Intro
Discover 5 surprising submarine speed facts, exploring underwater velocity, naval technology, and maritime engineering, revealing the fastest subs and their propulsion systems.
The world of submarines is a fascinating one, filled with incredible feats of engineering and technology that allow these underwater vessels to operate with remarkable speed and agility. Submarines have been a crucial part of naval operations for decades, and their capabilities continue to evolve with advancements in design and propulsion systems. For those interested in the maritime and military sectors, understanding the speed of submarines can provide insights into their operational effectiveness and strategic importance.
Submarines are complex machines that require a delicate balance of power, stealth, and maneuverability to fulfill their missions, which can range from reconnaissance and surveillance to combat and deterrence. The speed at which a submarine can travel is a critical factor in its ability to perform these tasks, as it directly affects the vessel's ability to reach its destination quickly, evade detection, and respond to changing situations. Whether operating in the depths of the ocean or near coastal waters, the speed of a submarine is a key determinant of its overall performance and utility.
The development of submarine technology has seen significant advancements over the years, with modern submarines boasting sophisticated propulsion systems, advanced materials, and cutting-edge designs that enhance their speed, endurance, and versatility. From conventional diesel-electric submarines to nuclear-powered ones, each type has its unique characteristics and capabilities, including varying speed ranges that are adapted to specific operational requirements. As the global maritime landscape continues to evolve, the importance of submarines and their speed will only continue to grow, making them a vital component of naval strategies and operations worldwide.
Introduction to Submarine Speed

Factors Influencing Submarine Speed
Propulsion Systems
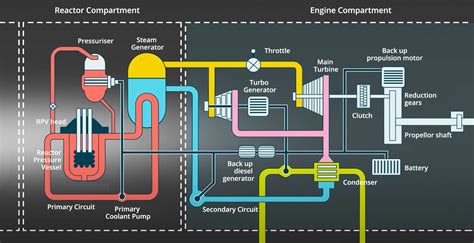
The propulsion system is perhaps the most critical factor influencing a submarine's speed. Diesel-electric submarines use diesel generators to charge batteries, which then power electric motors for propulsion. This system is quieter and more suitable for stealth operations but generally offers lower speeds. In contrast, nuclear-powered submarines utilize a nuclear reactor to generate steam, which drives turbines connected to generators and propulsion motors. This system provides more power and enables higher speeds and longer endurance but is noisier and more complex.Hull Design
The design of a submarine's hull is optimized for different operational requirements, including speed, stealth, and depth capability. Streamlined hulls can reduce drag and enhance speed, while more conventional shapes might prioritize stability and maneuverability. The materials used in hull construction, such as steel or titanium, also affect the submarine's weight, strength, and overall performance.Types of Submarines and Their Speeds
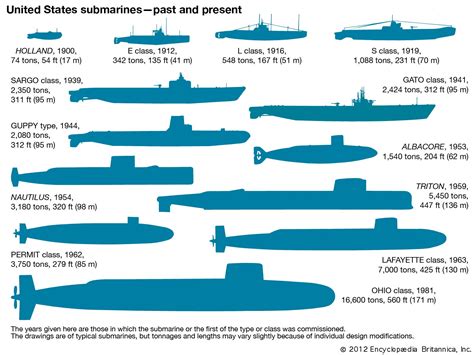
Nuclear-Powered Submarines
Nuclear-powered submarines are the fastest type, with some models capable of exceeding 25 knots (46 km/h) when submerged. Their high power output and virtually unlimited endurance make them ideal for long-range missions and rapid response scenarios.Diesel-Electric Submarines
Diesel-electric submarines typically have lower top speeds, usually around 10-15 knots (18-28 km/h) when submerged, due to the limitations of their propulsion system. However, they are generally quieter and more suitable for coastal operations and stealth missions.Air-Independent Propulsion (AIP) Submarines
AIP submarines, which use closed-cycle diesel engines or fuel cells, offer a compromise between conventional diesel-electric and nuclear-powered submarines. They can stay submerged for longer periods than traditional diesel-electric submarines and are quieter than nuclear ones, with speeds comparable to or slightly higher than diesel-electric submarines.Operational Considerations and Speed

Mission Objectives
The speed at which a submarine operates can be tailored to its mission. For surveillance or reconnaissance missions, slower speeds may be preferred to maintain stealth and gather detailed information. In contrast, for rapid deployment or pursuit scenarios, maximum speed may be necessary.Water Conditions
The conditions of the water, including its temperature, salinity, and currents, can affect a submarine's speed. Optimal speeds may vary in different environments to maximize efficiency, maneuverability, or stealth.Stealth Considerations
Maintaining stealth is a critical aspect of submarine operations. Speed can be adjusted to minimize noise generation, with slower speeds generally being quieter. However, there are situations where the need for speed outweighs the requirement for stealth, necessitating a balanced approach to operational planning.Future Developments in Submarine Speed

Advanced Propulsion Systems
Research into new propulsion systems, such as advanced diesel-electric hybrids, fuel cells, and potentially even more exotic propulsion methods, could lead to significant improvements in submarine speed and endurance.Materials and Design
Advancements in materials science and computational design tools are enabling the creation of more efficient hull shapes and stronger, lighter materials. These developments can contribute to faster, more agile submarines with improved depth capabilities.Autonomous Systems
The integration of autonomous systems and artificial intelligence into submarine operations could revolutionize how speed and maneuverability are utilized in future missions, potentially enabling more complex and dynamic operational scenarios.Submarine Speed Image Gallery



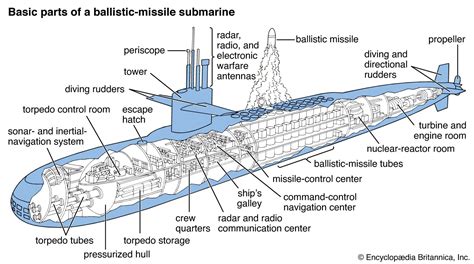




What is the fastest type of submarine?
+Nuclear-powered submarines are the fastest type, with some models capable of exceeding 25 knots (46 km/h) when submerged.
How does the hull design affect a submarine's speed?
+The hull design affects a submarine's speed by influencing its hydrodynamics and drag. Streamlined hulls can reduce drag and enhance speed.
What role does stealth play in submarine operations and speed?
+Stealth is critical in submarine operations, and speed can be adjusted to minimize noise generation. Slower speeds are generally quieter, but there are situations where the need for speed outweighs the requirement for stealth.
How are future developments in submarine technology expected to impact speed?
+Future developments, including advanced propulsion systems, new materials, and design innovations, are expected to enhance submarine speed, stealth, and operational capabilities.
What is the importance of autonomous systems in future submarine operations?
+Autonomous systems are expected to revolutionize submarine operations by enabling more complex and dynamic scenarios, potentially enhancing speed and maneuverability in mission execution.
As we delve into the complexities of submarine speed and its multifaceted influences, it becomes clear that the development and operation of these vessels are at the forefront of maritime technology and strategy. Whether considering the technical aspects of propulsion and design or the operational nuances of stealth and maneuverability, the speed of submarines plays a pivotal role in their effectiveness and utility. As the world looks to the future of submarine technology, with its promises of advanced materials, propulsion systems, and autonomous capabilities, the importance of understanding and optimizing submarine speed will only continue to grow. We invite readers to share their thoughts and insights on the future of submarine technology and its implications for global maritime security and operations. Your perspectives and comments are invaluable in fostering a deeper understanding of this critical aspect of modern naval capabilities.
