling the secrets of swift and silent aircraft operations.
The concept of stealth speed has garnered significant attention in recent years, particularly in the realm of automotive and aerospace engineering. Stealth speed refers to the ability of an object or vehicle to move at high velocities while minimizing its detectability by radar, sonar, or other detection systems. This technology has far-reaching implications for various industries, including defense, aviation, and even sports. In this article, we will delve into the world of stealth speed, exploring its importance, benefits, and the latest developments in this field.
The importance of stealth speed cannot be overstated, as it has the potential to revolutionize the way we design and operate vehicles. By reducing the radar cross-section of an object, stealth technology enables it to evade detection, thereby gaining a significant tactical advantage. This is particularly crucial in military applications, where stealth capabilities can mean the difference between life and death. Moreover, stealth speed also has implications for the automotive industry, where it can be used to improve the aerodynamics and fuel efficiency of vehicles.
As we explore the concept of stealth speed, it becomes clear that it is a complex and multifaceted field, requiring expertise from various disciplines, including materials science, aerodynamics, and electrical engineering. The development of stealth technology involves the creation of specialized materials and designs that can absorb or scatter radar waves, reducing the object's visibility to detection systems. This requires a deep understanding of the underlying physics and a ability to simulate and test various scenarios using advanced computer models and wind tunnels.
Introduction to Stealth Speed

The concept of stealth speed is closely tied to the development of stealth technology, which has its roots in the military. The first stealth aircraft, the Lockheed F-117 Nighthawk, was developed in the 1970s and 1980s, using a combination of radar-absorbing materials and unique design features to minimize its radar cross-section. Since then, stealth technology has evolved significantly, with advances in materials science and computer simulations enabling the creation of more sophisticated stealth designs.
Benefits of Stealth Speed
The benefits of stealth speed are numerous and far-reaching. In military applications, stealth capabilities can provide a significant tactical advantage, enabling aircraft and other vehicles to evade detection and complete their missions with greater success. In the automotive industry, stealth speed can be used to improve the aerodynamics and fuel efficiency of vehicles, reducing wind resistance and drag. Additionally, stealth technology can also be used to reduce the noise signature of vehicles, making them quieter and more comfortable to operate.How Stealth Speed Works
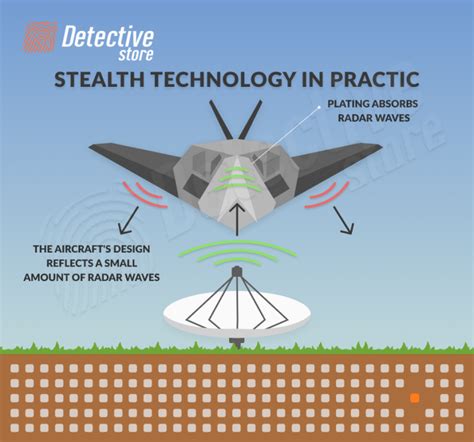
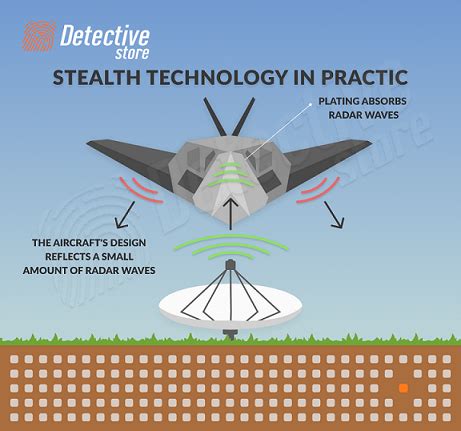
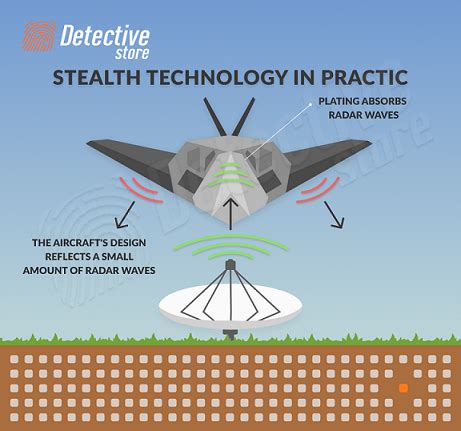
Stealth speed works by using a combination of specialized materials and design features to minimize the radar cross-section of an object. This can be achieved through the use of radar-absorbing materials, such as ferromagnetic materials or radar-absorbing coatings. Additionally, stealth designs often incorporate unique shapes and geometries, such as faceted surfaces or curved lines, to scatter radar waves and reduce the object's visibility.
Types of Stealth Technology
There are several types of stealth technology, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. These include:- Radar-absorbing materials: These materials are designed to absorb radar waves, reducing the object's visibility to detection systems.
- Faceted surfaces: These surfaces are designed to scatter radar waves, reducing the object's radar cross-section.
- Curved lines: These lines are designed to deflect radar waves, reducing the object's visibility to detection systems.
- Active stealth: This technology uses electronic systems to detect and adapt to radar waves, reducing the object's visibility to detection systems.
Applications of Stealth Speed
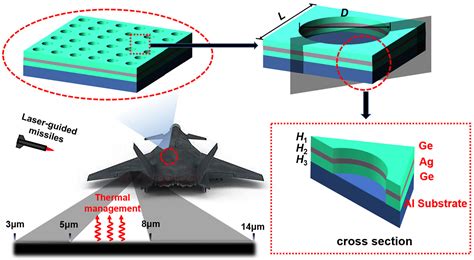
The applications of stealth speed are numerous and varied. In military applications, stealth capabilities can provide a significant tactical advantage, enabling aircraft and other vehicles to evade detection and complete their missions with greater success. In the automotive industry, stealth speed can be used to improve the aerodynamics and fuel efficiency of vehicles, reducing wind resistance and drag. Additionally, stealth technology can also be used to reduce the noise signature of vehicles, making them quieter and more comfortable to operate.
Future Developments in Stealth Speed
The future of stealth speed is exciting and rapidly evolving. Advances in materials science and computer simulations are enabling the creation of more sophisticated stealth designs, with improved performance and reduced costs. Additionally, the development of new technologies, such as metamaterials and nanotechnology, is expected to further enhance the capabilities of stealth technology.Challenges and Limitations of Stealth Speed

While stealth speed offers many benefits, it also presents several challenges and limitations. One of the main challenges is the high cost of developing and implementing stealth technology, which can be prohibitively expensive for many applications. Additionally, stealth designs can be complex and difficult to manufacture, requiring specialized materials and production techniques.
Real-World Examples of Stealth Speed
There are several real-world examples of stealth speed in action. These include:- The Lockheed F-117 Nighthawk, a stealth aircraft developed in the 1970s and 1980s.
- The Northrop Grumman B-2 Spirit, a stealth bomber developed in the 1980s and 1990s.
- The Mercedes-Benz CLA, a car that uses stealth technology to improve its aerodynamics and fuel efficiency.
Gallery of Stealth Speed
Stealth Speed Image Gallery
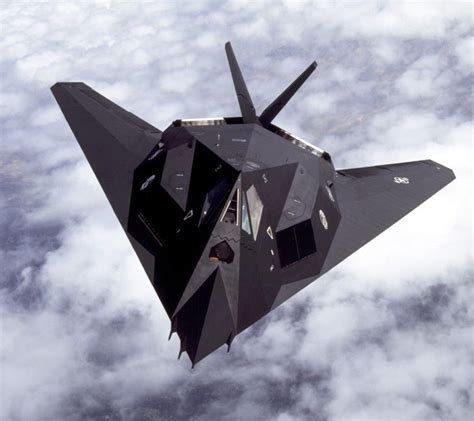








Frequently Asked Questions
What is stealth speed?
+Stealth speed refers to the ability of an object or vehicle to move at high velocities while minimizing its detectability by radar, sonar, or other detection systems.
How does stealth speed work?
+Stealth speed works by using a combination of specialized materials and design features to minimize the radar cross-section of an object, making it less visible to detection systems.
What are the benefits of stealth speed?
+The benefits of stealth speed include improved tactical advantage in military applications, improved aerodynamics and fuel efficiency in automotive applications, and reduced noise signature in various applications.
What are the challenges and limitations of stealth speed?
+The challenges and limitations of stealth speed include high development and implementation costs, complexity and difficulty of manufacture, and limited applicability to certain industries or applications.
What are some real-world examples of stealth speed?
+Some real-world examples of stealth speed include the Lockheed F-117 Nighthawk, the Northrop Grumman B-2 Spirit, and the Mercedes-Benz CLA, which uses stealth technology to improve its aerodynamics and fuel efficiency.
As we conclude our exploration of stealth speed, it is clear that this technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries and applications. With its ability to minimize detectability and improve performance, stealth speed is an exciting and rapidly evolving field that warrants further research and development. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions on this topic, and to explore the many resources and references available for further learning. Whether you are a professional in the field or simply an interested enthusiast, we hope that this article has provided a comprehensive and informative introduction to the fascinating world of stealth speed.

