Intro
Discover the power of Mach 3 speed, exploring supersonic flight, aerodynamics, and sonic booms, to understand this high-velocity phenomenon.
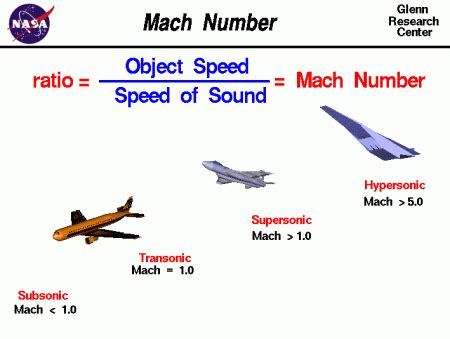
The concept of Mach 3 speed has fascinated many, especially those interested in aerospace and military technology. Mach 3 refers to an object's speed that is three times the speed of sound, which is approximately 2,280 miles per hour (3,670 kilometers per hour) at sea level in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius). To understand the significance of Mach 3 speed, it's essential to delve into the basics of supersonic flight and the challenges associated with achieving such high velocities.
The speed of sound, also known as Mach 1, is the threshold beyond which an object is considered supersonic. As an object approaches the speed of sound, it encounters a significant increase in air resistance, which can lead to a substantial rise in temperature and a decrease in efficiency. Breaking the sound barrier requires an enormous amount of energy, and maintaining supersonic speeds for an extended period is even more challenging. However, achieving Mach 3 speed is a remarkable feat that has been accomplished by a select few aircraft, including the Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird and the North American X-15.
Introduction to Supersonic Flight

Supersonic flight is the regime of flight where an object travels at speeds greater than the speed of sound. As an object approaches Mach 1, the air in front of it becomes compressed, forming a shockwave that produces a sonic boom. The shockwave creates a region of high pressure and temperature, which can cause significant drag and heat buildup. To overcome these challenges, supersonic aircraft are designed with unique features, such as sharp noses, swept wings, and powerful engines.
Challenges of Supersonic Flight
The primary challenges of supersonic flight are managing the heat generated by friction with the atmosphere and overcoming the significant drag forces that occur at high speeds. As an object travels faster, the air molecules in front of it have less time to move out of the way, resulting in a higher density of air and increased drag. Additionally, the friction generated by supersonic flight causes the air to heat up, which can lead to a range of problems, including thermal damage to the aircraft's structure and a decrease in engine efficiency.History of Mach 3 Speed
The pursuit of Mach 3 speed has been an ongoing effort in the field of aerospace engineering. One of the earliest attempts to achieve Mach 3 was made by the Bell X-2, a rocket-powered aircraft that reached a top speed of Mach 3.19 in 1956. However, it was the Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird that truly demonstrated the potential of Mach 3 flight. The SR-71, developed in the 1950s and 1960s, was a supersonic reconnaissance plane that could maintain speeds above Mach 3 for extended periods.
Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird
The Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird is widely considered one of the most iconic and impressive aircraft ever built. With its unique design and powerful engines, the SR-71 was capable of reaching speeds above Mach 3.5 and altitudes over 80,000 feet (24,400 meters). The SR-71's ability to operate at such extreme conditions made it an invaluable asset for reconnaissance and surveillance missions.Benefits of Mach 3 Speed
Achieving Mach 3 speed offers several benefits, including increased efficiency, reduced travel time, and enhanced reconnaissance capabilities. Supersonic aircraft can cover vast distances in a relatively short period, making them ideal for missions that require rapid deployment and response. Additionally, the high speeds achieved by Mach 3 aircraft enable them to gather intelligence and conduct surveillance over a wide area, providing valuable insights for military and civilian applications.
Applications of Mach 3 Speed
The applications of Mach 3 speed are diverse and far-reaching. In the military, supersonic aircraft are used for reconnaissance, surveillance, and strike missions. Civilian applications include supersonic transport, which could revolutionize the way we travel, and scientific research, where high-speed aircraft can be used to study the upper atmosphere and gather data on supersonic flight.Challenges and Limitations
Despite the benefits of Mach 3 speed, there are several challenges and limitations associated with supersonic flight. One of the primary concerns is the sonic boom, which can be a significant disturbance to people on the ground. Additionally, supersonic aircraft require specialized materials and designs to withstand the extreme temperatures and stresses generated by high-speed flight.
Future Developments
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see new developments in supersonic flight and Mach 3 speed. Researchers are exploring new materials and designs that can withstand the extreme conditions of supersonic flight, and advancements in engine technology are expected to improve efficiency and reduce emissions. Additionally, the development of supersonic transport could revolutionize the way we travel, making it possible to travel from one continent to another in a matter of hours.Gallery of Supersonic Aircraft
Supersonic Aircraft Image Gallery









Frequently Asked Questions
What is the speed of sound?
+The speed of sound is approximately 768 miles per hour (1,236 kilometers per hour) at sea level in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius).
What is Mach 3 speed?
+Mach 3 speed is three times the speed of sound, which is approximately 2,280 miles per hour (3,670 kilometers per hour) at sea level in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius).
What are the benefits of Mach 3 speed?
+The benefits of Mach 3 speed include increased efficiency, reduced travel time, and enhanced reconnaissance capabilities. Supersonic aircraft can cover vast distances in a relatively short period, making them ideal for missions that require rapid deployment and response.
What are the challenges of supersonic flight?
+The primary challenges of supersonic flight are managing the heat generated by friction with the atmosphere and overcoming the significant drag forces that occur at high speeds. As an object travels faster, the air molecules in front of it have less time to move out of the way, resulting in a higher density of air and increased drag.
What is the future of supersonic flight?
+As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see new developments in supersonic flight and Mach 3 speed. Researchers are exploring new materials and designs that can withstand the extreme conditions of supersonic flight, and advancements in engine technology are expected to improve efficiency and reduce emissions.
In conclusion, Mach 3 speed is a remarkable achievement that has been accomplished by a select few aircraft. The benefits of Mach 3 speed, including increased efficiency and reduced travel time, make it an attractive option for various applications. However, the challenges associated with supersonic flight, such as managing heat and drag, require careful consideration and innovative solutions. As research and development continue to advance, we can expect to see new breakthroughs in supersonic flight and Mach 3 speed, leading to exciting possibilities for the future of aerospace technology. We invite you to share your thoughts and opinions on the topic of Mach 3 speed and its potential applications, and we encourage you to explore the fascinating world of supersonic flight.
