Intro
Discover the F35 Radar Cross Section, featuring stealth technology, low observability, and reduced radar signatures for enhanced combat survivability and tactical advantage.
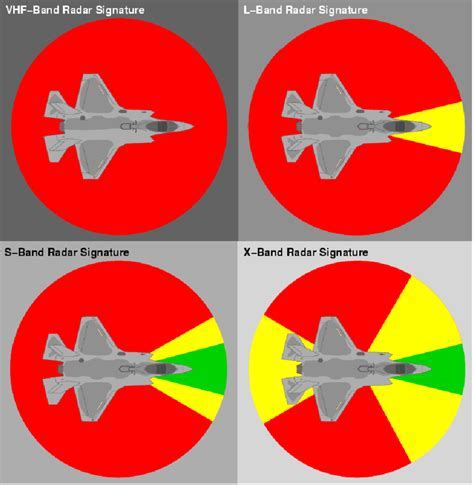
The F35 Lightning II is a fifth-generation, single-seat, single-engine, multirole fighter aircraft developed by Lockheed Martin. One of the key features that make the F35 a stealthy aircraft is its low radar cross-section (RCS). The radar cross-section is a measure of how much radar energy is reflected back to the radar antenna by an object, such as an aircraft. A low RCS means that the aircraft is less visible to radar systems, making it harder to detect and track.
The F35's low RCS is achieved through a combination of design features and materials. The aircraft's shape is designed to scatter radar energy in different directions, reducing the amount of energy that is reflected back to the radar antenna. The F35's skin is also made of advanced materials, such as radar-absorbing materials (RAMs), that absorb radar energy rather than reflecting it. These materials are made up of specialized coatings and paints that are applied to the aircraft's surface.
The F35's low RCS is a critical component of its stealth capability. By reducing the amount of radar energy that is reflected back to the radar antenna, the F35 can evade detection by enemy radar systems. This makes it an ideal aircraft for missions that require a high degree of stealth, such as reconnaissance or strike missions.
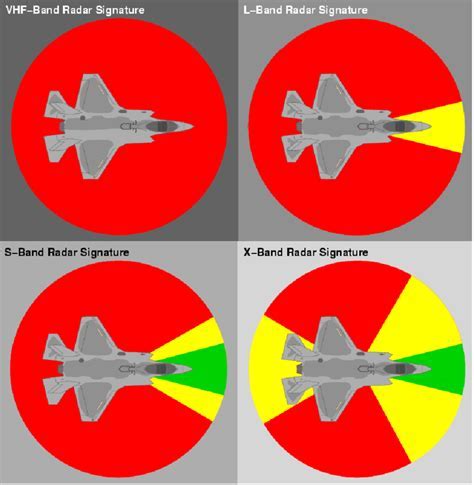
Introduction to Radar Cross Section
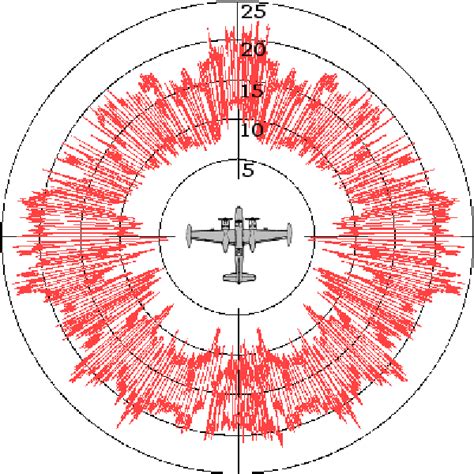
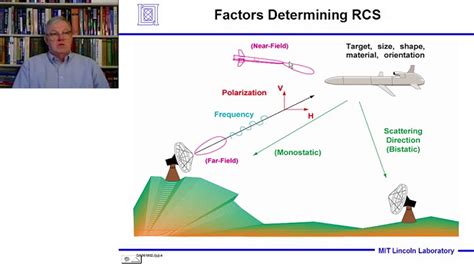
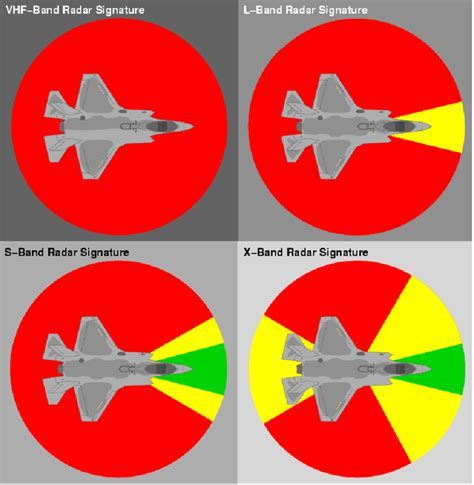
The radar cross-section is a measure of the amount of radar energy that is reflected back to the radar antenna by an object. It is typically measured in square meters (m²) and is a function of the object's size, shape, and material properties. The RCS of an object can be affected by a variety of factors, including its orientation, speed, and distance from the radar antenna.The RCS of an aircraft is a critical factor in its detectability by radar systems. A high RCS means that the aircraft is more visible to radar systems, making it easier to detect and track. Conversely, a low RCS means that the aircraft is less visible to radar systems, making it harder to detect and track.
Factors Affecting Radar Cross Section
There are several factors that can affect the RCS of an aircraft, including:- Size: The larger the aircraft, the higher its RCS.
- Shape: The shape of the aircraft can affect the way that radar energy is scattered, with some shapes scattering energy more efficiently than others.
- Material: The material properties of the aircraft's skin can affect the way that radar energy is absorbed or reflected.
- Orientation: The orientation of the aircraft can affect the way that radar energy is scattered, with some orientations scattering energy more efficiently than others.
- Speed: The speed of the aircraft can affect the way that radar energy is scattered, with faster aircraft scattering energy more efficiently than slower aircraft.
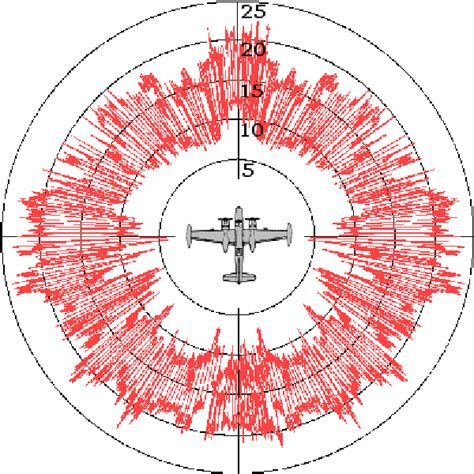
Design Features of the F35
The F35 is designed to have a low RCS, with several design features that contribute to its stealth capability. These include:- Shape: The F35's shape is designed to scatter radar energy in different directions, reducing the amount of energy that is reflected back to the radar antenna.
- Materials: The F35's skin is made of advanced materials, such as RAMs, that absorb radar energy rather than reflecting it.
- Coatings: The F35 is coated with specialized paints and coatings that absorb radar energy.
- Engine: The F35's engine is designed to be stealthy, with a low RCS.
The F35's design features are designed to work together to reduce its RCS. By combining a stealthy shape, advanced materials, and specialized coatings, the F35 is able to achieve a low RCS that makes it difficult to detect by radar systems.

Benefits of Low Radar Cross Section
The F35's low RCS provides several benefits, including:- Increased survivability: By reducing the amount of radar energy that is reflected back to the radar antenna, the F35 is less visible to enemy radar systems, making it harder to detect and track.
- Improved stealth: The F35's low RCS makes it an ideal aircraft for missions that require a high degree of stealth, such as reconnaissance or strike missions.
- Enhanced effectiveness: The F35's low RCS allows it to penetrate enemy airspace without being detected, making it more effective in combat.
The F35's low RCS is a critical component of its overall design, and is a key factor in its ability to evade detection by enemy radar systems.

Challenges and Limitations
While the F35's low RCS provides several benefits, there are also several challenges and limitations associated with its design. These include:- Cost: The F35 is a highly complex and expensive aircraft, with a high development and production cost.
- Maintenance: The F35's advanced materials and coatings require specialized maintenance, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Vulnerability: The F35's low RCS makes it vulnerable to detection by other types of sensors, such as infrared or optical sensors.
Despite these challenges and limitations, the F35's low RCS is a critical component of its overall design, and is a key factor in its ability to evade detection by enemy radar systems.

Future Developments
The F35's low RCS is a critical component of its overall design, and is a key factor in its ability to evade detection by enemy radar systems. As radar technology continues to evolve, it is likely that the F35's design will also evolve to incorporate new materials and technologies that can further reduce its RCS.Some potential future developments that could affect the F35's RCS include:
- Advanced materials: New materials and coatings that can absorb or scatter radar energy more efficiently.
- Design changes: Changes to the F35's shape or design that can reduce its RCS.
- Electronic warfare: The use of electronic warfare systems to detect and disrupt enemy radar systems.
These future developments will likely play a critical role in the ongoing evolution of the F35's design, and will help to ensure that it remains a highly effective and stealthy aircraft.
Gallery of F35 Radar Cross Section
F35 Radar Cross Section Image Gallery


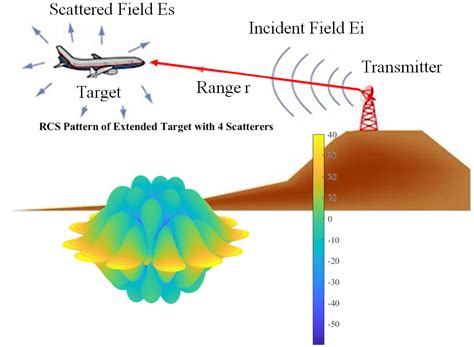

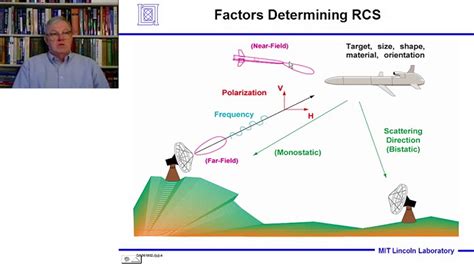
What is the F35's radar cross section?
+The F35's radar cross section is a measure of the amount of radar energy that is reflected back to the radar antenna by the aircraft. It is typically measured in square meters (m²) and is a function of the aircraft's size, shape, and material properties.
How does the F35's design reduce its radar cross section?
+The F35's design features a combination of shape, materials, and coatings that reduce its radar cross section. The aircraft's shape is designed to scatter radar energy in different directions, reducing the amount of energy that is reflected back to the radar antenna. The F35's skin is also made of advanced materials, such as radar-absorbing materials (RAMs), that absorb radar energy rather than reflecting it.
What are the benefits of the F35's low radar cross section?
+The F35's low radar cross section provides several benefits, including increased survivability, improved stealth, and enhanced effectiveness. By reducing the amount of radar energy that is reflected back to the radar antenna, the F35 is less visible to enemy radar systems, making it harder to detect and track.
What are the challenges and limitations of the F35's design?
+The F35's design is highly complex and expensive, with a high development and production cost. The aircraft's advanced materials and coatings require specialized maintenance, which can be time-consuming and expensive. Additionally, the F35's low radar cross section makes it vulnerable to detection by other types of sensors, such as infrared or optical sensors.
What future developments may affect the F35's radar cross section?
+Future developments that may affect the F35's radar cross section include advanced materials, design changes, and electronic warfare systems. These developments may further reduce the F35's radar cross section, making it even more stealthy and effective in combat.
We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the F35's radar cross section and its importance in modern warfare. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about this topic, please do not hesitate to contact us. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about the F35 and its capabilities. By sharing this article, you can help to spread awareness and understanding of this important topic, and contribute to a more informed and knowledgeable community. Thank you for reading!
