Intro
Explore the speed of Mach 3, a high-supersonic velocity, and discover its applications in aerospace, military jets, and breaking sound barriers with supersonic flight and aerodynamics.
The speed of Mach 3 is approximately 2,280 miles per hour (3,669 kilometers per hour) at sea level in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius). To put this speed into perspective, consider that the fastest military jet, the Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird, has a top speed of over Mach 3.5, which is more than 2,600 miles per hour (4,200 kilometers per hour). The speed of Mach 3 is incredibly fast, and it's essential to understand the concept of Mach numbers to appreciate its significance.
Mach numbers are a measure of an object's speed relative to the speed of sound. The speed of sound varies depending on the temperature and air pressure, but at sea level, it is approximately 768 miles per hour (1,236 kilometers per hour). When an object travels at Mach 1, it is moving at the speed of sound. As the Mach number increases, so does the speed of the object. For example, Mach 2 is twice the speed of sound, while Mach 3 is three times the speed of sound. The speed of Mach 3 is not only impressive but also crucial in various fields, including aviation, aerospace, and defense.
The importance of understanding Mach numbers and the speed of Mach 3 cannot be overstated. In aviation, for instance, pilots need to be aware of the Mach number to ensure safe and efficient flight. Exceeding the maximum allowable Mach number can lead to structural damage or even loss of control. In aerospace, the speed of Mach 3 is critical in the development of supersonic and hypersonic vehicles. These vehicles are designed to operate at extremely high speeds, and understanding the effects of Mach numbers on their performance is essential. In defense, the speed of Mach 3 is vital in the development of missiles and other military systems.
Understanding Mach Numbers
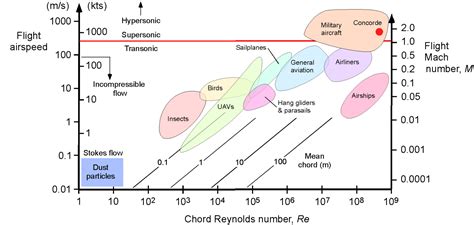
To comprehend the speed of Mach 3, it's essential to understand the concept of Mach numbers. Mach numbers are a dimensionless quantity that represents the ratio of an object's speed to the speed of sound. The speed of sound is approximately 768 miles per hour (1,236 kilometers per hour) at sea level, but it can vary depending on the temperature and air pressure. As an object approaches the speed of sound, it creates a series of pressure waves that radiate outward from the object. When the object exceeds the speed of sound, it creates a shockwave that can produce a sonic boom.
Mach numbers are used to describe the speed of objects in various fields, including aviation, aerospace, and defense. In aviation, Mach numbers are used to determine the maximum allowable speed for an aircraft. Exceeding the maximum Mach number can lead to structural damage or even loss of control. In aerospace, Mach numbers are used to design supersonic and hypersonic vehicles. These vehicles are designed to operate at extremely high speeds, and understanding the effects of Mach numbers on their performance is essential.
How Mach Numbers Are Calculated
The calculation of Mach numbers is relatively straightforward. The Mach number is calculated by dividing the speed of the object by the speed of sound. The formula for calculating Mach numbers is:Mach Number = Speed of Object / Speed of Sound
For example, if an object is traveling at 1,500 miles per hour (2,414 kilometers per hour), and the speed of sound is 768 miles per hour (1,236 kilometers per hour), the Mach number would be:
Mach Number = 1,500 / 768 = 1.95
This means that the object is traveling at approximately 1.95 times the speed of sound.
The Speed of Mach 3 in Different Environments
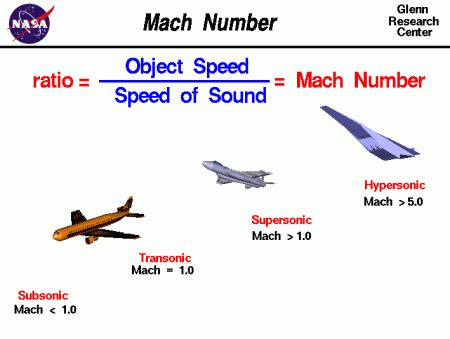
The speed of Mach 3 can vary depending on the environment in which it is measured. At sea level, the speed of Mach 3 is approximately 2,280 miles per hour (3,669 kilometers per hour). However, at higher altitudes, the speed of sound decreases, and the speed of Mach 3 increases. For example, at an altitude of 30,000 feet (9,144 meters), the speed of sound is approximately 678 miles per hour (1,091 kilometers per hour), and the speed of Mach 3 would be:
Mach 3 = 3 x 678 = 2,034 miles per hour (3,273 kilometers per hour)
In addition to altitude, the speed of Mach 3 can also be affected by temperature and air pressure. In general, the speed of sound increases with temperature and decreases with air pressure. Therefore, the speed of Mach 3 can vary depending on the specific conditions in which it is measured.
Factors That Affect the Speed of Mach 3
Several factors can affect the speed of Mach 3, including:- Altitude: The speed of sound decreases with altitude, and the speed of Mach 3 increases.
- Temperature: The speed of sound increases with temperature, and the speed of Mach 3 decreases.
- Air pressure: The speed of sound decreases with air pressure, and the speed of Mach 3 increases.
- Humidity: The speed of sound can be affected by humidity, and the speed of Mach 3 can vary depending on the specific conditions.
Understanding these factors is essential in various fields, including aviation, aerospace, and defense. By taking into account the effects of altitude, temperature, air pressure, and humidity, engineers and designers can develop vehicles and systems that operate efficiently and safely at high speeds.
Applications of Mach 3

The speed of Mach 3 has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Aviation: The speed of Mach 3 is critical in the development of supersonic aircraft. These aircraft are designed to operate at speeds above Mach 1, and understanding the effects of Mach numbers on their performance is essential.
- Aerospace: The speed of Mach 3 is vital in the development of hypersonic vehicles. These vehicles are designed to operate at speeds above Mach 5, and understanding the effects of Mach numbers on their performance is crucial.
- Defense: The speed of Mach 3 is essential in the development of missiles and other military systems. These systems are designed to operate at high speeds, and understanding the effects of Mach numbers on their performance is vital.
In addition to these applications, the speed of Mach 3 also has implications for space exploration. As spacecraft travel through the atmosphere, they must withstand the intense heat and friction generated by their high speeds. Understanding the effects of Mach numbers on spacecraft performance is essential for the development of efficient and safe space exploration systems.
Benefits of Mach 3
The benefits of Mach 3 are numerous, including:- Increased efficiency: Operating at high speeds can increase efficiency and reduce travel time.
- Improved performance: Understanding the effects of Mach numbers on performance can lead to the development of more efficient and effective systems.
- Enhanced safety: By understanding the effects of Mach numbers on safety, engineers and designers can develop systems that operate safely and efficiently at high speeds.
However, there are also challenges associated with operating at Mach 3, including:
- Heat generation: High speeds can generate intense heat, which can damage systems and structures.
- Friction: High speeds can generate significant friction, which can lead to wear and tear on systems and structures.
- Sonic booms: Operating at supersonic speeds can generate sonic booms, which can be a concern for noise pollution and environmental impact.
Challenges of Mach 3

Despite the benefits of Mach 3, there are also significant challenges associated with operating at such high speeds. One of the primary challenges is heat generation. As an object travels at high speeds, it generates intense heat due to friction with the air. This heat can damage systems and structures, and it can also lead to a loss of efficiency and performance.
Another challenge associated with Mach 3 is friction. High speeds can generate significant friction, which can lead to wear and tear on systems and structures. This friction can also generate heat, which can further exacerbate the challenges associated with operating at high speeds.
In addition to these challenges, operating at Mach 3 can also generate sonic booms. Sonic booms are a concern for noise pollution and environmental impact, and they can also be a challenge for systems and structures that are not designed to withstand the intense pressure waves generated by supersonic flight.
Overcoming the Challenges of Mach 3
To overcome the challenges associated with Mach 3, engineers and designers must develop innovative solutions that can mitigate the effects of heat generation, friction, and sonic booms. Some potential solutions include:- Advanced materials: Developing materials that can withstand the intense heat and friction generated by high speeds.
- Cooling systems: Developing cooling systems that can efficiently dissipate heat and maintain system performance.
- Sonic boom reduction: Developing technologies that can reduce the intensity of sonic booms and minimize their impact on the environment.
By overcoming the challenges associated with Mach 3, engineers and designers can develop systems and structures that operate efficiently and safely at high speeds. This can lead to significant benefits, including increased efficiency, improved performance, and enhanced safety.
Future of Mach 3

The future of Mach 3 is exciting and promising. As engineers and designers continue to develop innovative solutions to overcome the challenges associated with high speeds, we can expect to see significant advancements in various fields, including aviation, aerospace, and defense.
One potential area of development is the creation of hypersonic vehicles that can operate at speeds above Mach 5. These vehicles have the potential to revolutionize transportation and exploration, enabling humans to travel faster and more efficiently than ever before.
Another area of development is the creation of advanced materials and cooling systems that can withstand the intense heat and friction generated by high speeds. These technologies have the potential to significantly improve the efficiency and performance of systems and structures, enabling them to operate safely and efficiently at high speeds.
Emerging Trends in Mach 3
Some emerging trends in Mach 3 include:- Hypersonic flight: The development of vehicles that can operate at speeds above Mach 5.
- Advanced materials: The development of materials that can withstand the intense heat and friction generated by high speeds.
- Cooling systems: The development of cooling systems that can efficiently dissipate heat and maintain system performance.
- Sonic boom reduction: The development of technologies that can reduce the intensity of sonic booms and minimize their impact on the environment.
By staying at the forefront of these emerging trends, engineers and designers can develop innovative solutions that can overcome the challenges associated with Mach 3 and enable the creation of systems and structures that operate efficiently and safely at high speeds.
Mach 3 Image Gallery







What is Mach 3?
+Mach 3 is a speed that is three times the speed of sound, approximately 2,280 miles per hour (3,669 kilometers per hour) at sea level.
What are the applications of Mach 3?
+The applications of Mach 3 include aviation, aerospace, and defense. It is used in the development of supersonic and hypersonic vehicles, as well as in the design of missiles and other military systems.
What are the challenges of Mach 3?
+The challenges of Mach 3 include heat generation, friction, and sonic booms. These challenges must be overcome through the development of advanced materials, cooling systems, and sonic boom reduction technologies.
What is the future of Mach 3?
+The future of Mach 3 is promising, with emerging trends in hypersonic flight, advanced materials, cooling systems, and sonic boom reduction. These advancements have the potential to enable the creation of systems and structures that operate efficiently and safely at high speeds.
How is Mach 3 calculated?
+Mach 3 is calculated by dividing the speed of the object by the speed of sound. The formula for calculating Mach numbers is: Mach Number = Speed of Object / Speed of Sound.
In conclusion, the speed of Mach 3 is an exciting and promising area of development, with numerous applications in aviation, aerospace, and defense. By understanding the challenges and benefits associated with Mach 3, engineers and designers can develop innovative solutions that can overcome the challenges and enable the creation of systems and structures that operate efficiently and safely at high speeds. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about Mach 3 in the comments below, and we look forward to exploring this fascinating topic further in future articles.
