Intro
Compare F15, F16, and F18 fighter jets, highlighting their unique features, combat capabilities, and tactical advantages in aerial warfare, including dogfighting, air superiority, and multirole operations.
The world of military aviation is filled with impressive machines, each designed with specific capabilities and purposes. Among the most renowned fighter jets are the F-15, F-16, and F-18, each serving in various roles and garnering respect for their performance, maneuverability, and firepower. Understanding the differences and similarities between these aircraft can provide insight into the strategic decisions made by military forces and the evolution of aerial combat technology.
The F-15, F-16, and F-18 are products of different design philosophies, reflecting the needs of their time and the vision of their creators. The F-15 Eagle, for instance, was designed as an air superiority fighter, with a focus on beyond-visual-range (BVR) combat and exceptional maneuverability. Its large size, twin engines, and advanced avionics make it a formidable opponent in the skies. The F-16 Fighting Falcon, on the other hand, was conceived as a lightweight, multi-role fighter that could perform a variety of tasks, from air-to-air combat to ground attack missions, with its small size and single engine making it highly agile and cost-effective. The F-18 Hornet, initially designed as a multi-role fighter for the U.S. Navy, combines the attributes of both, offering air-to-air and air-to-ground capabilities with the added feature of carrier compatibility, making it a versatile asset for naval operations.

The design and development of these fighter jets were influenced by the geopolitical climate and technological advancements of their era. The F-15, with its emphasis on air superiority, was a response to the need for a dominant fighter that could counter the emerging threats of the Soviet Union during the Cold War. The F-16, with its multi-role capability and lower operational costs, reflected a shift towards more versatile and affordable military solutions. The F-18, designed with the challenges of naval aviation in mind, including the need for durability, versatility, and the ability to operate from aircraft carriers, underscores the importance of sea-based air power.
Operational History and Combat Performance
Each of these fighter jets has seen action in various conflicts, with their performance in combat providing valuable lessons for military strategists and aircraft designers. The F-15 has an impressive record, with no losses in air-to-air combat, a testament to its design as a superior air fighter. The F-16 has been used in numerous conflicts, showcasing its versatility and effectiveness in both air-to-air and air-to-ground roles. The F-18, with its naval orientation, has played critical roles in conflicts requiring carrier-based air power, demonstrating its capability to perform a wide range of missions.

The operational history of these jets also highlights the importance of adaptability and continuous upgrading. As technology advances and new threats emerge, these aircraft have undergone numerous modernizations to remain relevant. The F-15, for example, has seen significant upgrades, including advanced radar systems and missile capabilities, to maintain its edge in air-to-air combat. The F-16 has also been upgraded, with improvements in avionics, radar, and weaponry, ensuring it remains a capable multi-role fighter. The F-18, particularly in its Super Hornet variant, has incorporated advanced technologies, including stealth capabilities and advanced electronic warfare systems, to enhance its performance in contemporary and future combat environments.
Technological Advancements and Upgrades
The evolution of the F-15, F-16, and F-18 reflects the rapid pace of technological change in the field of military aviation. Advances in materials, electronics, and computer systems have enabled significant improvements in performance, capability, and sustainability. For instance, the integration of advanced radar systems, such as the Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radars, has dramatically enhanced the air-to-air and air-to-ground capabilities of these fighters. Additionally, the development of precision-guided munitions and advanced missile systems has increased their effectiveness in combat, allowing for more precise and less risky engagements.

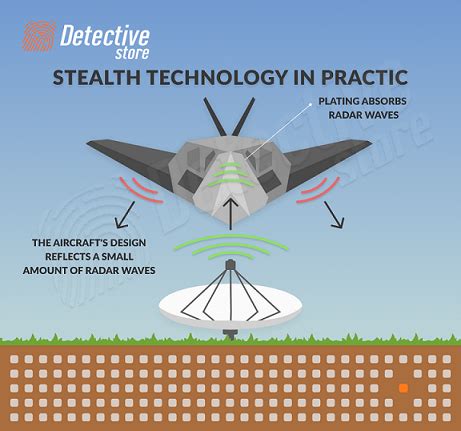
The incorporation of stealth technology, particularly in the F-18's Super Hornet variant, represents a significant leap forward in reducing the radar cross-section of these aircraft, making them less detectable and more survivable in hostile airspace. Furthermore, advancements in pilot interfaces, including the use of helmet-mounted displays and advanced cockpit systems, have enhanced situational awareness and reduced pilot workload, allowing for more effective mission execution.
Comparison of Capabilities
A comparison of the F-15, F-16, and F-18 reveals distinct strengths and weaknesses, each tailored to specific operational requirements. The F-15 excels in air-to-air combat, with its large size, powerful engines, and advanced avionics making it a superior dogfighter and BVR combatant. The F-16, with its smaller size, lower cost, and multi-role capability, is highly effective in a variety of missions, from air defense to ground attack, offering a balance of performance and affordability. The F-18, particularly in its latest variants, combines the attributes of both, with its naval capability, advanced avionics, and stealth features making it a versatile and potent force in modern naval aviation.

The choice between these fighter jets depends on the specific needs of the military force, including the nature of the threats faced, the operational environment, and the budgetary constraints. For air superiority and BVR combat, the F-15 remains a top choice. For multi-role capabilities and cost-effectiveness, the F-16 is highly regarded. For naval operations requiring a balance of air-to-air and air-to-ground performance, along with stealth and advanced avionics, the F-18 is unparalleled.
Future Developments and Replacement Programs
As military aviation continues to evolve, the F-15, F-16, and F-18 are facing challenges from newer, more advanced fighter jets. The development of fifth-generation fighters, such as the F-22 Raptor and the F-35 Lightning II, marks a significant shift towards stealth, advanced avionics, and network-centric warfare. These newer aircraft are designed to operate in highly contested environments, leveraging advanced materials, propulsion systems, and electronic warfare capabilities to maintain air superiority and execute precision strikes.

The future of the F-15, F-16, and F-18 will likely involve continued upgrades and modernizations to extend their service lives and maintain their relevance in the face of emerging threats. However, as the production and deployment of fifth-generation fighters increase, these legacy aircraft will gradually be phased out, making way for the next generation of military aviation technology.
Gallery of Fighter Jets
Fighter Jets Image Gallery









Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary differences between the F-15, F-16, and F-18 fighter jets?
+The F-15 is primarily an air superiority fighter, the F-16 is a multi-role fighter, and the F-18 is a multi-role fighter with naval capabilities. Each has distinct design features, operational roles, and performance characteristics tailored to their specific missions.
Which of these fighter jets has seen the most combat action?
+The F-16 has been involved in numerous conflicts and has seen extensive combat action, given its wide deployment and multi-role capabilities. However, the combat history of these jets can vary based on the specific variant and the military force operating them.
Are the F-15, F-16, and F-18 still in production?
+While the original production runs of these aircraft have concluded, various upgrades and modernization programs continue. Additionally, some variants, like the F-18 Super Hornet, are still being produced or upgraded for existing and new customers.
What are the future plans for these legacy fighter jets?
+As newer, fifth-generation fighters like the F-22 and F-35 enter service, the F-15, F-16, and F-18 will gradually be phased out or upgraded to maintain their relevance. The exact timeline depends on the military's strategic needs and budget considerations.
Can these fighter jets operate in contested airspace?
+Yes, with their advanced avionics, stealth capabilities (in the case of the F-18 Super Hornet), and electronic warfare systems, these jets are designed to operate in contested airspace. However, their effectiveness can vary based on the level of threat and the specific capabilities of the aircraft.
As we delve into the complexities and capabilities of the F-15, F-16, and F-18, it becomes clear that each of these fighter jets has played a significant role in shaping the modern landscape of military aviation. Their operational histories, technological advancements, and future development paths offer valuable insights into the strategic considerations and technological innovations that drive the evolution of air power. Whether you're a military aviation enthusiast, a historian, or simply someone interested in the intricacies of modern warfare, the stories of these iconic aircraft are sure to captivate and inform. We invite you to share your thoughts, ask questions, and explore further the fascinating world of military aviation, where technology, strategy, and human skill come together in the pursuit of air superiority.
