Intro
Discover 5 ways flew techniques to boost online presence, featuring search engine optimization, keyword research, and content marketing strategies for improved visibility.
The world of aviation has seen tremendous growth and innovation over the years, with various airlines and aircraft manufacturers striving to provide the best possible experience for passengers. One aspect that has gained significant attention in recent years is the development of more efficient and environmentally friendly flight systems. In this article, we will delve into the concept of "5 Ways Flew" and explore its significance in the aviation industry.
The term "5 Ways Flew" refers to the five primary methods by which an aircraft can generate lift and stay aloft. These methods include lift generated by the wings, thrust produced by the engines, weight of the aircraft, drag caused by air resistance, and the control surfaces that enable pilots to steer the plane. Understanding these fundamental principles is crucial for designing and operating safe and efficient aircraft.
As the aviation industry continues to evolve, manufacturers and researchers are exploring new ways to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance overall performance. The "5 Ways Flew" concept serves as a foundation for these efforts, providing a framework for analyzing and optimizing the complex interactions between an aircraft's various systems. By grasping the intricacies of lift, thrust, weight, drag, and control, engineers can develop more advanced and sustainable flight technologies.
Introduction to the 5 Ways Flew

Breaking Down the 5 Ways Flew
To gain a deeper understanding of the "5 Ways Flew" concept, it is essential to break down each of its components and explore their roles in the flight process. The following sections will provide an in-depth examination of lift, thrust, weight, drag, and control, highlighting their significance and interrelationships.Lift and Its Role in Flight
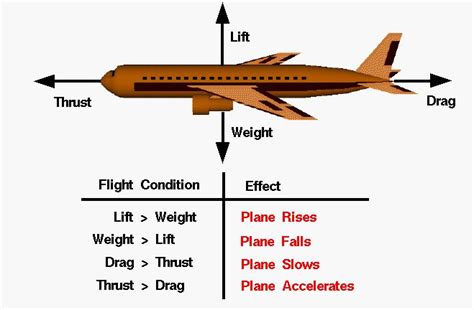
Factors Affecting Lift
Several factors can influence the amount of lift generated by an aircraft's wings, including the shape and size of the wing, the angle of attack, and the air density. Understanding these factors is crucial for designing and operating aircraft that can produce sufficient lift to overcome their weight and stay aloft.Thrust and Its Importance in Flight
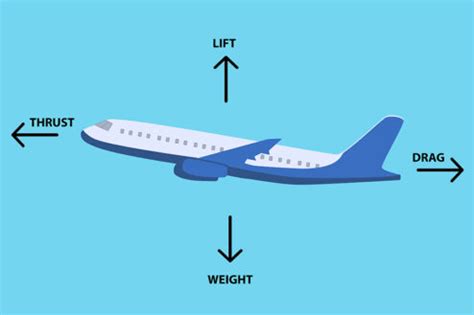
Types of Thrust
There are several types of thrust, including jet thrust, propeller thrust, and rocket thrust. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of thrust type depends on the specific requirements of the aircraft and its intended use.Weight and Its Effect on Flight
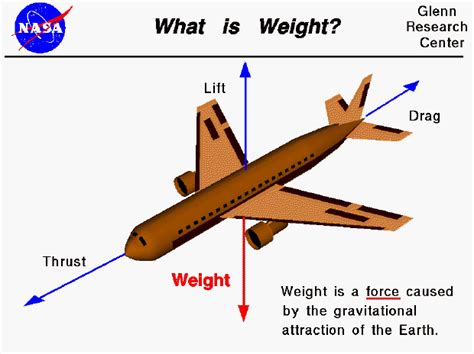
Factors Affecting Weight
Several factors can influence the weight of an aircraft, including its design and construction, the materials used in its build, and the amount of fuel and cargo it carries. Minimizing weight while maintaining strength and stability is a key challenge in aircraft design.Drag and Its Impact on Flight
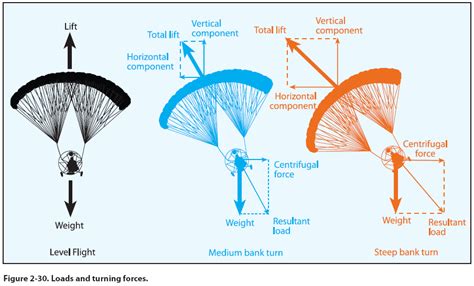
Types of Drag
There are several types of drag, including form drag, friction drag, and induced drag. Each type has its characteristics and effects on aircraft performance, and understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing aircraft design and operation.Control Surfaces and Their Role in Flight
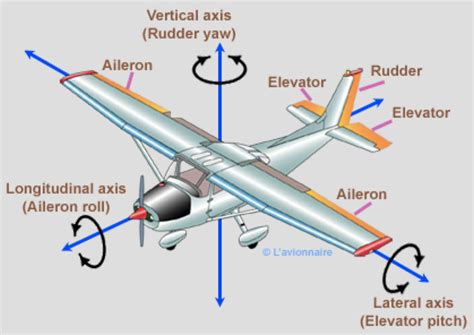
Factors Affecting Control Surface Performance
Several factors can influence the performance of control surfaces, including their design and size, the air density, and the aircraft's speed and altitude. Understanding these factors is crucial for designing and operating aircraft that can respond effectively to pilot inputs and maintain control during various flight regimes.5 Ways Flew Image Gallery

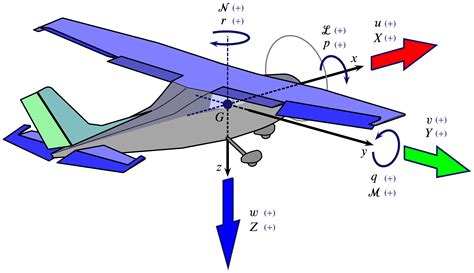
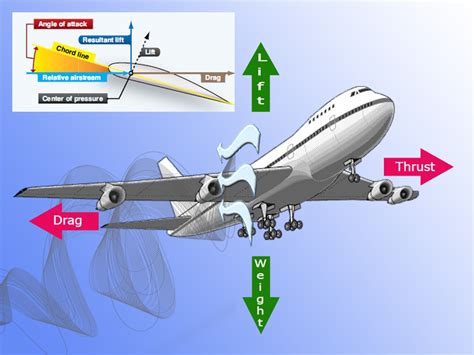

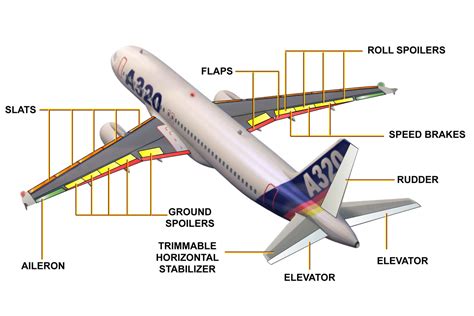





What is the significance of the 5 Ways Flew concept in aviation?
+The 5 Ways Flew concept is essential in aviation as it provides a framework for understanding the fundamental principles of flight, including lift, thrust, weight, drag, and control. By grasping these principles, pilots and engineers can design and operate safe and efficient aircraft.
How do the 5 Ways Flew components interact with each other?
+The 5 Ways Flew components interact with each other in a complex manner. Lift and weight are opposing forces, while thrust and drag are also opposing forces. Control surfaces enable pilots to manipulate the aircraft's motion by adjusting the lift, thrust, and drag forces.
What are the benefits of understanding the 5 Ways Flew concept?
+Understanding the 5 Ways Flew concept provides numerous benefits, including improved aircraft design, enhanced safety, and increased efficiency. By grasping the fundamental principles of flight, pilots and engineers can optimize aircraft performance, reduce fuel consumption, and minimize the risk of accidents.
How can the 5 Ways Flew concept be applied in real-world aviation scenarios?
+The 5 Ways Flew concept can be applied in various real-world aviation scenarios, such as aircraft design, flight planning, and pilot training. By understanding the fundamental principles of flight, pilots and engineers can make informed decisions about aircraft configuration, flight routes, and safety procedures.
What are the future implications of the 5 Ways Flew concept in the aviation industry?
+The 5 Ways Flew concept will continue to play a vital role in the aviation industry, as it provides a foundation for innovation and advancement. As new technologies and materials are developed, the 5 Ways Flew concept will remain essential for designing and operating safe, efficient, and sustainable aircraft.
In conclusion, the "5 Ways Flew" concept is a fundamental principle in aviation that provides a framework for understanding the complex interactions between an aircraft's various systems. By grasping the intricacies of lift, thrust, weight, drag, and control, pilots and engineers can design and operate safe and efficient aircraft. As the aviation industry continues to evolve, the "5 Ways Flew" concept will remain essential for innovation and advancement. We invite readers to share their thoughts and insights on the significance of the "5 Ways Flew" concept and its applications in the aviation industry.
