Intro
Discover how cold air sinks affect temperature, density, and atmospheric pressure, and learn 5 ways it impacts environments, including insulation, ventilation, and climate regulation, to understand its role in heat transfer and energy efficiency.
The concept of cold air sinking is a fundamental principle in physics and meteorology, playing a crucial role in shaping our climate and weather patterns. This phenomenon occurs because cold air is denser than warm air, causing it to sink to the ground while warmer air rises. Understanding how and why cold air sinks is essential for predicting weather conditions, managing heating and cooling systems, and even navigating through daily life. In this article, we will delve into the details of cold air sinking, exploring its mechanisms, impacts, and practical applications.
Cold air sinking is not just a theoretical concept; it has real-world implications that affect us daily. From the formation of frost on winter mornings to the creation of temperature inversions that can trap pollutants in valleys, the sinking of cold air influences various aspects of our environment. By grasping the principles behind cold air sinking, we can better appreciate the complex dynamics of our atmosphere and make more informed decisions about energy consumption, environmental conservation, and personal comfort.
The importance of understanding cold air sinking extends beyond the realm of science into our everyday lives. For instance, knowing how cold air moves and accumulates can help homeowners optimize their heating systems, reducing energy bills and environmental impact. Similarly, farmers can benefit from this knowledge by taking preventive measures against frost, which can be devastating to crops. As we explore the ways in which cold air sinks, we will uncover the intricate relationships between temperature, density, and the behavior of air masses, shedding light on the fascinating processes that govern our weather and climate.
Introduction to Cold Air Sinking

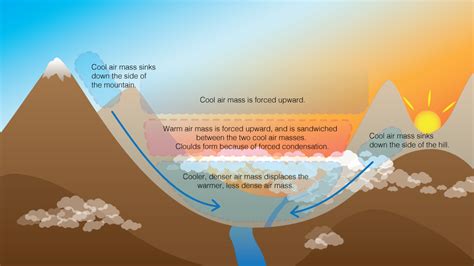
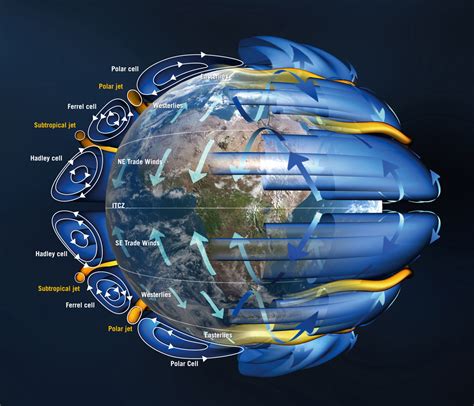
Cold air sinking is a natural process driven by the difference in density between cold and warm air. When air cools, its molecules move slower and come closer together, increasing its density. This denser air then sinks to the ground, displacing warmer, less dense air that rises. This basic principle underlies various atmospheric phenomena, including the formation of high and low-pressure systems, wind patterns, and even the global circulation of air.
Mechanisms of Cold Air Sinking
The mechanisms behind cold air sinking can be attributed to several key factors: - **Temperature Differences:** The primary driver of cold air sinking is the temperature difference between air masses. Cooler air, being denser, will always sink below warmer air. - **Humidity:** The humidity of air also plays a role, as moist air is less dense than dry air at the same temperature. However, the effect of humidity on air density is less significant than that of temperature. - **Topography:** The shape and features of the Earth's surface, such as mountains and valleys, can influence the flow and sinking of cold air. For example, cold air can accumulate in valleys, creating temperature inversions.Practical Applications of Understanding Cold Air Sinking
Understanding how cold air sinks has numerous practical applications across various fields:
- Heating and Cooling Systems: Knowledge of cold air sinking can help in designing more efficient heating and cooling systems. For instance, understanding how cold air accumulates in certain areas can inform the placement of heating vents.
- Agriculture: Farmers can use this knowledge to protect their crops from frost damage by employing techniques such as smudging or using wind machines to mix warmer air above with the colder air near the surface.
- Environmental Conservation: Recognizing the role of cold air sinking in trapping pollutants in valleys can inform strategies for reducing air pollution, such as promoting the use of cleaner energy sources in affected areas.
Impacts of Cold Air Sinking on Daily Life
The impacts of cold air sinking are felt in many aspects of daily life: - **Weather Forecasting:** Understanding cold air sinking is crucial for accurate weather forecasting. It helps predict temperature changes, fog formation, and even the potential for severe weather events. - **Energy Efficiency:** By knowing how cold air moves and accumulates, individuals can take steps to reduce heat loss from their homes, such as sealing drafts and using insulation, thereby saving energy and reducing their carbon footprint. - **Outdoor Activities:** For those who enjoy outdoor activities like hiking or skiing, understanding cold air sinking can provide valuable insights into weather conditions, helping them prepare for their adventures more effectively.Cold Air Sinking in Different Environments

Cold air sinking manifests differently in various environments:
- Valleys and Basins: Cold air tends to accumulate in valleys and basins, leading to colder temperatures in these areas compared to surrounding hills or mountains.
- Urban Areas: In cities, the urban heat island effect can sometimes mitigate the impact of cold air sinking, but it can also create unique microclimates where cold air accumulates in certain areas.
- Coastal Regions: Near coastlines, the temperature of the sea can influence the air temperature, affecting how cold air sinks and moves in these regions.
Research and Studies on Cold Air Sinking
Ongoing research and studies continue to refine our understanding of cold air sinking: - **Meteorological Models:** Advances in meteorological modeling have improved predictions of cold air sinking events, enabling better forecasting of weather patterns and extreme weather events. - **Climate Change:** Studies are also exploring how climate change might alter patterns of cold air sinking, potentially leading to changes in regional climate conditions and extreme weather events.Technologies for Observing Cold Air Sinking

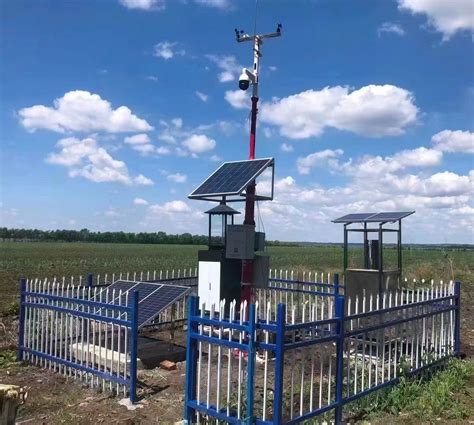
Several technologies are used to observe and study cold air sinking:
- Weather Stations: Ground-based weather stations provide crucial data on temperature, humidity, and wind patterns, which are essential for understanding cold air sinking.
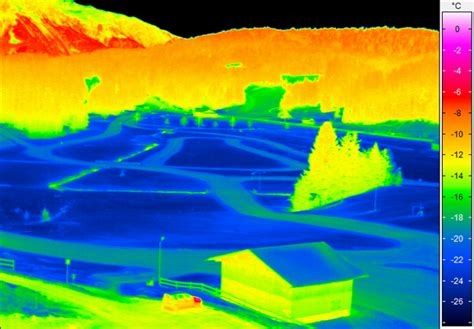
- Satellite Imagery: Satellite images can visualize the movement and accumulation of cold air masses, offering a broader perspective on atmospheric conditions.
- Radar and Lidar: These technologies can detect detailed patterns of air movement and temperature gradients, further enhancing our understanding of cold air sinking phenomena.
Future Directions in Cold Air Sinking Research
Future research directions include: - **High-Resolution Modeling:** Developing models that can predict cold air sinking at higher resolutions will improve forecasting accuracy and our ability to understand local climate phenomena. - **Integration with Other Atmospheric Processes:** Studying cold air sinking in conjunction with other atmospheric processes, such as precipitation patterns and atmospheric circulation, will provide a more comprehensive understanding of our climate system.Gallery of Cold Air Sinking
Cold Air Sinking Image Gallery

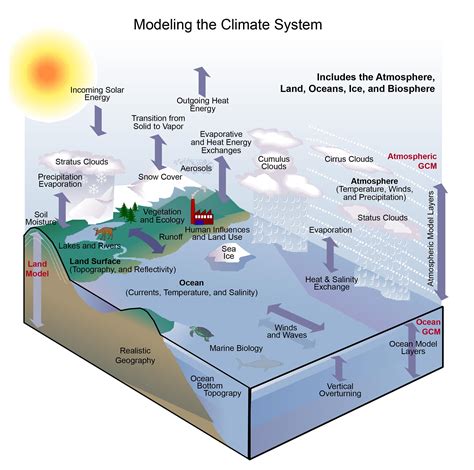
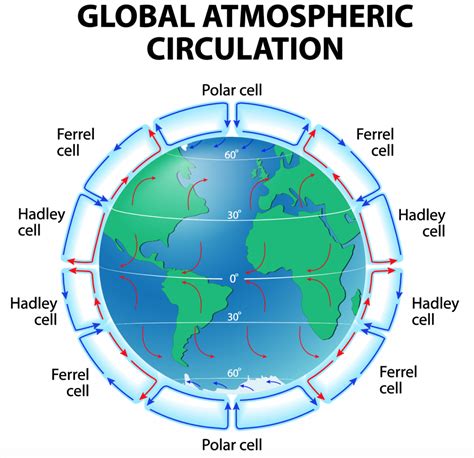

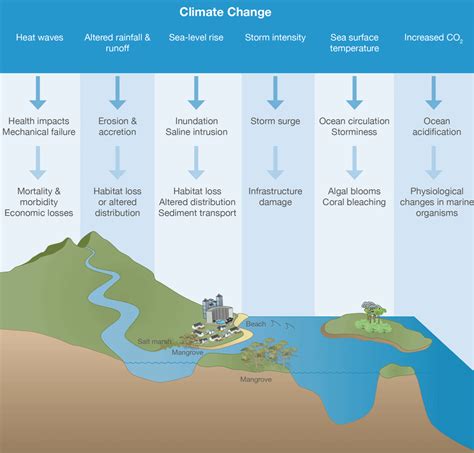


What causes cold air to sink?
+Cold air sinks because it is denser than warm air. This density difference is primarily due to the temperature of the air; cooler air has slower-moving molecules that are packed more tightly together.
How does topography affect cold air sinking?
+Topography, or the shape and features of the Earth's surface, can significantly affect the flow and accumulation of cold air. Valleys and basins, for example, can trap cold air, leading to colder conditions in these areas compared to surrounding higher ground.
What are some practical applications of understanding cold air sinking?
+Understanding cold air sinking has practical applications in heating and cooling system design, agriculture (for protecting crops from frost), and environmental conservation (by recognizing how cold air sinking can trap pollutants in certain areas).
As we conclude our exploration of cold air sinking, it becomes clear that this phenomenon plays a vital role in shaping our daily lives and the world around us. From the simple act of dressing warmly on a chilly morning to the complex task of predicting weather patterns, understanding how and why cold air sinks is essential. By continuing to study and learn about this aspect of our atmosphere, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that govern our climate and weather, ultimately leading to more informed decisions and actions that promote sustainability and comfort in our lives. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences related to cold air sinking, and to explore further the many fascinating aspects of our atmosphere that continue to inspire scientific inquiry and personal curiosity.
