Intro
The high bypass ratio turbofan engine has revolutionized the aviation industry with its exceptional efficiency, reduced noise, and lower emissions. This type of engine has become the backbone of modern commercial aviation, powering many of the world's most popular airliners. The importance of high bypass ratio turbofan engines cannot be overstated, as they have enabled the development of more efficient, comfortable, and environmentally friendly air travel.
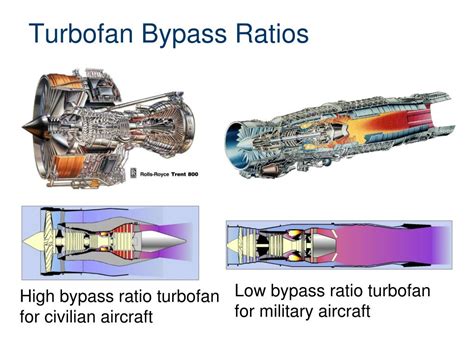
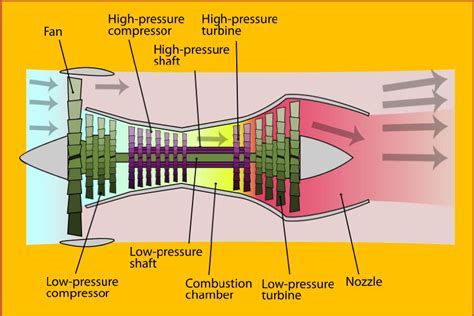
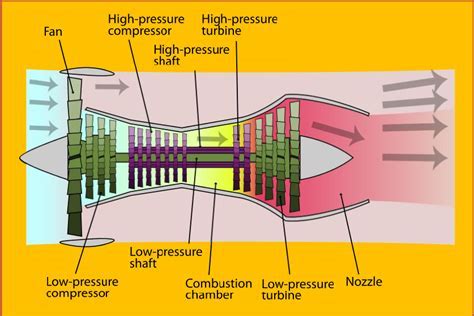
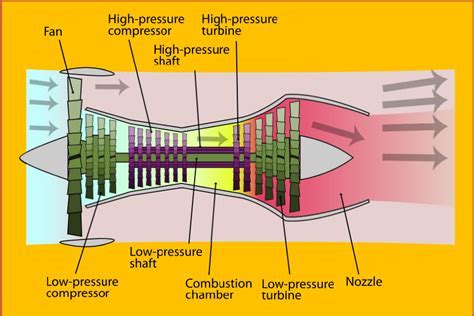
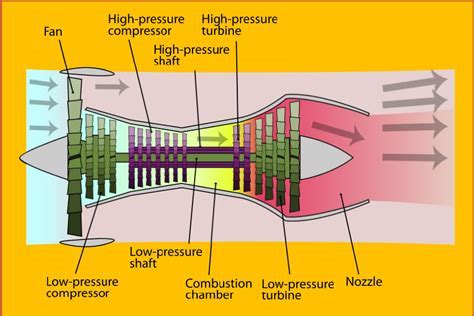
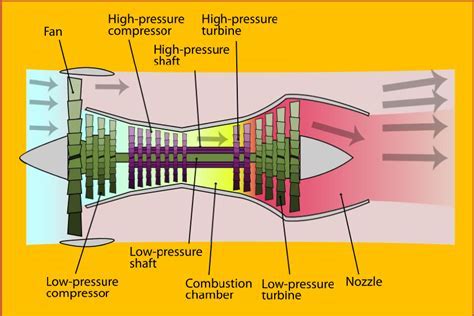
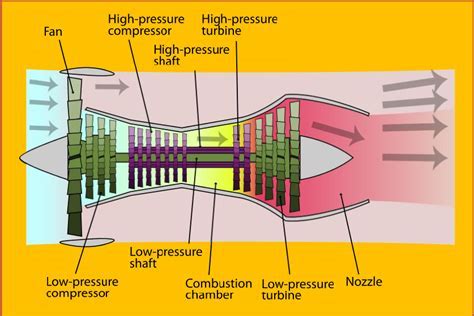
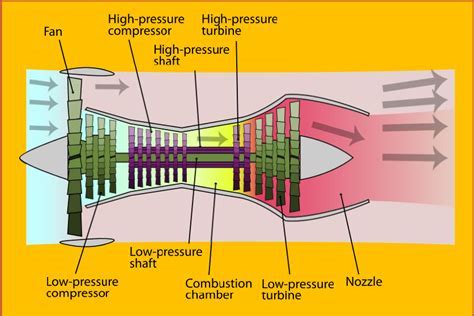
The high bypass ratio turbofan engine is a type of jet engine that uses a large fan at the front to accelerate a significant portion of the air that enters the engine. This fan, which can be up to 10 feet in diameter, accelerates the air to high speeds, creating a large amount of thrust. The remaining air is compressed and mixed with fuel, which is then ignited, producing a high-temperature and high-pressure gas that expands through a turbine, driving the fan and the compressor. The high bypass ratio refers to the fact that a large proportion of the air that enters the engine bypasses the core engine, instead being accelerated by the fan.
The benefits of high bypass ratio turbofan engines are numerous. They offer significant improvements in fuel efficiency, with some engines achieving reductions in fuel consumption of up to 20% compared to older engine designs. This not only reduces operating costs for airlines but also decreases the environmental impact of air travel. Additionally, high bypass ratio turbofan engines are much quieter than older engine designs, reducing noise pollution and making them more suitable for operation in urban areas.
History of High Bypass Ratio Turbofan Engines

The development of high bypass ratio turbofan engines began in the 1960s, with the introduction of the first high bypass turbofan engine, the Rolls-Royce Conway. This engine, which powered the Boeing 707 and Douglas DC-8, was the first to use a large fan at the front to accelerate a significant portion of the air that entered the engine. However, it was not until the 1970s, with the introduction of the General Electric CF6 and the Pratt & Whitney JT8D, that high bypass ratio turbofan engines became widely used in commercial aviation.
Key Components of High Bypass Ratio Turbofan Engines
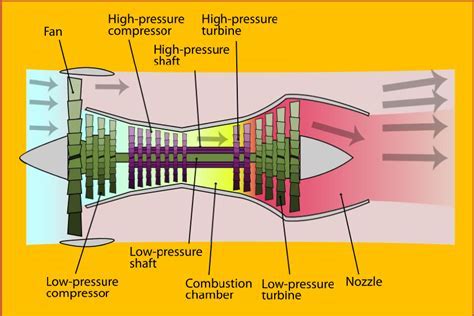
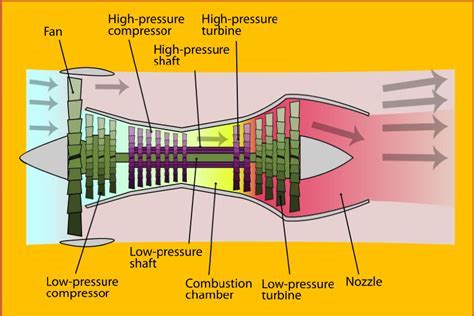
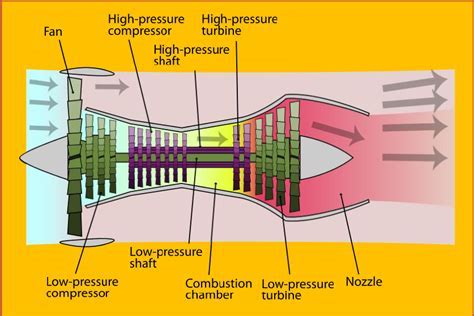
The key components of a high bypass ratio turbofan engine include the fan, the compressor, the combustor, the turbine, and the nozzle. The fan, which is located at the front of the engine, is responsible for accelerating a large portion of the air that enters the engine. The compressor, which is driven by the turbine, compresses the air that enters the engine, raising its temperature and pressure. The combustor, where fuel is added to the compressed air, ignites the mixture, producing a high-temperature and high-pressure gas. The turbine, which is driven by the expanding gas, drives the compressor and the fan. The nozzle, which is located at the rear of the engine, accelerates the exhaust gases to high speeds, producing a large amount of thrust.Benefits of High Bypass Ratio Turbofan Engines
The benefits of high bypass ratio turbofan engines are numerous. Some of the key benefits include:
- Improved fuel efficiency: High bypass ratio turbofan engines offer significant improvements in fuel efficiency, with some engines achieving reductions in fuel consumption of up to 20% compared to older engine designs.
- Reduced noise: High bypass ratio turbofan engines are much quieter than older engine designs, reducing noise pollution and making them more suitable for operation in urban areas.
- Lower emissions: High bypass ratio turbofan engines produce fewer emissions than older engine designs, reducing the environmental impact of air travel.
- Increased reliability: High bypass ratio turbofan engines are more reliable than older engine designs, with some engines achieving time between overhauls of up to 20,000 hours.
Applications of High Bypass Ratio Turbofan Engines
High bypass ratio turbofan engines are used in a wide range of applications, including commercial aviation, military aviation, and business aviation. Some of the most common applications include: * Commercial airliners: High bypass ratio turbofan engines are used to power many of the world's most popular commercial airliners, including the Boeing 737, 747, 767, and 777, and the Airbus A320, A330, and A350. * Military aircraft: High bypass ratio turbofan engines are used to power many military aircraft, including the Boeing F-15 and F/A-18, and the Lockheed Martin F-22 and F-35. * Business aircraft: High bypass ratio turbofan engines are used to power many business aircraft, including the Gulfstream G650 and the Bombardier Global 7500.Future Developments in High Bypass Ratio Turbofan Engines
The future of high bypass ratio turbofan engines is exciting, with many new developments and technologies being researched and developed. Some of the key areas of research include:
- Advanced materials: New materials, such as advanced composites and alloys, are being developed to improve the efficiency and durability of high bypass ratio turbofan engines.
- Electric propulsion: Electric propulsion systems, which use electric motors to drive the fan and compressor, are being developed to improve the efficiency and reduce the emissions of high bypass ratio turbofan engines.
- Hybrid propulsion: Hybrid propulsion systems, which combine traditional fossil-fuel engines with electric motors, are being developed to improve the efficiency and reduce the emissions of high bypass ratio turbofan engines.
Challenges Facing High Bypass Ratio Turbofan Engines
Despite the many benefits of high bypass ratio turbofan engines, there are several challenges facing the industry. Some of the key challenges include: * Emissions: High bypass ratio turbofan engines produce emissions, including carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, which contribute to climate change and air pollution. * Noise: High bypass ratio turbofan engines can be noisy, particularly during takeoff and landing, which can be a problem for communities located near airports. * Cost: High bypass ratio turbofan engines are complex and expensive to develop and maintain, which can make them inaccessible to some airlines and operators.Gallery of High Bypass Ratio Turbofan Engines
High Bypass Ratio Turbofan Engine Image Gallery

Frequently Asked Questions
What is a high bypass ratio turbofan engine?
+A high bypass ratio turbofan engine is a type of jet engine that uses a large fan at the front to accelerate a significant portion of the air that enters the engine.
What are the benefits of high bypass ratio turbofan engines?
+The benefits of high bypass ratio turbofan engines include improved fuel efficiency, reduced noise, and lower emissions.
What are the applications of high bypass ratio turbofan engines?
+High bypass ratio turbofan engines are used in a wide range of applications, including commercial aviation, military aviation, and business aviation.
In conclusion, high bypass ratio turbofan engines have revolutionized the aviation industry with their exceptional efficiency, reduced noise, and lower emissions. As the industry continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see even more advanced and efficient engine designs, such as electric and hybrid propulsion systems. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on this topic, and to explore the many resources and references available for further learning. Whether you are an aviation professional, a student, or simply an enthusiast, we hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive and informative overview of high bypass ratio turbofan engines.
