Intro
Discover what is 1 Mach, the speed of sound, and its significance in aerodynamics, aviation, and supersonic flight, exploring Mach numbers, sonic booms, and high-speed phenomena.
The concept of speed is a fundamental aspect of our daily lives, and when it comes to measuring the speed of objects, particularly in the context of aviation and aerospace, the term "Mach" is often used. But what exactly is 1 Mach? To understand this, let's delve into the basics of speed measurement and the significance of the Mach number.
The speed of sound, denoted by the letter "c," is approximately 768 miles per hour (mph) or 1,236 kilometers per hour (km/h) at sea level in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius). This speed is a crucial reference point for measuring the velocity of objects, especially aircraft and spacecraft. The Mach number, named after Austrian physicist Ernst Mach, is a dimensionless quantity that represents the ratio of an object's speed to the speed of sound.
In essence, 1 Mach is equivalent to the speed of sound. When an object travels at 1 Mach, it is moving at the same speed as the sound waves it produces. This speed is approximately 768 mph (1,236 km/h) at sea level. As an object approaches or exceeds the speed of sound, it creates a series of pressure waves that produce the characteristic "sonic boom" sound.
The Mach number is a critical factor in aerodynamics, as it determines the behavior of air around an object in motion. At subsonic speeds (less than 1 Mach), air behaves predictably, and the pressure waves generated by the object are able to propagate freely. However, as the object approaches supersonic speeds (greater than 1 Mach), the air becomes compressed, and the pressure waves are unable to propagate ahead of the object, resulting in a shockwave that produces the sonic boom.
Understanding the concept of 1 Mach is essential for aircraft designers, pilots, and engineers, as it plays a crucial role in determining the performance and safety of aircraft. For instance, when an aircraft breaks the sound barrier, it must be designed to withstand the intense forces generated by the shockwave, which can cause significant stress on the airframe and potentially lead to structural failure.
Introduction to Mach Numbers
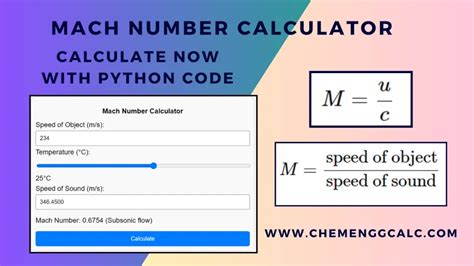
The Mach number is a dimensionless quantity that can be calculated using the following formula: M = v / c, where M is the Mach number, v is the velocity of the object, and c is the speed of sound. By using this formula, we can determine the Mach number of an object and understand its behavior in relation to the speed of sound.
For example, if an aircraft is traveling at a speed of 500 mph (805 km/h), and the speed of sound is approximately 768 mph (1,236 km/h), the Mach number would be M = 500 / 768 = 0.65. This means that the aircraft is traveling at approximately 65% of the speed of sound.
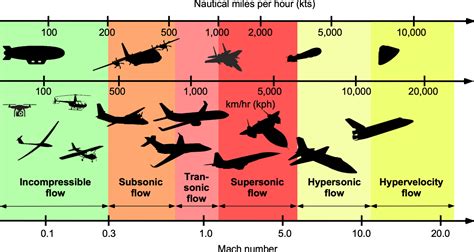
Subsonic, Transonic, and Supersonic Speeds
The Mach number is used to classify the speed of objects into three main categories: subsonic, transonic, and supersonic.- Subsonic speeds: Less than 1 Mach (approximately 768 mph or 1,236 km/h)
- Transonic speeds: Between 0.8 and 1.2 Mach (approximately 614-922 mph or 988-1,483 km/h)
- Supersonic speeds: Greater than 1 Mach (approximately 768 mph or 1,236 km/h)
Each of these categories has distinct characteristics and challenges. Subsonic speeds are typically associated with commercial airliners and general aviation aircraft, while transonic speeds are characteristic of high-performance military aircraft and some business jets. Supersonic speeds, on the other hand, are achieved by specialized aircraft, such as fighter jets and spacecraft.
Applications of Mach Numbers
The concept of Mach numbers has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Aerospace engineering: Mach numbers are used to design and optimize aircraft and spacecraft for efficient and safe flight.
- Aerodynamics: Understanding Mach numbers is crucial for predicting the behavior of air around objects in motion.
- Materials science: The study of Mach numbers helps researchers develop materials that can withstand the stresses generated by high-speed flight.
- Military applications: Mach numbers are used to design and operate high-performance military aircraft, such as fighter jets and bombers.
In addition to these applications, the concept of Mach numbers has also been used in other fields, such as automotive engineering and biomedical research.
Calculating Mach Numbers
Calculating Mach numbers is a straightforward process that involves using the formula M = v / c. However, there are several factors that can affect the accuracy of the calculation, such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure.For example, if the temperature increases, the speed of sound also increases, which can affect the Mach number calculation. Similarly, changes in air pressure and humidity can also impact the accuracy of the calculation.
To ensure accurate calculations, it is essential to use reliable data and to consider the various factors that can affect the speed of sound.
Real-World Examples of Mach Numbers
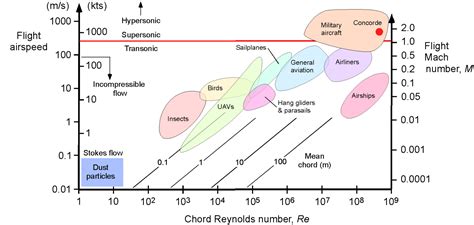
There are several real-world examples of Mach numbers in action. For instance:
- The Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird, a supersonic reconnaissance plane, has a top speed of over Mach 3.5 (approximately 2,193 mph or 3,529 km/h).
- The Concorde, a supersonic jet that was in commercial service from 1976 to 2003, had a cruising speed of Mach 2.04 (approximately 1,354 mph or 2,180 km/h).
- The X-15, a rocket-powered aircraft developed in the 1950s and 1960s, reached speeds of up to Mach 6.72 (approximately 4,520 mph or 7,274 km/h).
These examples demonstrate the importance of Mach numbers in achieving high-speed flight and pushing the boundaries of aerospace engineering.
Challenges and Limitations of Mach Numbers
While Mach numbers are a crucial concept in aerospace engineering, there are several challenges and limitations associated with achieving high Mach numbers.- One of the main challenges is the generation of heat, which can cause damage to the airframe and engines.
- Another challenge is the creation of shockwaves, which can produce sonic booms and affect the stability of the aircraft.
- Additionally, high Mach numbers can also lead to increased drag, which can reduce the efficiency and range of the aircraft.
To overcome these challenges, researchers and engineers are developing new materials and technologies that can withstand the stresses generated by high-speed flight.
Future Developments in Mach Numbers

As technology advances, we can expect to see significant developments in the field of Mach numbers. Some potential areas of research include:
- Hypersonic flight: Achieving speeds above Mach 5 (approximately 3,800 mph or 6,116 km/h) could revolutionize transportation and exploration.
- Advanced materials: Developing materials that can withstand the stresses generated by high-speed flight could enable the creation of more efficient and durable aircraft.
- Computational modeling: Improving computational models of aerodynamics and thermodynamics could help researchers better understand the behavior of air and heat at high Mach numbers.
These developments have the potential to transform the field of aerospace engineering and enable the creation of faster, more efficient, and more sustainable aircraft.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the concept of 1 Mach is a fundamental aspect of aerospace engineering, and understanding Mach numbers is crucial for designing and optimizing aircraft and spacecraft for efficient and safe flight. As technology advances, we can expect to see significant developments in the field of Mach numbers, including hypersonic flight, advanced materials, and computational modeling.The study of Mach numbers has numerous applications in various fields, and its importance cannot be overstated. As researchers and engineers continue to push the boundaries of aerospace engineering, the concept of Mach numbers will remain a vital tool for achieving high-speed flight and exploring the unknown.
Mach Number Image Gallery





What is the speed of sound?
+The speed of sound is approximately 768 miles per hour (mph) or 1,236 kilometers per hour (km/h) at sea level in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius).
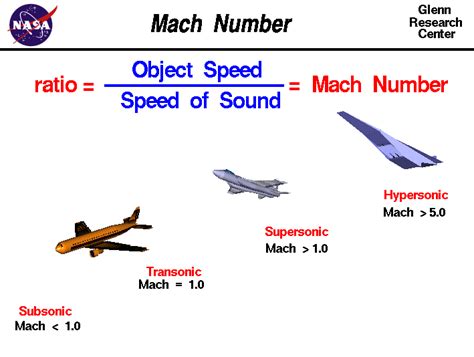
What is the Mach number?
+The Mach number is a dimensionless quantity that represents the ratio of an object's speed to the speed of sound.
What is the difference between subsonic, transonic, and supersonic speeds?
+Subsonic speeds are less than 1 Mach, transonic speeds are between 0.8 and 1.2 Mach, and supersonic speeds are greater than 1 Mach.
What are some real-world examples of Mach numbers?
+Some examples include the Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird, the Concorde, and the X-15 rocket-powered aircraft.
What are some potential future developments in Mach numbers?
+Some potential areas of research include hypersonic flight, advanced materials, and computational modeling.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the concept of 1 Mach and its significance in aerospace engineering. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about this topic, please don't hesitate to comment or share this article with others. By working together, we can continue to advance our knowledge and push the boundaries of what is possible in the field of aerospace engineering.
