Intro
Discover how catapults work, exploring their mechanism, physics, and engineering, including torsion, tension, and projectile motion, to understand these medieval siege engines.
The concept of catapults has been around for centuries, with ancient civilizations using these devices to launch projectiles over long distances. From medieval sieges to modern-day competitions, catapults have played a significant role in shaping human history. But have you ever wondered how these machines work? In this article, we'll delve into the fascinating world of catapults and explore their working mechanisms in detail.
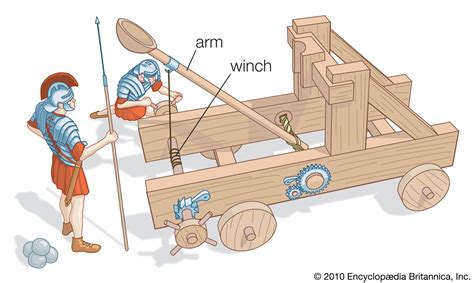
Catapults are complex devices that rely on a combination of physics and engineering to propel objects through the air. At their core, catapults consist of a few key components, including a throwing arm, a counterweight, and a torsion spring. The throwing arm is the long, wooden or metal beam that propels the projectile, while the counterweight is the heavy object that provides the energy needed to launch the projectile. The torsion spring, on the other hand, is the coiled piece of wood or metal that stores energy as the catapult is loaded.
As we explore the world of catapults, it's essential to understand the historical context in which they were developed. From ancient Greece to medieval Europe, catapults were used as powerful siege engines, capable of breaching fortifications and destroying enemy strongholds. The earliest catapults were simple devices, relying on torsion or tension to propel projectiles. However, as technology improved, catapults became more sophisticated, with the addition of counterweights and other mechanisms to increase their range and accuracy.
Introduction to Catapults
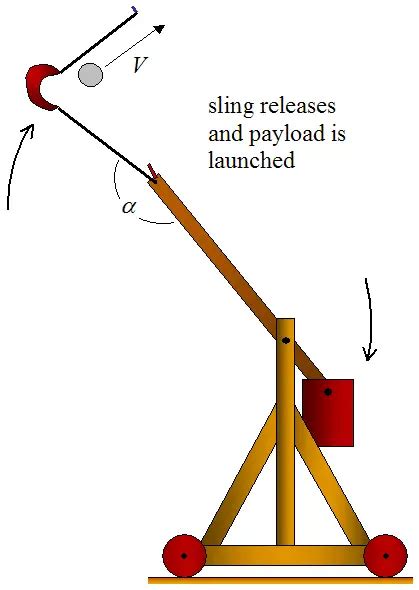
The basic principle behind a catapult is simple: as the counterweight falls, it transfers its energy to the throwing arm, which then propels the projectile into the air. This process relies on the concept of conservation of energy, where the potential energy stored in the counterweight is converted into kinetic energy as the projectile is launched. By adjusting the size and weight of the counterweight, as well as the length and angle of the throwing arm, catapult operators can control the range and accuracy of their projectiles.
In addition to their historical significance, catapults have also played a crucial role in modern-day competitions and events. From pumpkin-chucking contests to medieval reenactments, catapults continue to fascinate audiences with their raw power and precision. Whether used for entertainment or education, catapults offer a unique glimpse into the world of physics and engineering, demonstrating the fundamental principles that govern our universe.
History of Catapults
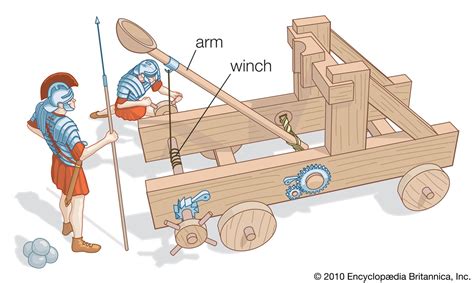
The history of catapults dates back to ancient Greece, where they were used as siege engines to breach fortifications. The earliest catapults were simple devices, relying on torsion or tension to propel projectiles. However, as technology improved, catapults became more sophisticated, with the addition of counterweights and other mechanisms to increase their range and accuracy. During the Middle Ages, catapults played a crucial role in medieval warfare, with armies using them to attack enemy strongholds and fortifications.
One of the most significant advantages of catapults is their ability to launch projectiles over long distances. By adjusting the size and weight of the counterweight, as well as the length and angle of the throwing arm, catapult operators can control the range and accuracy of their projectiles. This makes catapults ideal for siege warfare, where the goal is to breach enemy fortifications or destroy enemy strongholds. Additionally, catapults can be used to launch a variety of projectiles, from stones and rocks to flaming arrows and other incendiary devices.
Types of Catapults
There are several types of catapults, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. The most common types of catapults include:
- Torsion catapults: These catapults rely on twisted animal sinew or human hair to store energy.
- Tension catapults: These catapults rely on stretched animal sinew or human hair to store energy.
- Counterweight catapults: These catapults rely on a heavy counterweight to store energy.
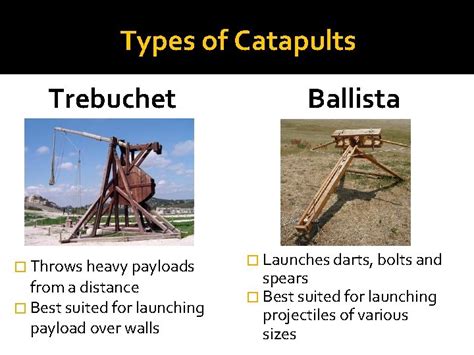
- Trebuchet catapults: These catapults rely on a combination of counterweight and torsion to store energy.
Each type of catapult has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of which one to use depends on the specific application and requirements. For example, torsion catapults are ideal for launching small projectiles over short distances, while counterweight catapults are better suited for launching larger projectiles over longer distances.
Working Mechanism of Catapults

The working mechanism of catapults is based on the principle of conservation of energy. As the counterweight falls, it transfers its energy to the throwing arm, which then propels the projectile into the air. This process relies on the concept of potential energy, where the energy stored in the counterweight is converted into kinetic energy as the projectile is launched.
The key components of a catapult include:
- Throwing arm: This is the long, wooden or metal beam that propels the projectile.
- Counterweight: This is the heavy object that provides the energy needed to launch the projectile.
- Torsion spring: This is the coiled piece of wood or metal that stores energy as the catapult is loaded.
- Trigger: This is the mechanism that releases the energy stored in the torsion spring, allowing the catapult to launch the projectile.
By adjusting the size and weight of the counterweight, as well as the length and angle of the throwing arm, catapult operators can control the range and accuracy of their projectiles. This makes catapults ideal for a variety of applications, from siege warfare to modern-day competitions and events.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Catapults
Catapults have several advantages and disadvantages, depending on the specific application and requirements. Some of the advantages of catapults include:
- High range and accuracy: Catapults can launch projectiles over long distances with high accuracy.
- Versatility: Catapults can be used to launch a variety of projectiles, from stones and rocks to flaming arrows and other incendiary devices.
- Low cost: Catapults are relatively inexpensive to build and maintain, making them an attractive option for siege warfare and other applications.
However, catapults also have several disadvantages, including:
- Limited payload capacity: Catapults can only launch projectiles of a certain size and weight, limiting their effectiveness in certain situations.
- Slow reload time: Catapults can take several minutes to reload, making them less effective in rapid-fire situations.
- Vulnerability to countermeasures: Catapults can be vulnerable to countermeasures, such as enemy catapults or other siege engines.
Modern-Day Applications of Catapults

Despite their historical origins, catapults continue to have modern-day applications. From pumpkin-chucking contests to medieval reenactments, catapults offer a unique glimpse into the world of physics and engineering. Additionally, catapults are used in a variety of educational settings, such as physics and engineering classes, to demonstrate fundamental principles and concepts.
Some of the modern-day applications of catapults include:
- Entertainment: Catapults are used in a variety of entertainment settings, such as medieval reenactments and pumpkin-chucking contests.
- Education: Catapults are used in educational settings, such as physics and engineering classes, to demonstrate fundamental principles and concepts.
- Research: Catapults are used in research settings, such as materials science and engineering, to test and develop new materials and technologies.
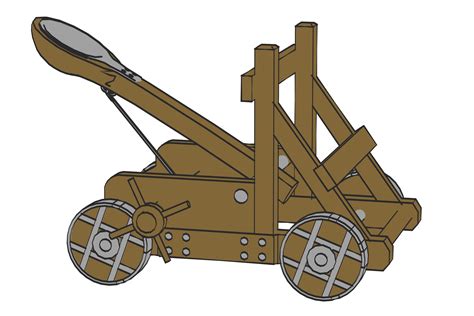
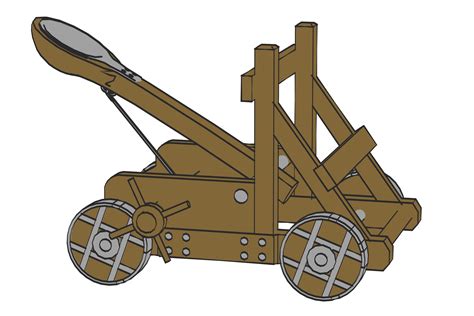
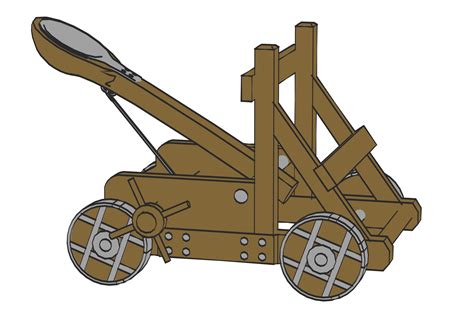
Gallery of Catapults
Catapults Image Gallery





Frequently Asked Questions
What is a catapult?
+A catapult is a device that uses a combination of physics and engineering to launch projectiles over long distances.
How does a catapult work?
+A catapult works by using a counterweight to store energy, which is then transferred to the throwing arm as the counterweight falls.
What are the advantages of catapults?
+Catapults have several advantages, including high range and accuracy, versatility, and low cost.
What are the disadvantages of catapults?
+Catapults have several disadvantages, including limited payload capacity, slow reload time, and vulnerability to countermeasures.
What are the modern-day applications of catapults?
+Catapults have several modern-day applications, including entertainment, education, and research.
As we conclude our exploration of catapults, we hope that you have gained a deeper understanding of these fascinating devices. From their historical origins to their modern-day applications, catapults continue to captivate audiences with their raw power and precision. Whether used for entertainment, education, or research, catapults offer a unique glimpse into the world of physics and engineering, demonstrating the fundamental principles that govern our universe. We encourage you to share your thoughts and questions about catapults in the comments below, and to explore the many resources available online to learn more about these incredible machines.
