Intro
Explore Germanys debt to GDP ratio, including public debt, fiscal policy, and economic impact, to understand its financial stability and sovereign credit rating amidst EU debt crisis and global market trends.
The debt-to-GDP ratio is a crucial indicator of a country's economic health, and Germany is no exception. As one of the world's leading economies, Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio is closely watched by economists, investors, and policymakers alike. In this article, we will delve into the importance of the debt-to-GDP ratio, its current state in Germany, and the factors that influence it.
Germany's economy is known for its stability and resilience, with a strong manufacturing sector, a highly skilled workforce, and a favorable business environment. However, like many other countries, Germany has not been immune to the challenges posed by the global financial crisis, the European sovereign-debt crisis, and the COVID-19 pandemic. These events have led to an increase in Germany's debt levels, which has raised concerns about the country's fiscal sustainability.
The debt-to-GDP ratio is a simple yet effective metric that measures a country's debt burden relative to its economic output. It is calculated by dividing the total government debt by the country's GDP. A high debt-to-GDP ratio can indicate that a country is over-indebted and may struggle to service its debt, while a low ratio suggests that a country has a more manageable debt burden.
Understanding Germany's Debt-to-GDP Ratio
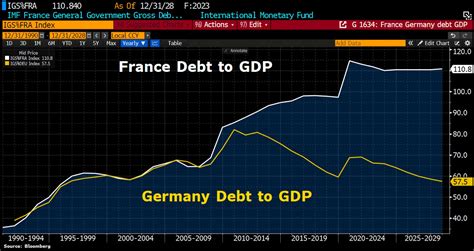
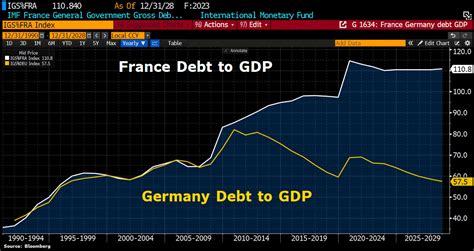
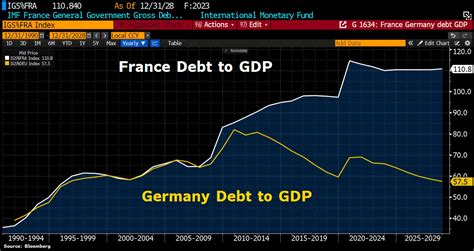
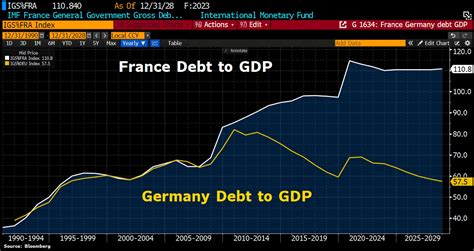
Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio has fluctuated over the years, influenced by various factors such as government spending, taxation, and economic growth. In the early 2000s, Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio was relatively low, around 50%. However, the global financial crisis and the subsequent European sovereign-debt crisis led to a significant increase in Germany's debt levels. By 2010, the debt-to-GDP ratio had risen to around 80%, and it continued to climb in the following years.
In recent years, Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio has stabilized, thanks to a combination of fiscal consolidation efforts and robust economic growth. According to the latest data from the German Federal Statistical Office, the debt-to-GDP ratio stood at around 59% in 2022. While this is still above the European Union's benchmark of 60%, it is a significant improvement from the peak of over 80% in 2010.
Factors Influencing Germany's Debt-to-GDP Ratio
Several factors contribute to Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio, including:
- Government spending: Germany's government spending has increased in recent years, driven by rising social expenditure, infrastructure investments, and defense spending.
- Taxation: Germany's tax revenue has been relatively stable, but the country has implemented various tax cuts and reforms to boost economic growth.
- Economic growth: Germany's economy has experienced robust growth in recent years, driven by a strong manufacturing sector, a highly skilled workforce, and a favorable business environment.
- Demographics: Germany's aging population and low birth rates pose significant challenges to the country's fiscal sustainability, as a smaller workforce will have to support a larger retired population.
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio. The government has implemented various measures to mitigate the economic impact of the pandemic, including fiscal stimulus packages, loan guarantees, and social support programs. These measures have led to an increase in government spending and a decline in tax revenue, resulting in a higher debt-to-GDP ratio.Challenges and Opportunities

Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio poses both challenges and opportunities for the country's economy. On the one hand, a high debt-to-GDP ratio can limit the government's ability to respond to future economic shocks and may lead to higher borrowing costs. On the other hand, a relatively low debt-to-GDP ratio compared to other European countries provides Germany with some flexibility to implement fiscal policies that support economic growth.
To address the challenges posed by its debt-to-GDP ratio, Germany has implemented various fiscal consolidation measures, including:
- Reducing government spending: Germany has implemented various measures to reduce government spending, including cuts to social expenditure and infrastructure investments.
- Increasing tax revenue: Germany has implemented various tax reforms to boost tax revenue, including the introduction of a financial transaction tax.
- Promoting economic growth: Germany has implemented various measures to promote economic growth, including investments in education and training, and support for start-ups and small businesses.
Comparison with Other European Countries
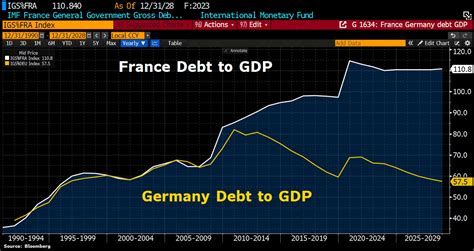
Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio is relatively low compared to other European countries. According to the latest data from the European Commission, the average debt-to-GDP ratio for the euro area stood at around 86% in 2022. Countries such as Greece, Italy, and Portugal have significantly higher debt-to-GDP ratios, while countries such as Denmark and Sweden have lower ratios.
Policy Implications
Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio has significant policy implications for the country's economy. A high debt-to-GDP ratio can limit the government's ability to respond to future economic shocks and may lead to higher borrowing costs. Therefore, it is essential for Germany to maintain a stable and sustainable fiscal policy, including reducing government spending, increasing tax revenue, and promoting economic growth.Gallery of Germany Debt To GDP Ratio
Germany Debt To GDP Ratio Image Gallery






Frequently Asked Questions
What is Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio?
+Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio stood at around 59% in 2022, according to the latest data from the German Federal Statistical Office.
What factors influence Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio?
+Several factors contribute to Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio, including government spending, taxation, economic growth, and demographics.
How does Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio compare to other European countries?
+Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio is relatively low compared to other European countries, with an average debt-to-GDP ratio of around 86% for the euro area in 2022.
What are the policy implications of Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio?
+Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio has significant policy implications, including the need to maintain a stable and sustainable fiscal policy, reduce government spending, increase tax revenue, and promote economic growth.
How can Germany reduce its debt-to-GDP ratio?
+Germany can reduce its debt-to-GDP ratio by implementing fiscal consolidation measures, including reducing government spending, increasing tax revenue, and promoting economic growth.
In conclusion, Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio is a critical indicator of the country's economic health, and it is essential to monitor and manage it effectively. By understanding the factors that influence Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio and implementing appropriate policy measures, the country can maintain a stable and sustainable fiscal policy, reduce its debt burden, and promote economic growth. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on this topic, and we hope that this article has provided valuable insights into Germany's debt-to-GDP ratio and its implications for the country's economy.
