Intro
Discover 3 pivotal ways World War started, exploring historical triggers, diplomatic crises, and military invasions that sparked global conflict, revealing causes and consequences.
The onset of World War I, World War II, and other global conflicts have been subjects of extensive study and debate among historians. Understanding the causes and events leading up to these wars is crucial for grasping the complexities of international relations, diplomacy, and the consequences of political and military actions. In this context, examining how world wars started can provide valuable insights into the dynamics of global conflict and the importance of diplomacy and international cooperation.
The world has witnessed several global conflicts, but the most notable ones are World War I and World War II. These wars involved multiple countries and resulted in significant loss of life and widespread destruction. The causes of these wars are multifaceted and involve a combination of political, economic, and social factors. To understand how world wars started, it's essential to look at the specific events and circumstances that led to the outbreak of these conflicts.
World War I, for example, was sparked by the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary in 1914. This event triggered a chain reaction of diplomatic crises and military mobilizations that eventually led to the outbreak of war. The complex system of alliances between European powers, including the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance, played a significant role in the escalation of the conflict. The war involved many countries, including major powers like Germany, France, Britain, and the United States, and resulted in one of the deadliest conflicts in history.
Similarly, World War II was caused by a combination of factors, including the rise of fascist and nationalist ideologies in Europe and Asia, the policy of appeasement, and the aggressive expansion of Germany, Italy, and Japan. The invasion of Poland by Germany in 1939 is often cited as the immediate cause of the war. However, the roots of the conflict go back to the aftermath of World War I and the Treaty of Versailles, which imposed harsh penalties on Germany and contributed to widespread resentment and a desire for revenge.
In both cases, the start of the war was the result of a complex interplay of factors, including political tensions, economic rivalries, and social unrest. Understanding these factors is essential for grasping the dynamics of global conflict and the importance of diplomacy and international cooperation in preventing future wars.
Causes of World War I

The system of alliances, which divided Europe into two opposing camps, played a significant role in the outbreak of the war. The Triple Entente, consisting of France, Britain, and Russia, and the Triple Alliance, consisting of Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy, created a situation in which a small conflict between two countries could quickly escalate into a larger war.
Imperialism was another significant factor that contributed to the outbreak of World War I. The competition for colonies and resources in Africa and Asia created tensions between European powers, particularly between Britain, France, and Germany.
Militarism, or the glorification of military power, also played a significant role in the outbreak of the war. The buildup of military forces and the emphasis on military strength created an atmosphere in which war was seen as a viable solution to international disputes.
Nationalism, or the emphasis on national identity and the desire for self-determination, was another significant factor that contributed to the outbreak of the war. The rise of nationalist movements in various parts of Europe, particularly in the Balkans, created tensions and conflicts that eventually led to the war.
Causes of World War II

The Treaty of Versailles, which ended World War I, imposed harsh penalties on Germany, including significant territorial losses and reparations. This created widespread resentment and a desire for revenge among the German people, which contributed to the rise of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party.
The rise of fascist and nationalist ideologies in Europe and Asia also played a significant role in the outbreak of World War II. The aggressive expansion of Germany, Italy, and Japan, and the desire for territorial conquest and domination, created an atmosphere in which war was seen as a viable solution to international disputes.
The policy of appeasement, pursued by Britain and France, also contributed to the outbreak of the war. The decision to give in to Germany's demands, particularly with regard to the annexation of Austria and the Sudetenland, created an atmosphere in which Hitler believed that he could pursue his aggressive expansion without facing significant opposition.
Key Events Leading to World War I
The key events leading to World War I include the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the diplomatic crisis that followed, and the subsequent declarations of war. The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, which occurred on June 28, 1914, triggered a chain reaction of diplomatic crises and military mobilizations that eventually led to the outbreak of war.The diplomatic crisis that followed the assassination involved a complex series of events, including the ultimatum issued by Austria-Hungary to Serbia, the mobilization of Russian troops, and the declaration of war by Germany against Russia and France.
The subsequent declarations of war, including the declaration of war by Britain against Germany, marked the beginning of World War I. The war involved many countries, including major powers like Germany, France, Britain, and the United States, and resulted in one of the deadliest conflicts in history.
Key Events Leading to World War II
The key events leading to World War II include the invasion of Poland by Germany, the declaration of war by France and Britain, and the subsequent expansion of the war to include other countries. The invasion of Poland, which occurred on September 1, 1939, marked the beginning of World War II.The declaration of war by France and Britain, which occurred on September 3, 1939, marked the beginning of the war in Western Europe. The subsequent expansion of the war to include other countries, including the Soviet Union, the United States, and Japan, marked the beginning of a global conflict that would involve many countries and result in significant loss of life and widespread destruction.
Comparison of World War I and World War II
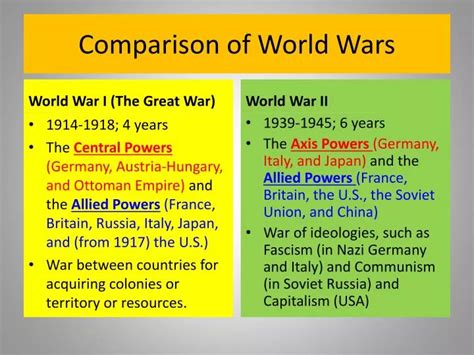
One of the main similarities between the two wars is the involvement of multiple countries. Both wars involved many countries, including major powers like Germany, France, Britain, and the United States.
Another similarity between the two wars is the significant loss of life and widespread destruction. Both wars resulted in millions of deaths and widespread destruction, particularly in Europe and Asia.
However, there are also some significant differences between the two wars. One of the main differences is the causes of the wars. World War I was caused by a complex series of events, including the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand and the subsequent diplomatic crisis. World War II, on the other hand, was caused by the aggressive expansion of Germany, Italy, and Japan, and the desire for territorial conquest and domination.
Another difference between the two wars is the outcome. World War I resulted in the defeat of the Central Powers, including Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire. World War II, on the other hand, resulted in the defeat of the Axis powers, including Germany, Italy, and Japan.
Lessons Learned from World War I and World War II
The lessons learned from World War I and World War II are significant and far-reaching. One of the main lessons is the importance of diplomacy and international cooperation in preventing future wars. The failure of diplomacy and the lack of international cooperation contributed to the outbreak of both wars.Another lesson learned from the two wars is the importance of addressing the root causes of conflict. The failure to address the root causes of conflict, including poverty, inequality, and political oppression, contributed to the outbreak of both wars.
The importance of promoting peace and stability is another lesson learned from the two wars. The promotion of peace and stability, particularly in regions prone to conflict, is essential for preventing future wars.
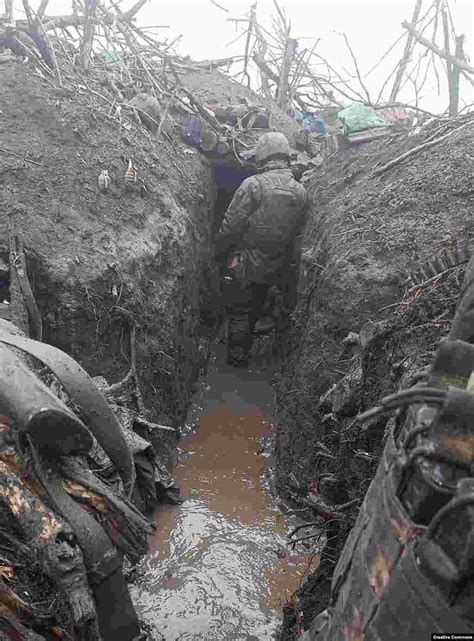
Gallery of World War Images
World War Image Gallery










Frequently Asked Questions
What were the main causes of World War I?
+The main causes of World War I were the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the system of alliances, imperialism, militarism, and nationalism.
What were the main causes of World War II?
+The main causes of World War II were the aggressive expansion of Germany, Italy, and Japan, the policy of appeasement, and the rise of fascist and nationalist ideologies.
What were the key events leading to World War I?
+The key events leading to World War I were the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the diplomatic crisis that followed, and the subsequent declarations of war.
What were the key events leading to World War II?
+The key events leading to World War II were the invasion of Poland by Germany, the declaration of war by France and Britain, and the subsequent expansion of the war to include other countries.
What are the lessons learned from World War I and World War II?
+The lessons learned from World War I and World War II include the importance of diplomacy and international cooperation, addressing the root causes of conflict, and promoting peace and stability.
In final thoughts, understanding how world wars started is crucial for grasping the complexities of international relations, diplomacy, and the consequences of political and military actions. By examining the causes and events leading up to these wars, we can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of global conflict and the importance of diplomacy and international cooperation in preventing future wars. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and opinions on this topic, and to explore further the complexities of world wars and their impact on global history.
