Intro
Discover the role of combat medics in warfare, including their fighting capabilities and medical responsibilities, to understand if they engage in combat and provide care on the battlefield.
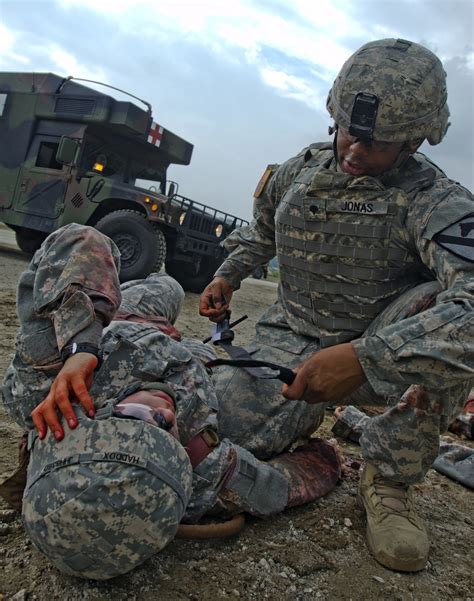
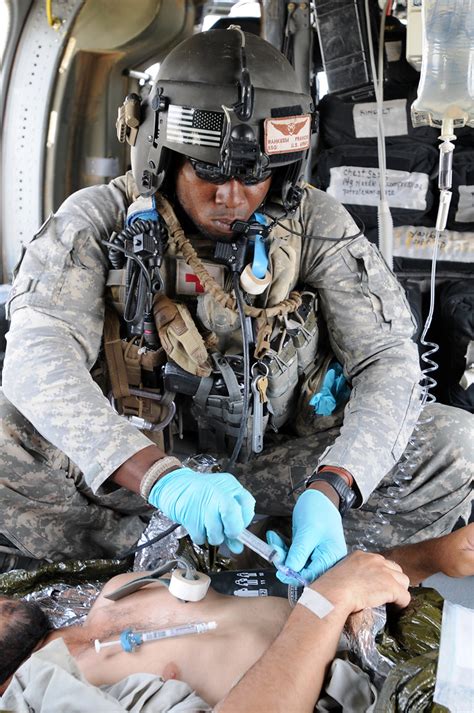
Combat medics play a crucial role in the military, providing medical care to wounded soldiers in the midst of battle. Their primary responsibility is to save lives, but the question remains: do combat medics fight? The answer is complex, as their role is multifaceted and often depends on the situation. On one hand, combat medics are trained to provide medical care, not to engage in combat. However, they often find themselves in the midst of battles, where they may be required to defend themselves or their patients.
In general, combat medics are not expected to fight, as their primary focus is on providing medical care. They are trained to treat wounds, stabilize patients, and evacuate them to safety. However, in certain situations, they may be required to defend themselves or their patients from enemy forces. This can include returning fire to protect their patients or using their weapons to defend themselves if they are under attack.
The role of combat medics is often misunderstood, with many people assuming that they are simply doctors or nurses in uniform. However, combat medics are highly trained soldiers who must be able to navigate the challenges of the battlefield while providing medical care. They must be able to think on their feet, make quick decisions, and prioritize their patients' needs in the midst of chaos.
Training and Responsibilities

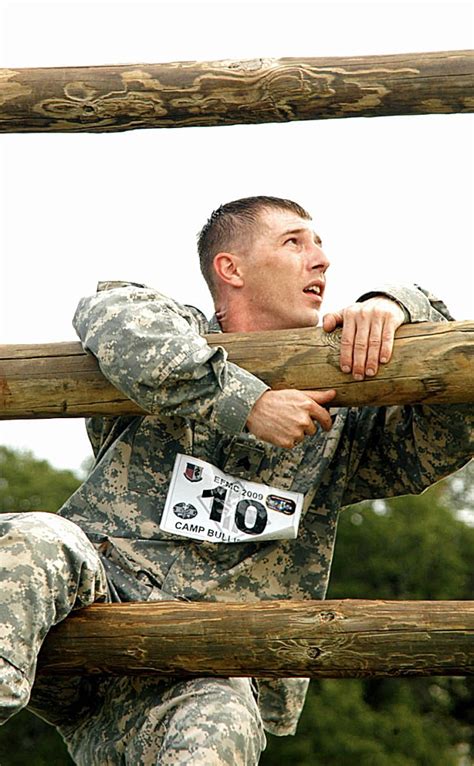
Combat medics undergo rigorous training to prepare them for the challenges of the battlefield. They learn basic first aid, advanced life support techniques, and how to treat a range of injuries, from gunshot wounds to burns. They also learn how to navigate the battlefield, communicate with other units, and work in high-stress environments.
In addition to their medical training, combat medics are also trained in basic combat skills, such as marksmanship and self-defense. They learn how to use their weapons, navigate the battlefield, and work in teams to achieve their objectives. However, their primary focus is always on providing medical care, not engaging in combat.
Combat Medic Roles and Specializations

There are several different types of combat medics, each with their own unique roles and specializations. Some combat medics work in hospitals or clinics, providing medical care to soldiers and civilians. Others work in the field, providing medical care to soldiers in the midst of battle.
Some common specializations for combat medics include:
- Tactical combat medic: Provides medical care in high-risk environments, such as combat zones.
- Special operations medic: Provides medical care to special operations forces, such as Navy SEALs or Army Rangers.
- Flight medic: Provides medical care to patients being transported by air.
- Combat medic specialist: Provides advanced medical care, such as surgery or anesthesia, in the field.
Combat Medic Equipment and Vehicles
Combat medics use a range of equipment and vehicles to provide medical care in the field. This can include:- Ambulances: Used to transport patients to medical facilities.
- Medical tents: Used to provide medical care in the field.
- Medical equipment: Such as defibrillators, ventilators, and surgical instruments.
- Communication equipment: Such as radios and satellite phones, used to communicate with other units and medical facilities.
Challenges Faced by Combat Medics

Combat medics face a range of challenges, from the physical demands of working in the field to the emotional toll of treating wounded soldiers. Some common challenges faced by combat medics include:
- Limited resources: Combat medics often have limited access to medical supplies, equipment, and personnel.
- High-stress environments: Combat medics work in high-stress environments, where they must make quick decisions and prioritize their patients' needs.
- Emotional toll: Combat medics often experience emotional trauma, particularly when treating wounded soldiers or dealing with the aftermath of combat.
Combat Medic Mental Health and Wellbeing
Combat medics are at risk of developing mental health problems, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety. This can be due to the trauma they experience, the stress of working in high-stress environments, and the emotional toll of treating wounded soldiers.To mitigate these risks, military organizations provide combat medics with access to mental health services, such as counseling and therapy. They also provide training on stress management, resilience, and self-care.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, combat medics play a vital role in the military, providing medical care to wounded soldiers in the midst of battle. While they are not expected to fight, they may be required to defend themselves or their patients in certain situations. Combat medics undergo rigorous training, work in high-stress environments, and face a range of challenges, from limited resources to emotional trauma.
As we reflect on the role of combat medics, it is essential to recognize their bravery, selflessness, and dedication to their patients. They are true heroes, who put their lives on the line every day to save others.
Combat Medics Image Gallery









What is the primary role of a combat medic?
+The primary role of a combat medic is to provide medical care to wounded soldiers in the midst of battle.
Do combat medics fight?
+Combat medics are not expected to fight, but they may be required to defend themselves or their patients in certain situations.
What kind of training do combat medics receive?
+Combat medics receive rigorous training in basic first aid, advanced life support techniques, and combat skills, such as marksmanship and self-defense.
What are some common challenges faced by combat medics?
+Combat medics face a range of challenges, including limited resources, high-stress environments, and emotional trauma.
How can combat medics prioritize their mental health and wellbeing?
+Combat medics can prioritize their mental health and wellbeing by seeking access to mental health services, such as counseling and therapy, and practicing stress management, resilience, and self-care.
We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of the role of combat medics and the challenges they face. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more, please do not hesitate to comment below. Share this article with others who may be interested, and let us know if you have any suggestions for future topics. Thank you for reading!
