Intro
Discover the hierarchy of Air Force ranks, comparing 5 key positions, including responsibilities, pay scales, and promotion requirements, to understand military career progression and advancement opportunities.
The United States Air Force is one of the most prestigious and technologically advanced military branches in the world. With a wide range of career paths and specialties, the Air Force offers numerous opportunities for individuals to serve their country and pursue their passions. At the heart of the Air Force's structure are its ranks, which signify an individual's level of responsibility, expertise, and leadership. In this article, we will delve into five key Air Force ranks, exploring their roles, responsibilities, and requirements.
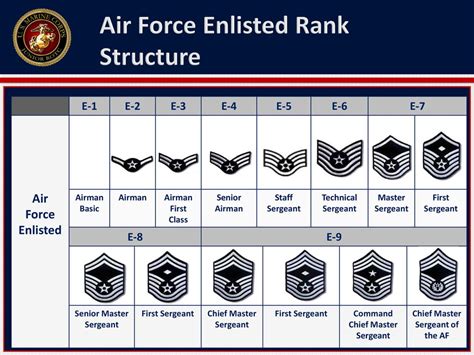
The Air Force ranks are divided into three main categories: enlisted, officer, and warrant officer. Enlisted personnel make up the majority of the Air Force and are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day tasks and operations. Officers, on the other hand, serve as leaders and managers, overseeing enlisted personnel and making strategic decisions. Warrant officers occupy a unique position, possessing specialized technical expertise and serving as advisors to senior officers. Understanding the different ranks and their functions is essential for navigating the Air Force's complex hierarchy.
As we explore the five Air Force ranks, it is essential to recognize the significance of each rank and its contribution to the overall mission of the Air Force. From the entry-level ranks to the senior leadership positions, each rank plays a vital role in ensuring the Air Force's effectiveness and efficiency. Whether you are a seasoned veteran or a new recruit, understanding the Air Force ranks is crucial for success and advancement in your career.
Air Force Ranks Overview
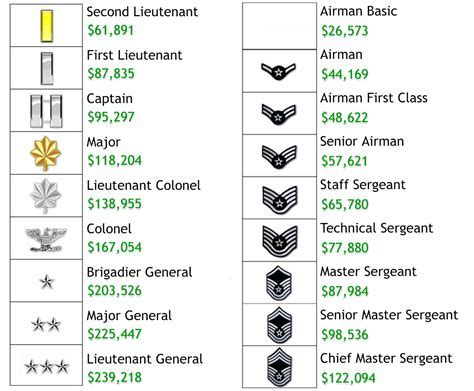
The Air Force ranks are designed to provide a clear chain of command and a well-defined career progression pathway. Each rank has its unique set of responsibilities, challenges, and opportunities. As individuals advance through the ranks, they acquire new skills, assume greater responsibilities, and develop into leaders and experts in their fields. The five Air Force ranks we will be comparing are: Airman (E-2), Airman First Class (E-3), Senior Airman (E-4), Staff Sergeant (E-5), and Technical Sergeant (E-6).
Airman (E-2) Rank
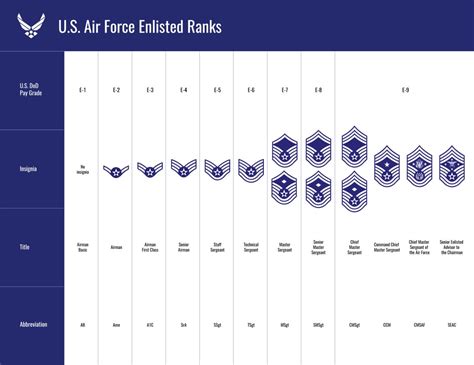
The Airman (E-2) rank is the second-lowest enlisted rank in the Air Force. Airmen typically hold entry-level positions and are still in the process of completing their initial training. At this rank, individuals are expected to demonstrate a basic understanding of Air Force policies, procedures, and core values. Airmen are usually assigned to a specific career field and begin to develop the skills and knowledge necessary for advancement.
Airman Responsibilities
The responsibilities of an Airman include: * Completing initial training and orientation * Developing a basic understanding of Air Force policies and procedures * Assisting senior personnel with daily tasks and operations * Participating in professional development and training programs * Demonstrating a commitment to the Air Force core valuesAirman First Class (E-3) Rank

The Airman First Class (E-3) rank is the third-lowest enlisted rank in the Air Force. At this rank, individuals have typically completed their initial training and have gained some experience in their career field. Airmen First Class are expected to demonstrate a higher level of proficiency and independence, taking on more responsibilities and contributing to team efforts.
Airman First Class Responsibilities
The responsibilities of an Airman First Class include: * Applying learned skills and knowledge in their career field * Assisting in the training and development of junior personnel * Participating in team-building and collaboration efforts * Demonstrating increased independence and self-motivation * Continuing to develop their professional skills and knowledgeSenior Airman (E-4) Rank

The Senior Airman (E-4) rank is a significant milestone in an enlisted Airman's career. At this rank, individuals have typically gained considerable experience and have developed a high level of proficiency in their career field. Senior Airmen are expected to demonstrate strong leadership and technical skills, taking on more complex tasks and responsibilities.
Senior Airman Responsibilities
The responsibilities of a Senior Airman include: * Leading and mentoring junior personnel * Coordinating team efforts and contributing to project planning * Applying advanced technical skills and knowledge * Demonstrating strong communication and problem-solving skills * Continuing to develop their professional skills and knowledgeStaff Sergeant (E-5) Rank

The Staff Sergeant (E-5) rank is a non-commissioned officer (NCO) rank, marking a significant shift in responsibilities and leadership expectations. Staff Sergeants are expected to demonstrate strong leadership and technical skills, taking on supervisory roles and contributing to the development of junior personnel.
Staff Sergeant Responsibilities
The responsibilities of a Staff Sergeant include: * Supervising and leading teams of Airmen * Coordinating and planning projects and operations * Applying advanced technical skills and knowledge * Demonstrating strong leadership and communication skills * Continuing to develop their professional skills and knowledgeTechnical Sergeant (E-6) Rank

The Technical Sergeant (E-6) rank is a senior NCO rank, requiring individuals to demonstrate exceptional technical expertise and leadership skills. Technical Sergeants are expected to serve as subject matter experts, providing guidance and mentorship to junior personnel and contributing to the development of Air Force policies and procedures.
Technical Sergeant Responsibilities
The responsibilities of a Technical Sergeant include: * Serving as a subject matter expert in their career field * Providing guidance and mentorship to junior personnel * Contributing to the development of Air Force policies and procedures * Demonstrating strong leadership and communication skills * Continuing to develop their professional skills and knowledgeAir Force Ranks Image Gallery







What is the highest rank in the Air Force?
+The highest rank in the Air Force is General of the Air Force (five-star general).
How long does it take to advance to the rank of Staff Sergeant?
+The time it takes to advance to the rank of Staff Sergeant varies depending on individual performance and career field, but typically requires 8-12 years of service.
What is the difference between a Technical Sergeant and a Staff Sergeant?
+A Technical Sergeant is a senior NCO rank that requires exceptional technical expertise, while a Staff Sergeant is a non-commissioned officer rank that focuses on leadership and supervision.
Can I join the Air Force as an officer?
+Yes, you can join the Air Force as an officer by attending the Air Force Academy, receiving a commission through the Air Force Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC) program, or by attending Officer Training School (OTS).
What are the core values of the Air Force?
+The core values of the Air Force are Integrity First, Service Before Self, and Excellence in All We Do.
In conclusion, the five Air Force ranks compared in this article demonstrate the complexity and nuance of the Air Force's rank structure. From the entry-level rank of Airman to the senior NCO rank of Technical Sergeant, each rank requires unique skills, knowledge, and leadership abilities. As individuals advance through the ranks, they take on greater responsibilities, develop their professional skills, and contribute to the success of the Air Force. Whether you are a seasoned veteran or a new recruit, understanding the Air Force ranks is essential for navigating the complex hierarchy and achieving success in your career. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the Air Force ranks in the comments section below, and to explore the many resources available for those interested in pursuing a career in the Air Force.
