Intro
Discover the 7 Enlisted Ranks, including Private, Corporal, and Sergeant, understanding military hierarchy, rank structures, and promotion requirements in the armed forces.
The enlisted ranks are the backbone of any military organization, comprising the largest percentage of personnel. These ranks are typically divided into several levels, each with its own set of responsibilities and requirements. In this article, we will explore the 7 enlisted ranks, their roles, and the significance of each rank in the military hierarchy.
The enlisted ranks are crucial to the smooth operation of military units, as they perform a wide range of tasks, from basic maintenance and administration to combat and tactical operations. The 7 enlisted ranks are typically categorized into three main groups: junior enlisted, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), and senior NCOs. Each group has its own set of responsibilities, and personnel are expected to progress through the ranks as they gain experience and develop their skills.
The first group, junior enlisted, comprises the lowest ranks, where new recruits typically start their military careers. These ranks are responsible for learning the basics of military life, including discipline, protocol, and job-specific skills. As personnel progress through the junior enlisted ranks, they take on more responsibilities and begin to develop their leadership skills.
The second group, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), is where personnel begin to take on more significant leadership roles. NCOs are responsible for guiding and mentoring junior personnel, as well as performing more complex tasks and making decisions that impact their units. The NCO ranks are critical to the military, as they provide the link between junior personnel and senior officers.
The third group, senior NCOs, comprises the highest enlisted ranks, where personnel have gained significant experience and expertise. Senior NCOs are responsible for leading and managing large units, making strategic decisions, and providing guidance and counsel to junior personnel. They are also responsible for developing and implementing policies and procedures that impact the entire military organization.
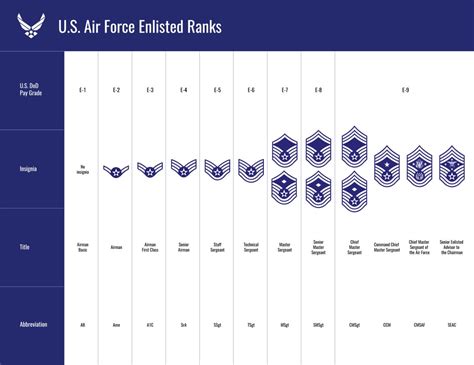
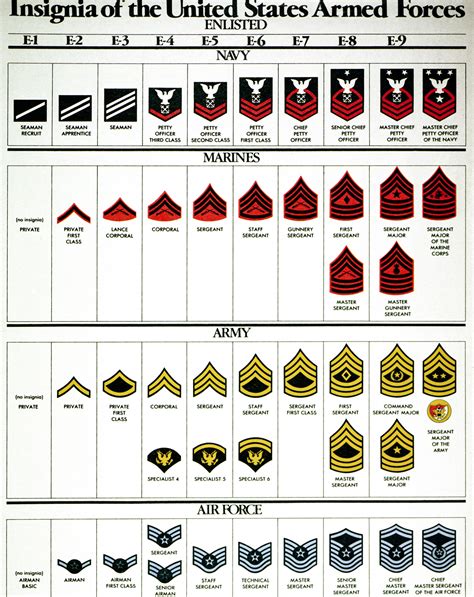
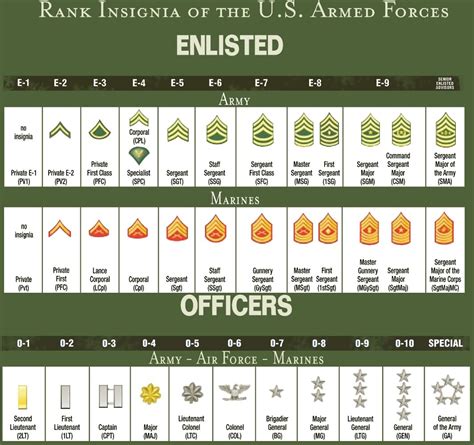
Understanding the 7 Enlisted Ranks
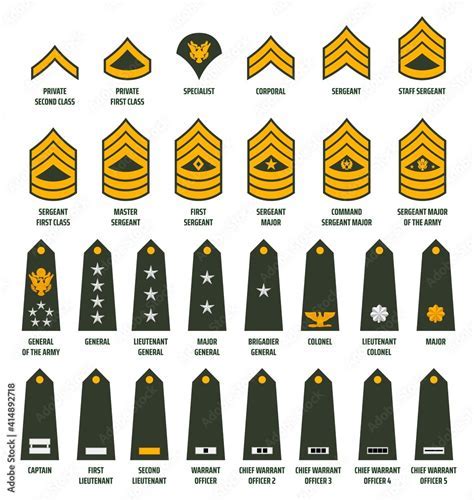

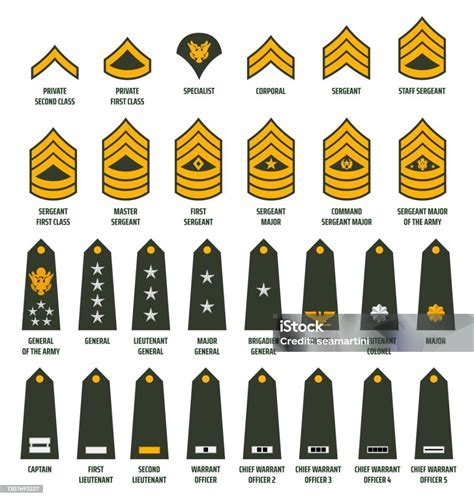
The 7 enlisted ranks are as follows:
- Private (PVT) - The lowest rank in the military, typically held by new recruits.
- Private First Class (PFC) - A junior enlisted rank, where personnel begin to take on more responsibilities.
- Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL) - An NCO rank, where personnel start to develop their leadership skills.
- Sergeant (SGT) - A senior NCO rank, where personnel take on more significant leadership roles.
- Staff Sergeant (SSG) - A senior NCO rank, where personnel are responsible for leading and managing large units.
- Sergeant First Class (SFC) - A senior NCO rank, where personnel have gained significant experience and expertise.
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG) - The highest enlisted rank, where personnel provide guidance and counsel to junior personnel and develop policies and procedures.
Roles and Responsibilities of Each Rank

Each of the 7 enlisted ranks has its own set of roles and responsibilities. Junior enlisted personnel are responsible for learning the basics of military life and performing basic tasks, such as maintenance and administration. NCOs are responsible for guiding and mentoring junior personnel, as well as performing more complex tasks and making decisions that impact their units. Senior NCOs are responsible for leading and managing large units, making strategic decisions, and providing guidance and counsel to junior personnel.
Leadership and Mentorship
Leadership and mentorship are critical components of the enlisted ranks. As personnel progress through the ranks, they are expected to develop their leadership skills and provide guidance and mentorship to junior personnel. This helps to ensure that junior personnel are equipped with the skills and knowledge they need to perform their duties effectively and progress through the ranks.Education and Training

Education and training are essential for personnel in the enlisted ranks. The military provides a wide range of educational and training opportunities, including basic training, advanced individual training, and non-commissioned officer education system (NCOES) courses. These opportunities help personnel develop the skills and knowledge they need to perform their duties effectively and progress through the ranks.
Basic Training
Basic training is the initial training that new recruits receive when they join the military. It is designed to teach personnel the basics of military life, including discipline, protocol, and job-specific skills. Basic training is typically conducted at a military base and lasts for several weeks.Advanced Individual Training
Advanced individual training (AIT) is specialized training that personnel receive after basic training. It is designed to teach personnel the specific skills they need to perform their duties effectively. AIT is typically conducted at a military base or a specialized training facility.Career Progression
Career progression is an important aspect of the enlisted ranks. As personnel gain experience and develop their skills, they can progress through the ranks and take on more significant leadership roles. The military provides a wide range of opportunities for career progression, including education and training, mentorship, and leadership development.
Promotion Requirements
Promotion requirements vary depending on the rank and the military branch. Typically, personnel must meet certain requirements, such as time in service, time in grade, and completion of certain education and training courses. They must also demonstrate leadership potential and a commitment to the military.Challenges and Opportunities

The enlisted ranks present a wide range of challenges and opportunities. Personnel must be prepared to face challenges such as deployment, combat, and leadership responsibilities. However, they also have the opportunity to develop their skills, progress through the ranks, and make a meaningful contribution to their country.
Deployment
Deployment is a significant challenge that personnel in the enlisted ranks may face. Deployment involves being sent to a foreign country or a combat zone, where personnel may be required to perform a wide range of tasks, including combat, security, and humanitarian assistance.Benefits and Rewards

The enlisted ranks offer a wide range of benefits and rewards. Personnel receive competitive pay and benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and education assistance. They also have the opportunity to develop their skills, progress through the ranks, and make a meaningful contribution to their country.
Education Assistance
Education assistance is a significant benefit that personnel in the enlisted ranks can receive. The military provides a wide range of education assistance programs, including the GI Bill, tuition assistance, and education counseling. These programs help personnel pay for college or vocational training, which can help them develop their skills and progress through the ranks.Enlisted Ranks Image Gallery








What are the 7 enlisted ranks in the military?
+The 7 enlisted ranks in the military are: Private (PVT), Private First Class (PFC), Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL), Sergeant (SGT), Staff Sergeant (SSG), Sergeant First Class (SFC), and Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG).
What are the roles and responsibilities of each enlisted rank?
+Each enlisted rank has its own set of roles and responsibilities, ranging from basic tasks and maintenance to leadership and mentorship. Junior enlisted personnel are responsible for learning the basics of military life, while NCOs and senior NCOs take on more significant leadership roles and responsibilities.
How do personnel progress through the enlisted ranks?
+Personnel progress through the enlisted ranks by meeting certain requirements, such as time in service, time in grade, and completion of certain education and training courses. They must also demonstrate leadership potential and a commitment to the military.
What benefits and rewards do personnel in the enlisted ranks receive?
+Personnel in the enlisted ranks receive competitive pay and benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and education assistance. They also have the opportunity to develop their skills, progress through the ranks, and make a meaningful contribution to their country.
What challenges do personnel in the enlisted ranks face?
+Personnel in the enlisted ranks face a wide range of challenges, including deployment, combat, and leadership responsibilities. However, they also have the opportunity to develop their skills, progress through the ranks, and make a meaningful contribution to their country.
In conclusion, the 7 enlisted ranks are a critical component of the military hierarchy, providing a framework for personnel to develop their skills, progress through the ranks, and make a meaningful contribution to their country. By understanding the roles and responsibilities of each rank, as well as the benefits and rewards of serving in the enlisted ranks, personnel can make informed decisions about their military careers and achieve their goals. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about the enlisted ranks, please do not hesitate to comment or share this article with others.
